|
Cyclovirus
The viral genus ''Cyclovirus'' is a genus in the family ''Circoviridae''. Viruses in this genus have been isolated from Dragonfly, dragonflies, as well as chickens, goats, sheep, and other farm animals. Cycloviruses have also been found in the feces of healthy humans and chimpanzees and in samples of cerebrospinal fluid from patients with unexplained paraplegia. Species The following species are recognized: *''Ant associated cyclovirus 1'' *''Bat associated cyclovirus 1'' *''Bat associated cyclovirus 2'' *''Bat associated cyclovirus 3'' *''Bat associated cyclovirus 4'' *''Bat associated cyclovirus 5'' *''Bat associated cyclovirus 6'' *''Bat associated cyclovirus 7'' *''Bat associated cyclovirus 8'' *''Bat associated cyclovirus 9'' *''Bat associated cyclovirus 10'' *''Bat associated cyclovirus 11'' *''Bat associated cyclovirus 12'' *''Bat associated cyclovirus 13'' *''Bat associated cyclovirus 14'' *''Bat associated cyclovirus 15'' *''Bat associated cyclovirus 16'' *''Bovine associ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circoviridae
''Circoviridae'' is a family of DNA viruses. Birds and mammals serve as natural hosts. There are 101 species in this family, assigned to 2 genera. Diseases associated with this family include: PCV-2: postweaning multisystemic wasting syndrome; CAV: chicken infectious anemia. Structure Viruses in the family ''Circoviridae'' are non-enveloped, with icosahedral and round geometries, and T=1 symmetry. The diameter is around 20 nm. Genomes are circular and non-segmented, around 3.8kb in length. The capsid consists of 12 pentagonal trumpet-shaped pentamers. There are two main open reading frames arranged in opposite directions that encode the replication and capsid proteins. Alternative start codons are common in the avian species. Life cycle Viral replication is nuclear. Entry into the host cell is achieved by penetration into the host cell. Replication follows the ssDNA rolling circle model. DNA templated transcription, with some alternative splicing mechanism is the method ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bat Associated Cyclovirus 13
Bats are mammals of the order Chiroptera.''cheir'', "hand" and πτερόν''pteron'', "wing". With their forelimbs adapted as wings, they are the only mammals capable of true and sustained flight. Bats are more agile in flight than most birds, flying with their very long spread-out digits covered with a thin membrane or patagium. The smallest bat, and arguably the smallest extant mammal, is Kitti's hog-nosed bat, which is in length, across the wings and in mass. The largest bats are the flying foxes, with the giant golden-crowned flying fox, ''Acerodon jubatus'', reaching a weight of and having a wingspan of . The second largest order of mammals after rodents, bats comprise about 20% of all classified mammal species worldwide, with over 1,400 species. These were traditionally divided into two suborders: the largely fruit-eating megabats, and the echolocating microbats. But more recent evidence has supported dividing the order into Yinpterochiroptera and Yangochiroptera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
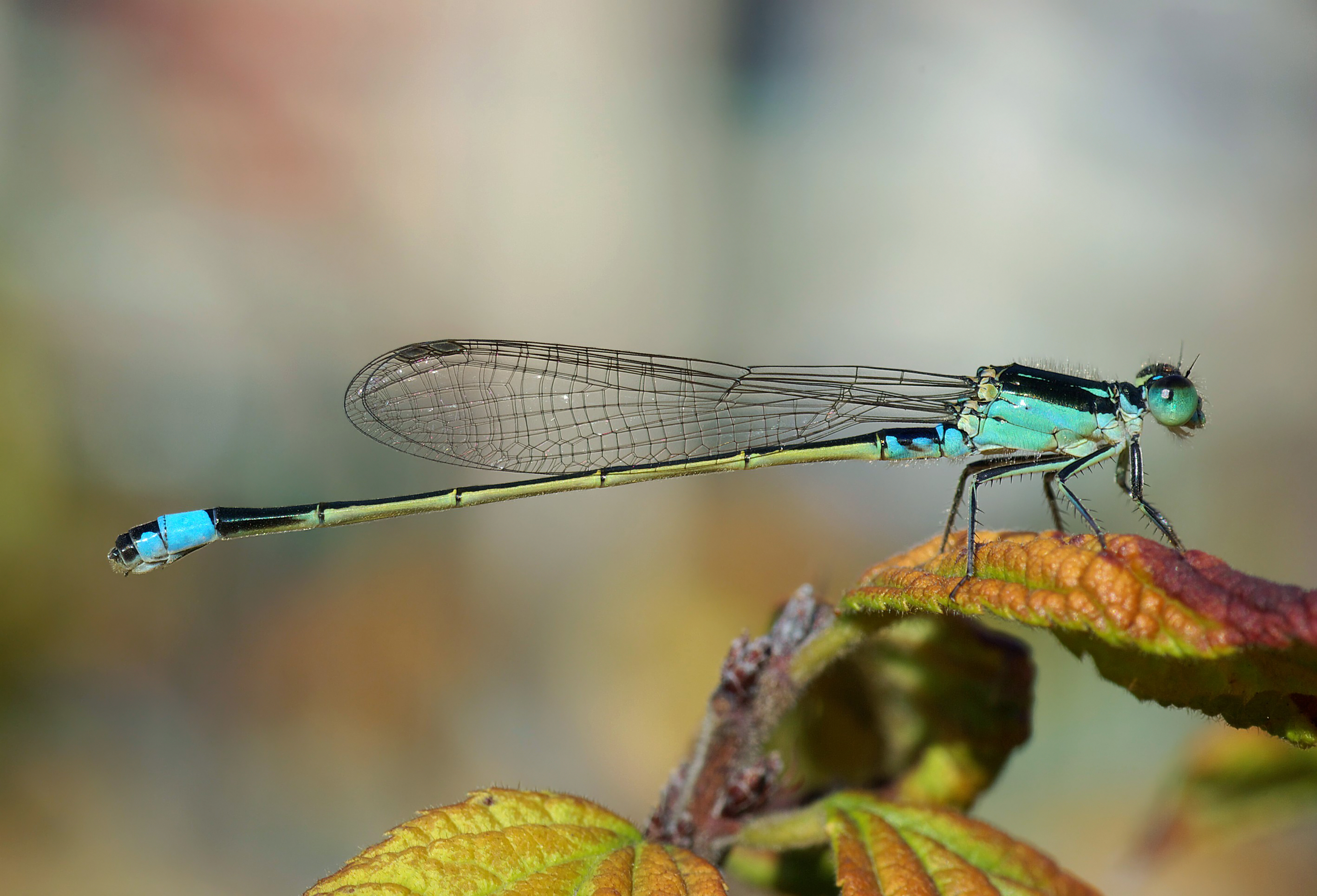
Dragonfly Associated Cyclovirus 4
A dragonfly is a flying insect belonging to the infraorder Anisoptera below the order Odonata. About 3,000 extant species of true dragonfly are known. Most are tropical, with fewer species in temperate regions. Loss of wetland habitat threatens dragonfly populations around the world. Adult dragonflies are characterized by a pair of large, multifaceted compound eyes, two pairs of strong, transparent wings, sometimes with coloured patches, and an elongated body. Many dragonflies have brilliant iridescent or metallic colours produced by structural colouration, making them conspicuous in flight. An adult dragonfly's compound eyes have nearly 24,000 ommatidia each. Dragonflies can be mistaken for the closely related damselflies, which make up the other odonatan infraorder ( Zygoptera) and are similar in body plan though usually lighter in build; however, the wings of most dragonflies are held flat and away from the body, while damselflies hold their wings folded at rest, along or ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dragonfly Associated Cyclovirus 3
A dragonfly is a flying insect belonging to the infraorder Anisoptera below the order Odonata. About 3,000 extant species of true dragonfly are known. Most are tropical, with fewer species in temperate regions. Loss of wetland habitat threatens dragonfly populations around the world. Adult dragonflies are characterized by a pair of large, multifaceted compound eyes, two pairs of strong, transparent wings, sometimes with coloured patches, and an elongated body. Many dragonflies have brilliant iridescent or metallic colours produced by structural colouration, making them conspicuous in flight. An adult dragonfly's compound eyes have nearly 24,000 ommatidia each. Dragonflies can be mistaken for the closely related damselflies, which make up the other odonatan infraorder ( Zygoptera) and are similar in body plan though usually lighter in build; however, the wings of most dragonflies are held flat and away from the body, while damselflies hold their wings folded at rest, along or ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dragonfly Associated Cyclovirus 2
A dragonfly is a flying insect belonging to the infraorder Anisoptera below the order Odonata. About 3,000 extant species of true dragonfly are known. Most are tropical, with fewer species in temperate regions. Loss of wetland habitat threatens dragonfly populations around the world. Adult dragonflies are characterized by a pair of large, multifaceted compound eyes, two pairs of strong, transparent wings, sometimes with coloured patches, and an elongated body. Many dragonflies have brilliant iridescent or metallic colours produced by structural colouration, making them conspicuous in flight. An adult dragonfly's compound eyes have nearly 24,000 ommatidia each. Dragonflies can be mistaken for the closely related damselflies, which make up the other odonatan infraorder ( Zygoptera) and are similar in body plan though usually lighter in build; however, the wings of most dragonflies are held flat and away from the body, while damselflies hold their wings folded at rest, along or ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dragonfly Associated Cyclovirus 1
A dragonfly is a flying insect belonging to the infraorder Anisoptera below the order Odonata. About 3,000 extant species of true dragonfly are known. Most are tropical, with fewer species in temperate regions. Loss of wetland habitat threatens dragonfly populations around the world. Adult dragonflies are characterized by a pair of large, multifaceted compound eyes, two pairs of strong, transparent wings, sometimes with coloured patches, and an elongated body. Many dragonflies have brilliant iridescent or metallic colours produced by structural colouration, making them conspicuous in flight. An adult dragonfly's compound eyes have nearly 24,000 ommatidia each. Dragonflies can be mistaken for the closely related damselflies, which make up the other odonatan infraorder ( Zygoptera) and are similar in body plan though usually lighter in build; however, the wings of most dragonflies are held flat and away from the body, while damselflies hold their wings folded at rest, along or ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cockroach Associated Cyclovirus 1
Cockroaches (or roaches) are a Paraphyly, paraphyletic group of insects belonging to Blattodea, containing all members of the group except termites. About 30 cockroach species out of 4,600 are associated with human habitats. Some species are well-known as Pest (organism), pests. The cockroaches are an ancient group, with their ancestors, known as "Roachoid, roachoids", originating during the Carboniferous period, some 320 million years ago. Those early ancestors, however, lacked the internal ovipositors of modern roaches. Cockroaches are somewhat generalized insects lacking special adaptations (such as the sucking Insect mouthparts, mouthparts of aphids and other Hemiptera, true bugs); they have chewing mouthparts and are probably among the most primitive of living Neopteran insects. They are common and hardy insects capable of tolerating a wide range of Köppen climate classification, climates, from Arctic cold to Tropics, tropical heat. Tropical cockroaches are often much larg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chimpanzee Associated Cyclovirus 1
The chimpanzee (''Pan troglodytes''), also known as simply the chimp, is a species of great ape native to the forest and savannah of tropical Africa. It has four confirmed subspecies and a fifth proposed subspecies. When its close relative the bonobo was more commonly known as the pygmy chimpanzee, this species was often called the common chimpanzee or the robust chimpanzee. The chimpanzee and the bonobo are the only species in the genus ''Pan''. Evidence from fossils and DNA sequencing shows that ''Pan'' is a sister taxon to the human lineage and is humans' closest living relative. The chimpanzee is covered in coarse black hair, but has a bare face, fingers, toes, palms of the hands, and soles of the feet. It is larger and more robust than the bonobo, weighing for males and for females and standing . The chimpanzee lives in groups that range in size from 15 to 150 members, although individuals travel and forage in much smaller groups during the day. The species lives in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chicken Associated Cyclovirus 2
The chicken (''Gallus gallus domesticus'') is a domestication, domesticated junglefowl species, with attributes of wild species such as the grey junglefowl, grey and the Ceylon junglefowl that are originally from Southeastern Asia. Rooster or cock is a term for an adult male bird, and a younger male may be called a cockerel. A male that has been castrated is a capon. An adult female bird is called a hen and a sexually immature female is called a pullet. Humans now keep chickens primarily as a source of food (consuming both their Chicken as food, meat and egg as food, eggs) and as pets. Traditionally they were also bred for cockfighting, which is still practiced in some places. Chickens are one of the most common and widespread domestic animals, with a total population of 23.7 billion , up from more than 19 billion in 2011. There are more chickens in the world than any other bird. There are numerous cultural references to chickens – in myth, folklore and religion, and in la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |