|
Cyanidin
Cyanidin is a natural organic compound. It is a particular type of anthocyanidin (glycoside version called anthocyanins). It is a pigment found in many red berries including grapes, bilberry, blackberry, blueberry, cherry, chokeberry, cranberry, elderberry, hawthorn, loganberry, açai berry and raspberry. It can also be found in other fruits such as apples and plums, and in red cabbage and red onion. It has a characteristic reddish-purple color, though this can change with pH; solutions of the compound are red at pH 11. In certain fruits, the highest concentrations of cyanidin are found in the seeds and skin. Cyanidin has been found to be a potent sirtuin 6 (SIRT6) activator. List of cyanidin derivatives * Antirrhinin (cyanidin-3-rutinoside or 3-C-R), found in black raspberry * Cyanidin-3-xylosylrutinoside, found in black raspberry * Cyanidin-3,4′-di-''O''-β-glucopyranoside, found in red onion * Cyanidin-4′-''O''-β-glucoside, found in red onion * Chrysanthemin ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chrysanthemin
Chrysanthemin is an anthocyanin. It is the 3-glucoside of cyanidin. Natural occurrences Chrysanthemin can be found in the roselle plant (''Hibiscus sabdariffa'', Malvaceae), different Japanese angiosperms, ''Rhaponticum'' (Asteraceae), The fruits of the smooth arrowwood (''Viburnum dentatum'', Caprifoliaceae) appear blue. One of the major pigments is cyanidin 3-glucoside, but the total mixture is very complex. In food Chrysanthemin has been detected in blackcurrant pomace, in European elderberry, in red raspberries, in soybean seed coats, in Victoria plum, in peach, lychee and açaí. It is found in red oranges and black rice. It is the major anthocyanin in purple corn (''Zea mays''). Purple corn is approved in Japan and listed in the "Existing Food Additive List" as ''purple corn color''. Biosynthesis The biosynthesis of cyanidin 3-O-glucoside in ''Escherichia coli'' was demonstrated by means of genetic engineering. In ''Arabidopsis thaliana'', a glycosyltransferase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antirrhinin
Antirrhinin is an anthocyanin. It is the 3-rutinoside of cyanidin. Occurrence It can be found in ''Antirrhinum majus'' (common snapdragon). It can be found in blackcurrant, açaí, black raspberry, litchi pericarp and common fig. Metabolism Cyanidin 3-O-rutinoside 5-O-glucosyltransferase uses UDP-glucose and cyanidin 3-O-rutinoside (antirrhinin) to produce UDP and cyanidin 3-O-rutinoside 5-O-beta-D-glucoside Cyanidin is a natural organic compound. It is a particular type of anthocyanidin (glycoside version called anthocyanins). It is a pigment found in many red berries including grapes, bilberry, blackberry, blueberry, cherry, chokeberry, cranb .... References Anthocyanin rutinosides {{Aromatic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyanidin-3,5-O-diglucoside
Cyanidin-3,5-''O''-diglucoside, also known as cyanin, is an anthocyanin. It is the 3,5-''O''-diglucoside of cyanidin. Natural occurrences Cyanin can be found in species of the genus ''Rhaponticum'' (Asteraceae). In food Cyanin can be found in red wine as well as pomegranate juice according to a study done by Graça Miguel, Susana Dandlen, Dulce Antunes, Alcinda Neves, and Denise Martins in the winter of 2004. Pomegranate juice extracted through centrifugal seed separation has higher amounts of cyanidin-3,5-''O''-diglucoside than juice extracted by squeezing fruit halves with an electric lemon squeezer. See also * Phenolic content in wine The phenolic content in wine refers to the phenolic compounds—natural phenol and polyphenols—in wine, which include a large group of several hundred chemical compounds that affect the taste, color and mouthfeel of wine. These compounds include ... References External links {{Anthocyanins Anthocyanins Flavonoid glucosides< ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthocyanidin
Anthocyanidins are common plant pigments, the sugar-free counterparts of anthocyanins. They are based on the flavylium cation, an oxonium ion, with various groups substituted for its hydrogen atoms. They generally change color from red through purple, blue, and bluish green as a function of pH. Anthocyanidins are an important subclass of the polymethine dyes and flavonoids. The flavylium cation is a chromenylium cation with a phenyl group substituted in position 2; and chromenylium (also called benzopyrylium) is a bicyclic version of pyrylium. The positive charge can move around the molecule. At least 31 monomeric anthocyanidins have been properly identified in living organisms, mostly as the core components of anthocyanins. The latter are responsible for the red, purple, blue, or black color of many fruits (like grapes and blueberries), flowers (like roses), leaves (like purple cabbage), and even tubers (like radishes and purple yams). They are also found in some animals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ideain
Ideain, the cyanidin 3-O-galactoside, is an anthocyanin, a type of plant pigment. Natural occurrences Ideain is the main anthocyanin in red-skinned or red-fleshed (for example Weirouge) apple varieties. It is also found in Chinese hawthorn fruits (''Crataegus spp.''). It is also the pigment in the copper beech (cultivar of ''Fagus sylvatica''), that was identified in 1932. While it is only one in the many anthocyanins present in bilberries (''Vaccinium myrtillus'') and cranberries (''Vaccinium macrocarpon''), it is the main anthocyanin in lingonberries (''Vaccinium vitis-idaea''). ''Quintinia serrata'', the tawheowheo, a species of evergreen trees endemic to New Zealand, has different patterns of anthocyanins (cyanidin 3-O-glucoside Chrysanthemin is an anthocyanin. It is the 3- glucoside of cyanidin. Natural occurrences Chrysanthemin can be found in the roselle plant (''Hibiscus sabdariffa'', Malvaceae), different Japanese angiosperms, ''Rhaponticum'' (Asteraceae), The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthocyanin
Anthocyanins (), also called anthocyans, are water-soluble vacuolar pigments that, depending on their pH, may appear red, purple, blue, or black. In 1835, the German pharmacist Ludwig Clamor Marquart gave the name Anthokyan to a chemical compound that gives flowers a blue color for the first time in his treatise "''Die Farben der Blüthen''". Food plants rich in anthocyanins include the blueberry, raspberry, black rice, and black soybean, among many others that are red, blue, purple, or black. Some of the colors of autumn leaves are derived from anthocyanins. Anthocyanins belong to a parent class of molecules called flavonoids synthesized via the phenylpropanoid pathway. They occur in all tissues of higher plants, including leaves, stems, roots, flowers, and fruits. Anthocyanins are derived from anthocyanidins by adding sugars. They are odorless and moderately astringent. Although approved as food and beverage colorant in the European Union, anthocyanins are not approved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Compound
In chemistry, organic compounds are generally any chemical compounds that contain carbon-hydrogen or carbon-carbon bonds. Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The study of the properties, reactions, and syntheses of organic compounds comprise the discipline known as organic chemistry. For historical reasons, a few classes of carbon-containing compounds (e.g., carbonate salts and cyanide salts), along with a few other exceptions (e.g., carbon dioxide, hydrogen cyanide), are not classified as organic compounds and are considered inorganic. Other than those just named, little consensus exists among chemists on precisely which carbon-containing compounds are excluded, making any rigorous definition of an organic compound elusive. Although organic compounds make up only a small percentage of Earth's crust, they are of central importance because all known life is based on organic compounds. Living t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyketide Synthase
Polyketides are a class of natural products derived from a precursor molecule consisting of a chain of alternating ketone (or reduced forms of a ketone) and methylene groups: (-CO-CH2-). First studied in the early 20th century, discovery, biosynthesis, and application of polyketides has evolved. It is a large and diverse group of secondary metabolites caused by its complex biosynthesis which resembles that of fatty acid synthesis. Because of this diversity, polyketides can have various medicinal, agricultural, and industrial applications. Many polyketides are medicinal or exhibit acute toxicity. Biotechnology has enabled discovery of more naturally-occurring polyketides and evolution of new polyketides with novel or improved bioactivity. History Naturally produced polyketides by various plants and organisms have been used by humans since before studies on them began in the 19th and 20th century. In 1893, J. Norman Collie synthesized detectable amounts of orcinol by heating dehy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
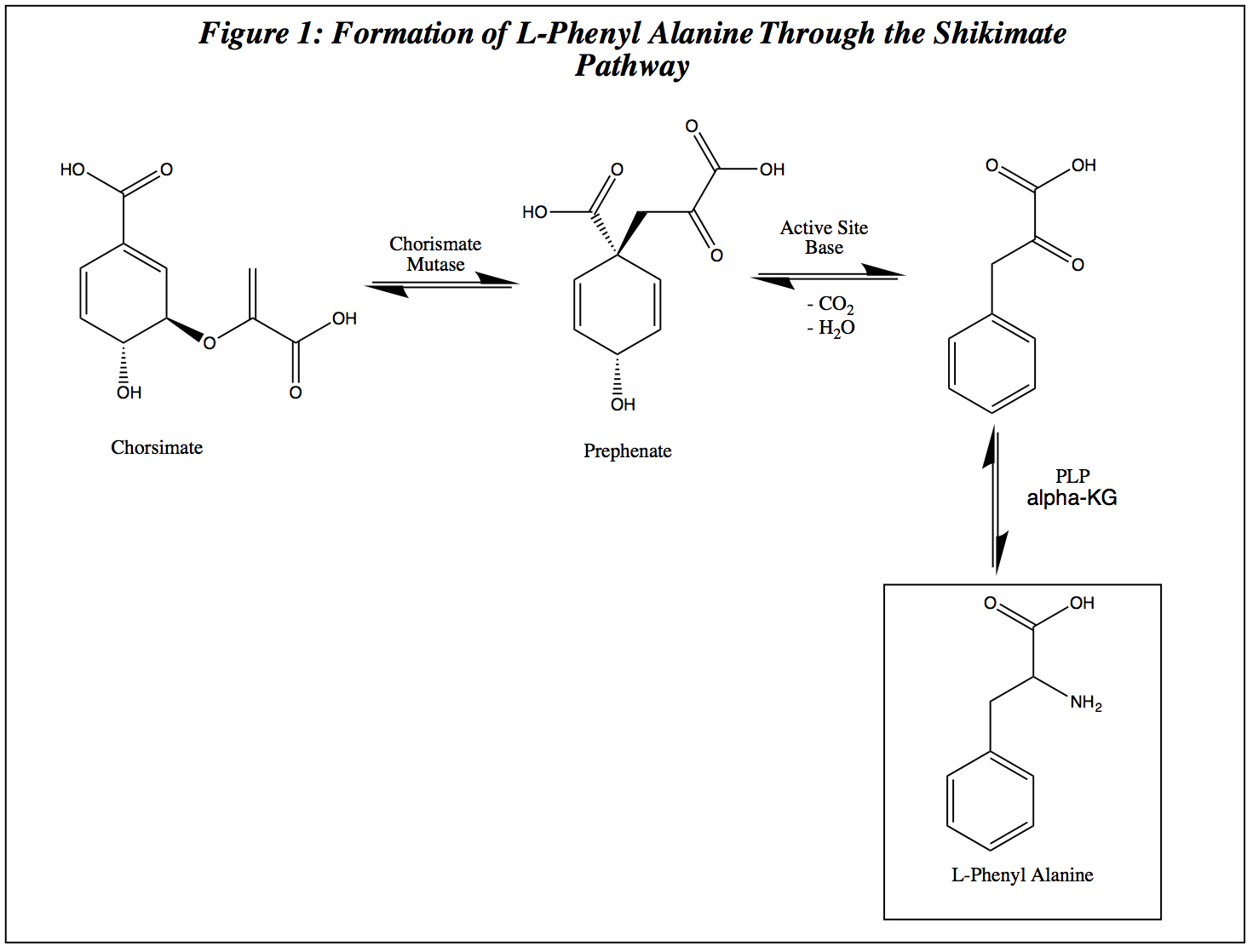
Shikimate Pathway
The shikimate pathway (shikimic acid pathway) is a seven-step metabolic pathway used by bacteria, archaea, fungi, algae, some protozoans, and plants for the biosynthesis of folates and aromatic amino acids (tryptophan, phenylalanine, and tyrosine). This pathway is not found in animal cells. The seven enzymes involved in the shikimate pathway are DAHP synthase, 3-dehydroquinate synthase, 3-dehydroquinate dehydratase, shikimate dehydrogenase, shikimate kinase, EPSP synthase, and chorismate synthase. The pathway starts with two substrates, phosphoenol pyruvate and erythrose-4-phosphate, and ends with chorismate, a substrate for the three aromatic amino acids. The fifth enzyme involved is the shikimate kinase, an enzyme that catalyzes the ATP-dependent phosphorylation of shikimate to form shikimate 3-phosphate (shown in the figure below). Shikimate 3-phosphate is then coupled with phosphoenol pyruvate to give 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate via the enzyme 5-enolpyruvylshikimate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Wine
Red wine is a type of wine made from dark-colored grape varieties. The color of the wine can range from intense violet, typical of young wines, through to brick red for mature wines and brown for older red wines. The juice from most purple grapes is greenish-white, the red color coming from anthocyan pigments present in the skin of the grape. Much of the red wine production process involves extraction of color and flavor components from the grape skin. Varieties The top 20 red grape varieties by acreage are: * Alicante Henri Bouschet * Barbera * Bobal * Cabernet Franc * Cabernet Sauvignon * Carignan * Cinsaut * Malbec * Douce noir * Gamay * Grenache * Isabella * Merlot * Montepulciano * Mourvèdre * Rose * Pinot noir * Sangiovese * Syrah * Tempranillo * Zinfandel The top 21—50 red grape varieties by acreage are: * Aglianico * Blaufränkisch * Bordô * Carménère * Castelão * Concord * Corvina Veronese * Criolla Grande * Croatina * Dolcetto * Dornfelder * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blackcurrant
The blackcurrant (''Ribes nigrum''), also known as black currant or cassis, is a deciduous shrub in the family Grossulariaceae grown for its edible berries. It is native to temperate parts of central and northern Europe and northern Asia, where it prefers damp fertile soils. It is widely cultivated both commercially and domestically. It is winter hardy, but cold weather at flowering time during the spring may reduce the size of the crop. Bunches of small, glossy black fruit develop along the stems in the summer and can be harvested by hand or by machine. Breeding is common in Scotland, Poland, Lithuania, Latvia, Norway, and New Zealand to produce fruit with better eating qualities and bushes with greater hardiness and disease resistance. The raw fruit is particularly rich in vitamin C and polyphenols. Blackcurrants can be eaten raw but are usually cooked in sweet or savoury dishes. They are used to make jams, preserves, and syrups and are grown commercially for the juice mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Raspberry
Black raspberry is a common name for three species of the genus ''Rubus'': *''Rubus leucodermis'', native to western North America *''Rubus occidentalis'', native to eastern North America *''Rubus coreanus 300px, (left to right) ''R. coreanus, R. thibetanus, R. corchorifolius'' ''Rubus coreanus'', known as bokbunja ( ko, 복분자), Korean blackberry, or Korean bramble, is a species of raspberry native to Korea, Japan, and China. It produces edi ...'', also known as Korean black raspberry, native to Korea, Japan, and China {{Plant common name Berries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |