|
Cylinder Stress
In mechanics, a cylinder stress is a stress distribution with rotational symmetry; that is, which remains unchanged if the stressed object is rotated about some fixed axis. Cylinder stress patterns include: * circumferential stress, or hoop stress, a normal stress in the tangential (azimuth) direction. * axial stress, a normal stress parallel to the axis of cylindrical symmetry. * radial stress, a normal stress in directions coplanar with but perpendicular to the symmetry axis. These three principal stresses- hoop, longitudinal, and radial can be calculated analytically using a mutually perpendicular tri-axial stress system. The classical example (and namesake) of hoop stress is the tension applied to the iron bands, or hoops, of a wooden barrel. In a straight, closed pipe, any force applied to the cylindrical pipe wall by a pressure differential will ultimately give rise to hoop stresses. Similarly, if this pipe has flat end caps, any force applied to them by static pressure w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circumferential Stress
In mechanics, a cylinder stress is a stress distribution with rotational symmetry; that is, which remains unchanged if the stressed object is rotated about some fixed axis. Cylinder stress patterns include: * circumferential stress, or hoop stress, a normal stress in the tangential (azimuth) direction. * axial stress, a normal stress parallel to the axis of cylindrical symmetry. * radial stress, a normal stress in directions coplanar with but perpendicular to the symmetry axis. These three principal stresses- hoop, longitudinal, and radial can be calculated analytically using a mutually perpendicular tri-axial stress system. The classical example (and namesake) of hoop stress is the tension applied to the iron bands, or hoops, of a wooden barrel. In a straight, closed pipe, any force applied to the cylindrical pipe wall by a pressure differential will ultimately give rise to hoop stresses. Similarly, if this pipe has flat end caps, any force applied to them by static pressure w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wrought Iron Straps, Chepstow Railway Bridge
Wrought is the archaic form of "worked," the more commonly used past tense and past participle of work. Wrought may also refer to: * Metalworking, the process of working with metals to create individual parts, assemblies, or large-scale structures. ** Wrought iron Wrought iron is an iron alloy with a very low carbon content (less than 0.08%) in contrast to that of cast iron (2.1% to 4%). It is a semi-fused mass of iron with fibrous slag Inclusion (mineral), inclusions (up to 2% by weight), which give it a ..., iron with a very low carbon content that has been wrought (hammered) by hand. See also * * Wright (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gut (zoology)
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans and other animals, including the esophagus, stomach, and intestines. Food taken in through the mouth is digested to extract nutrients and absorb energy, and the waste expelled at the anus as feces. ''Gastrointestinal'' is an adjective meaning of or pertaining to the stomach and intestines. Most animals have a "through-gut" or complete digestive tract. Exceptions are more primitive ones: sponges have small pores ( ostia) throughout their body for digestion and a larger dorsal pore (osculum) for excretion, comb jellies have both a ventral mouth and dorsal anal pores, while cnidarians and acoels have a single pore for both digestion and excretion. The human gastrointestinal tract consists of the esophagus, stomach, and intestines, and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diverticuli
In medicine or biology, a diverticulum is an outpouching of a hollow (or a fluid-filled) structure in the body. Depending upon which layers of the structure are involved, diverticula are described as being either true or false. In medicine, the term usually implies the structure is not normally present, but in embryology, the term is used for some normal structures arising from others, as for instance the thyroid diverticulum, which arises from the tongue. The word comes from Latin ''dīverticulum'', "bypath" or "byway". Classification Diverticula are described as being true or false depending upon the layers involved: *False diverticula (also known as "pseudodiverticula") do not involve muscular layers or adventitia. False diverticula, in the gastrointestinal tract for instance, involve only the submucosa and mucosa. *True diverticula involve all layers of the structure, including muscularis propria and adventitia, such as Meckel's diverticulum. Embryology *The kidneys are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aneurysm
An aneurysm is an outward bulging, likened to a bubble or balloon, caused by a localized, abnormal, weak spot on a blood vessel wall. Aneurysms may be a result of a hereditary condition or an acquired disease. Aneurysms can also be a nidus (starting point) for clot formation (thrombosis) and embolization. As an aneurysm increases in size, the risk of rupture, which leads to uncontrolled bleeding, increases. Although they may occur in any blood vessel, particularly lethal examples include aneurysms of the Circle of Willis in the brain, aortic aneurysms affecting the thoracic aorta, and abdominal aortic aneurysms. Aneurysms can arise in the heart itself following a heart attack, including both ventricular and atrial septal aneurysms. There are congenital atrial septal aneurysms, a rare heart defect. Etymology The word is from Greek: ἀνεύρυσμα, aneurysma, "dilation", from ἀνευρύνειν, aneurynein, "to dilate". Classification Aneurysms are classified by type, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
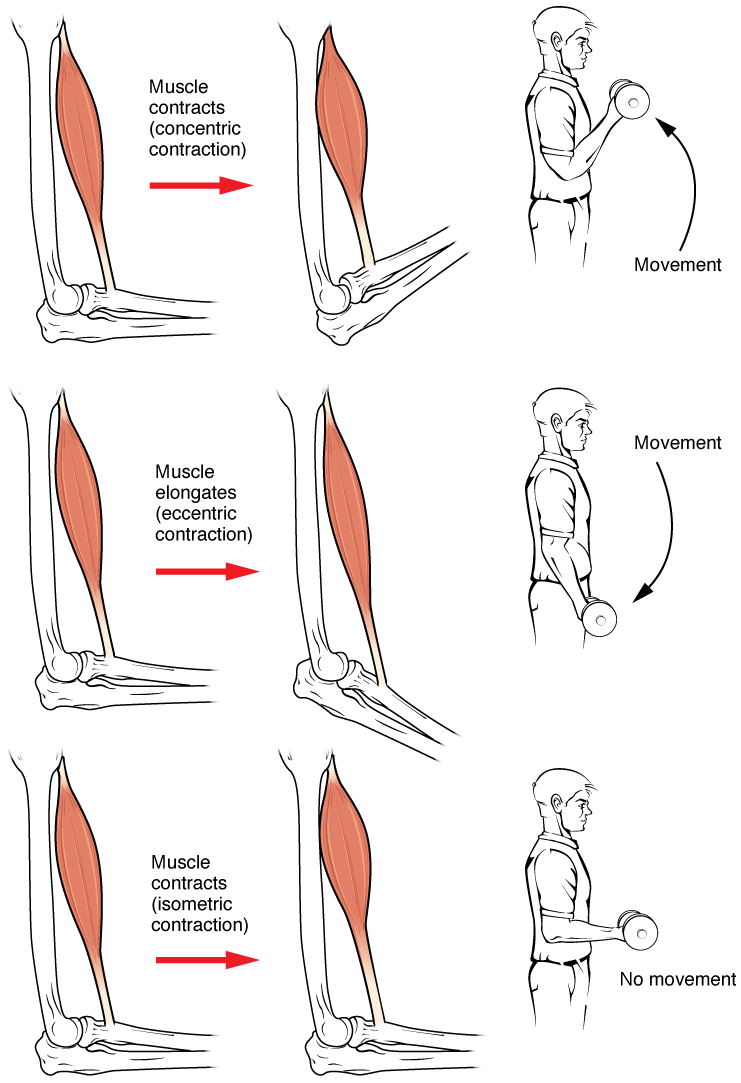
Muscle Contraction
Muscle contraction is the activation of tension-generating sites within muscle cells. In physiology, muscle contraction does not necessarily mean muscle shortening because muscle tension can be produced without changes in muscle length, such as when holding something heavy in the same position. The termination of muscle contraction is followed by muscle relaxation, which is a return of the muscle fibers to their low tension-generating state. For the contractions to happen, the muscle cells must rely on the interaction of two types of filaments which are the thin and thick filaments. Thin filaments are two strands of actin coiled around each, and thick filaments consist of mostly elongated proteins called myosin. Together, these two filaments form myofibrils which are important organelles in the skeletal muscle system. Muscle contraction can also be described based on two variables: length and tension. A muscle contraction is described as isometric if the muscle tension changes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastrointestinal Tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organ (biology), organs of the digestive system, in humans and other animals, including the esophagus, stomach, and intestines. Food taken in through the mouth is digestion, digested to extract nutrients and absorb energy, and the waste expelled at the anus as feces. ''Gastrointestinal'' is an adjective meaning of or pertaining to the stomach and intestines. Nephrozoa, Most animals have a "through-gut" or complete digestive tract. Exceptions are more primitive ones: sponges have small pores (ostium (sponges), ostia) throughout their body for digestion and a larger dorsal pore (osculum) for excretion, comb jellies have both a ventral mouth and dorsal anal pores, while cnidarians and acoels have a single pore for both digestion and excretion. The human gastrointestinal tract consists o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Vessel
The blood vessels are the components of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away from the tissues. Blood vessels are needed to sustain life, because all of the body's tissues rely on their functionality. There are five types of blood vessels: the arteries, which carry the blood away from the heart; the arterioles; the capillaries, where the exchange of water and chemicals between the blood and the tissues occurs; the venules; and the veins, which carry blood from the capillaries back towards the heart. The word ''vascular'', meaning relating to the blood vessels, is derived from the Latin ''vas'', meaning vessel. Some structures – such as cartilage, the epithelium, and the lens and cornea of the eye – do not contain blood vessels and are labeled ''avascular''. Etymology * artery: late Middle English; from Latin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathology
Pathology is the study of the causes and effects of disease or injury. The word ''pathology'' also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in the context of modern medical treatment, the term is often used in a narrower fashion to refer to processes and tests that fall within the contemporary medical field of "general pathology", an area which includes a number of distinct but inter-related medical specialties that diagnose disease, mostly through analysis of tissue, cell, and body fluid samples. Idiomatically, "a pathology" may also refer to the predicted or actual progression of particular diseases (as in the statement "the many different forms of cancer have diverse pathologies", in which case a more proper choice of word would be " pathophysiologies"), and the affix ''pathy'' is sometimes used to indicate a state of disease in cases of both physical ailment (as in cardiomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gabriel Lamé
Gabriel Lamé (22 July 1795 – 1 May 1870) was a French mathematician who contributed to the theory of partial differential equations by the use of curvilinear coordinates, and the mathematical theory of elasticity (for which linear elasticity and finite strain theory elaborate the mathematical abstractions). Biography Lamé was born in Tours, in today's ''département'' of Indre-et-Loire. He became well known for his general theory of curvilinear coordinates and his notation and study of classes of ellipse-like curves, now known as Lamé curves or superellipses, and defined by the equation: : \left, \,\,\^n + \left, \,\,\^n =1 where ''n'' is any positive real number. He is also known for his running time analysis of the Euclidean algorithm, marking the beginning of computational complexity theory. Using Fibonacci numbers, he proved that when finding the greatest common divisor of integers ''a'' and ''b'', the algorithm runs in no more than 5''k'' steps, where ''k'' is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)