|
Cytochrome P450 BM3
Cytochrome P450 BM3 is a Prokaryote Cytochrome P450 enzyme originally from ''Bacillus megaterium'' catalyzes the hydroxylation of several long-chain fatty acids at the ω–1 through ω–3 positions. This bacterial enzyme belongs to CYP family CYP102, with the CYP Symbol CYP102A1.This CYP family constitutes a natural fusion between the CYP domain and an NADPH Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, abbreviated NADP or, in older notation, TPN (triphosphopyridine nucleotide), is a cofactor used in anabolic reactions, such as the Calvin cycle and lipid and nucleic acid syntheses, which require NAD ...-dependent cytochrome P450 reductase. References Cytochrome P450 EC 1.6.2 EC 1.14.14 Prokaryote genes {{Enzyme-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytochrome P450
Cytochromes P450 (CYPs) are a Protein superfamily, superfamily of enzymes containing heme as a cofactor (biochemistry), cofactor that functions as monooxygenases. In mammals, these proteins oxidize steroids, fatty acids, and xenobiotics, and are important for the clearance (pharmacology), clearance of various compounds, as well as for hormone synthesis and breakdown. In 1963, Ronald W. Estabrook, Estabrook, David Y. Cooper, Cooper, and Otto Rosenthal, Rosenthal described the role of CYP as a catalyst in steroid hormone synthesis and drug metabolism. In plants, these proteins are important for the biosynthesis of secondary metabolite, defensive compounds, fatty acids, and hormones. CYP enzymes have been identified in all kingdom (biology), kingdoms of life: animals, plants, fungus, fungi, protists, bacteria, and archaea, as well as in viruses. However, they are not omnipresent; for example, they have not been found in ''Escherichia coli''. , more than 300,000 distinct CYP proteins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reaction ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
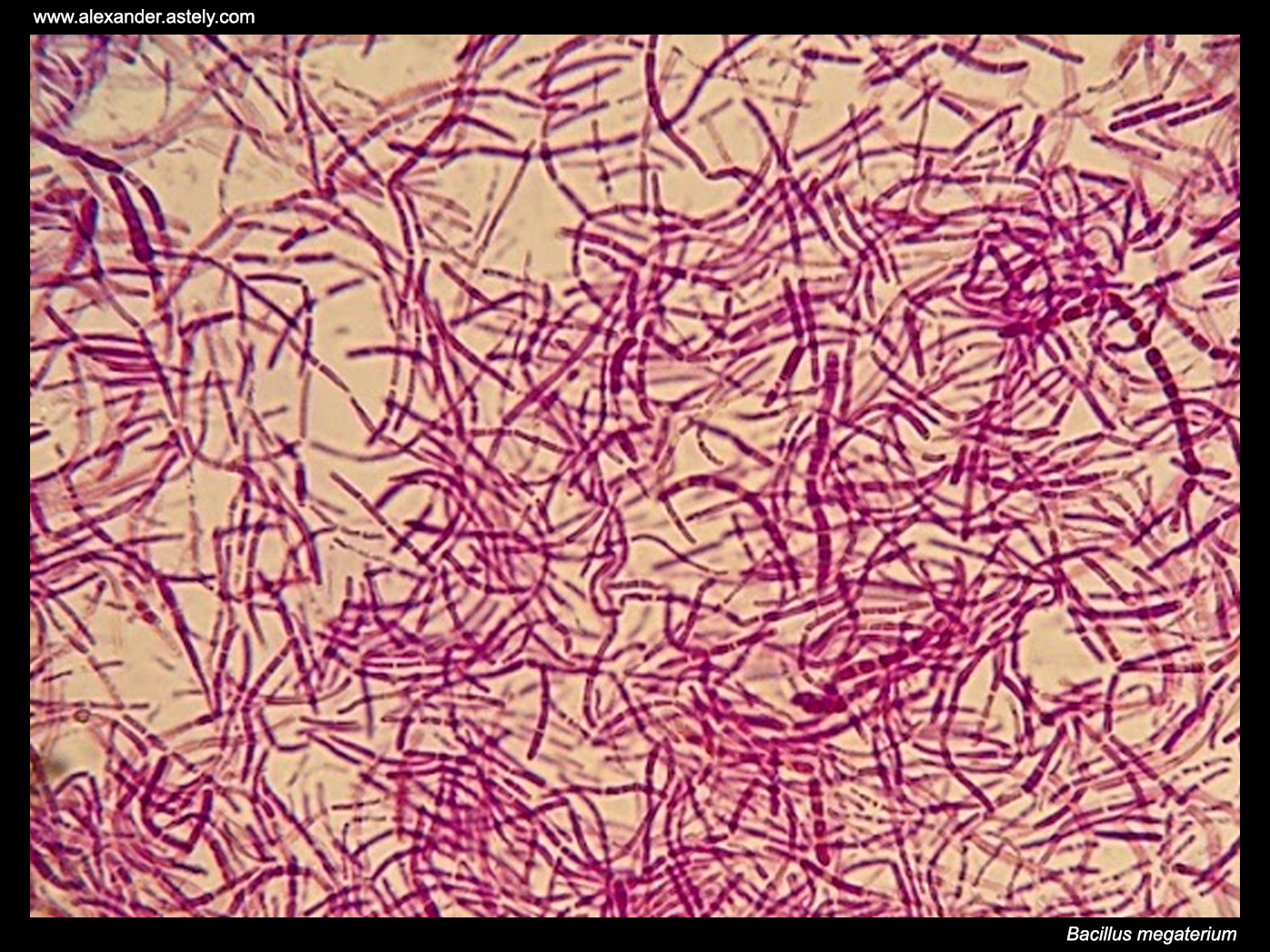
Bacillus Megaterium
''Bacillus megaterium'' is a rod-like, Gram-positive, mainly aerobic spore forming bacterium found in widely diverse habitats.De Vos, P. ''et al.'' Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology: Volume 3: The Firmicutes. ''Springer'' (2009) It has a cell length of up to 4 µm and a diameter of 1.5 µm, which is quite large for a bacteria. The cells often occur in pairs and chains, where the cells are joined together by polysaccharides on the cell walls. In the 1960s, prior to the utilization of ''Bacillus subtilis'' for this purpose, ''B. megaterium'' was the main model organism among Gram-positive bacteria for intensive studies on biochemistry, sporulation and bacteriophages. Recently, its popularity has started increasing in the field of biotechnology for its recombinant protein production capacity.Bunk, B. ''et al.'' A short story about a big magic bug. ''Bioengineered Bugs'' 1:85–91 (2010) This species has been recently transferred into the genus ''Priestia''. The c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroxylation
In chemistry, hydroxylation can refer to: *(i) most commonly, hydroxylation describes a chemical process that introduces a hydroxyl group () into an organic compound. *(ii) the ''degree of hydroxylation'' refers to the number of OH groups in a molecule. The ''pattern of hydroxylation'' refers to the location of hydroxy groups on a molecule or material. Hydroxylation reactions Synthetic hydroxylations Installing hydroxyl groups into organic compounds can be effected by various metal catalysts. Many such catalysts are biomimetic, i.e. they are inspired by or intended to mimic enzymes such as cytochrome P450. Whereas many hydroxylations insert O atoms into bonds, some reactions ''add'' OH groups to unsaturated substrates. The Sharpless dihydroxylation is such a reaction: it converts alkenes into diols. The hydroxy groups are provided by hydrogen peroxide, which adds across the double bond of alkenes. Biological hydroxylation In biochemistry, hydroxylation reactions are often ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long-chain Fatty Acid
In chemistry, particularly in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, from 4 to 28. Fatty acids are a major component of the lipids (up to 70% by weight) in some species such as microalgae but in some other organisms are not found in their standalone form, but instead exist as three main classes of esters: triglycerides, phospholipids, and cholesteryl esters. In any of these forms, fatty acids are both important dietary sources of fuel for animals and important structural components for cells. History The concept of fatty acid (''acide gras'') was introduced in 1813 by Michel Eugène Chevreul, though he initially used some variant terms: ''graisse acide'' and ''acide huileux'' ("acid fat" and "oily acid"). Types of fatty acids Fatty acids are classified in many ways: by length, by saturation vs unsaturation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NADPH
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, abbreviated NADP or, in older notation, TPN (triphosphopyridine nucleotide), is a cofactor used in anabolic reactions, such as the Calvin cycle and lipid and nucleic acid syntheses, which require NADPH as a reducing agent ('hydrogen source'). It is used by all forms of cellular life. NADPH is the reduced form of NADP. NADP differs from NAD by the presence of an additional phosphate group on the 2' position of the ribose ring that carries the adenine moiety. This extra phosphate is added by NAD+ kinase and removed by NADP+ phosphatase. Biosynthesis NADP In general, NADP+ is synthesized before NADPH is. Such a reaction usually starts with NAD+ from either the de-novo or the salvage pathway, with NAD+ kinase adding the extra phosphate group. ADP-ribosyl cyclase allows for synthesis from nicotinamide in the salvage pathway, and NADP+ phosphatase can convert NADPH back to NADH to maintain a balance. Some forms of the NAD+ kinas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |