|
Cullin 3
Cullin 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CUL3'' gene. Cullin 3 protein belongs to the family of cullins which in mammals contains eight proteins (Cullin 1, Cullin 2, Cullin 3, Cullin 4A, Cullin 4B, Cullin 5, Cullin 7 and Cullin 9). Cullin proteins are an evolutionarily conserved family of proteins throughout yeast, plants and mammals. Protein function Cullin 3 is a component of Cullin-RING E3 ubiquitin ligases complexes (CRLs) which are involved in protein ubiquitylation and represent a part of ubiquitin–proteasome system (UPS). Added ubiquitin moieties to the lysine residue by CRLs then target the protein for the proteasomal degradation. Cullin-RING E3 ubiquitin ligases are involved in many cellular processes responsible for cell cycle regulation, stress response, protein trafficking, signal transduction, DNA replication, transcription, protein quality control, circadian clock and development. Deletion of ''CUL3'' gene in mice causes embryonic lethality. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CAND1
Cullin-associated NEDD8-dissociated protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CAND1'' gene. Interactions CAND1 has been shown to interact with: * CUL1, * CUL2, * CUL3, * CUL4A, * CUL4B, * DCUN1D1, and * RBX1 RING-box protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''RBX1'' gene. Function This gene encodes an evolutionarily conserved protein that interacts with cullins. The protein plays a unique role in the ubiquitination reaction by heter .... References External links * Further reading * * * * * * * * * * {{gene-12-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DCUN1D1
DCN1-like protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''DCUN1D1'' gene. DCUN1D1 is amplified in several cancer types, including squamous cell cancers, and may act as an oncogenic driver in cancer cells. Interactions DCUN1D1 has been shown to interact with: * CAND1, * CUL1, * CUL2, * CUL3 and * RBX1 RING-box protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''RBX1'' gene. Function This gene encodes an evolutionarily conserved protein that interacts with cullins. The protein plays a unique role in the ubiquitination reaction by hetero .... References Further reading * * * * * * * * {{gene-3-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclin E1
G1/S-specific cyclin-E1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CCNE1'' gene. Function The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the highly conserved cyclin family, whose members are characterized by a dramatic periodicity in protein abundance through the cell cycle. Cyclins function as regulators of CDK. Different cyclins exhibit distinct expression and degradation patterns which contribute to the temporal coordination of each mitotic event. This cyclin forms a complex with and functions as a regulatory subunit of CDK2, whose activity is required for cell cycle G1/S transition. This protein accumulates at the G1-S phase boundary and is degraded as cells progress through S phase. Overexpression of this gene has been observed in many tumors, which results in chromosome instability, and thus may contribute to tumorigenesis. This protein was found to associate with, and be involved in, the phosphorylation of NPAT protein (nuclear protein mapped to the ATM locus), which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RhoBTB2
Rho-related BTB domain-containing protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''RHOBTB2'' gene. RHOBTB2 is a member of the evolutionarily-conserved RhoBTB subfamily of Rho GTPases. For background information on RhoBTBs, see RHOBTB1 (MIM 607351). upplied by OMIMref name="entrez"/> Clinical significance Mutations affecting ''RHOBTB2'' can cause epilepsy, learning difficulties and movement disorders. ''RHOBTB2''-related disorders are autosomal dominant In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the effect of a different variant of the same gene on the other copy of the chromosome. The first variant is termed dominant and t ..., meaning only one of the two copies of the gene needs to be mutated to cause disease. The mutations usually occur ''de novo'' – that is, as a new mutation occurring in the affected individual rather than having been inherited. References Further reading * * * * * * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NFE2L2
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NRF2), also known as nuclear factor erythroid-derived 2-like 2, is a transcription factor that in humans is encoded by the ''NFE2L2'' gene. NRF2 is a basic leucine zipper (bZIP) protein that may regulate the expression of antioxidant proteins that protect against oxidative damage triggered by injury and inflammation, according to preliminary research. In vitro, NRF2 binds to antioxidant response elements (AREs) in the promoter regions of genes encoding cytoprotective proteins. NRF2 induces the expression of heme oxygenase 1 ''in vitro'' leading to an increase in phase II enzymes. NRF2 also inhibits the NLRP3 inflammasome. NRF2 appears to participate in a complex regulatory network and performs a pleiotropic role in the regulation of metabolism, inflammation, autophagy, proteostasis, mitochondrial physiology, and immune responses. Several drugs that stimulate the NFE2L2 pathway are being studied for treatment of diseases that are ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WNK4
Serine/threonine protein kinase WNK4 also known as WNK lysine deficient protein kinase 4 or WNK4, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''WNK4'' gene. Missense mutations cause a genetic form of pseudohypoaldosteronism type 2, also called Gordon syndrome. WNK4 is a member of a serine/threonine kinase family that comprises four members. The family is so named because unlike other serine/threonine kinases, WNKs are characterized by the lack of the lysine in the subdomain II of the catalytic domain. Instead, a lysine in the β2 strand of subdomain I of the catalytic domain is responsible for the kinase activity. The ''WNK4'' gene is located on chromosome 17q21-q22. It produces a 1,243-amino acid protein encoded by a 3,732-nucleotide open reading frame within a 4 kb cDNA transcript. WNK4 protein is highly expressed in the distal convoluted tubule (DCT) and the cortical collecting duct (CDD) of the kidney. WNK4 is also present in the brain, lungs, liver, heart, and colon of vari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
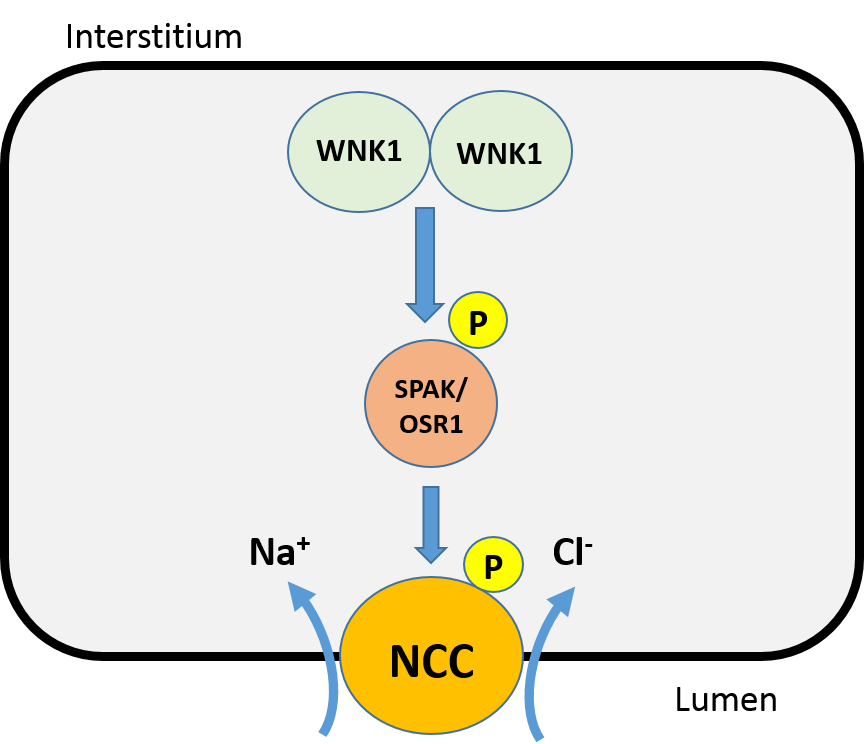
WNK1
WNK (lysine deficient protein kinase 1), also known as WNK1, is an enzyme that is encoded by the ''WNK1'' gene. WNK1 is serine-threonine protein kinase and part of the "with no lysine/K" kinase WNK family. The predominant role of WNK1 is the regulation of cation-Cl− cotransporters (CCCs) such as the sodium chloride cotransporter ( NCC), basolateral Na-K-Cl symporter (NKCC1), and potassium chloride cotransporter (KCC1) located within the kidney. CCCs mediate ion homeostasis and modulate blood pressure by transporting ions in and out of the cell. ''WNK1'' mutations as a result have been implicated in blood pressure disorders/diseases; a prime example being familial hyperkalemic hypertension (FHHt). Structure The WNK1 protein is composed of 2382 amino acids (molecular weight 230 kDa). The protein contains a kinase domain located within its short N-terminal domain and a long C-terminal tail. The kinase domain has some similarity to the MEKK protein kinase family. As a member ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Na/Cl Cotransporter
The sodium-chloride symporter (also known as Na+-Cl− cotransporter, NCC or NCCT, or as the thiazide-sensitive Na+-Cl− cotransporter or TSC) is a cotransporter in the kidney which has the function of reabsorbing sodium and chloride ions from the tubular fluid into the cells of the distal convoluted tubule of the nephron. It is a member of the SLC12 cotransporter family of electroneutral cation-coupled chloride cotransporters. In humans, it is encoded by the gene (solute carrier family 12 member 3) located in 16q13. A loss of NCC function causes Gitelman syndrome, an autosomic recessive disease characterized by salt wasting and low blood pressure, hypokalemic metabolic alkalosis, hypomagnesemia and hypocalciuria. Over a hundred different mutations in the NCC gene have been identified. Molecular biology The sodium-chloride symporter or NCC is a member of the SLC12 cotransporter family of electroneutral cation-coupled chloride cotransporter, along with the potassium-chlori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neddylation
Neddylation (also NEDDylation) is the process by which the ubiquitin-like protein NEDD8 is conjugated to its target proteins. This process is analogous to ubiquitination, although it relies on its own E1 and E2 enzymes. No NEDD8-specific E3 has yet been identified and it is possible that the Neddylation system relies on E3 ligases with dual specificity. NEDD8 NEDD8 (neural-precursor-cell-expressed developmentally down-regulated 8) is a protein involved in the regulation of cell growth, viability and development. Neddylation process NEDD8 links itself to a protein through an isopeptide linkage between its carboxy-terminal glycine and the lysine of the substrate. The neddylation of the substrate causes in a structural change, and there are three main biochemical effects that result. First, neddylation can cause a conformational change in the substrate which may restrict molecular movement and the positioning of different binding partners. Second, it can cause the target protein to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |