|
Croatia–Czech Republic Relations
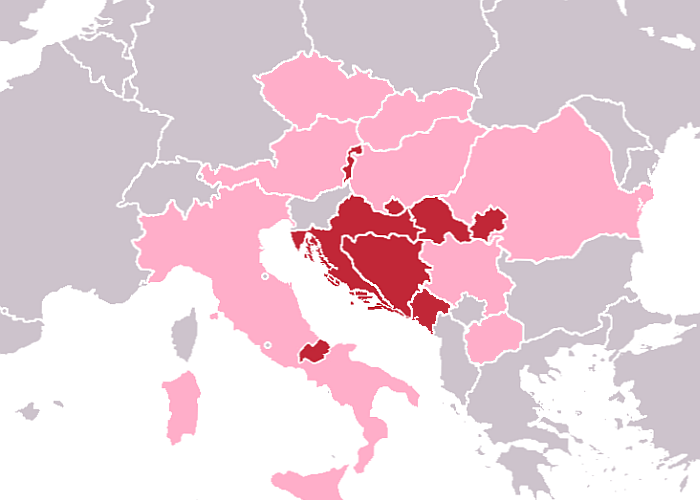
Croatia–Czech Republic relations are foreign relations between Croatia and the Czech Republic. Croatia has an embassy in Prague and an honorary consulate in Brno. The Czech Republic has an embassy in Zagreb (and 2 honorary consulates in Rijeka and Split). Both countries are full members of the European Union and NATO, and both countries are full members of the Council of Europe. History Teritorries of both countries used to be part of the Austria-Hungary until the end of WWI and later on were both part of the Eastern Bloc during the Cold War. Czechoslovakia recognized Croatia on 16 January 1992. After dissolution of Czechoslovakia, Croatia and the newly established Czech Republic mutually recognized and established diplomatic relations on 1 January 1993. Culture The Croatian and Czech languages both belong to the Slavic language family allowing a small degree of mutual intelligibility. There is a czech ethnic minority in Croatia. Croatia is a popular tourist destina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Croatia
, image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg , image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg , anthem = "Lijepa naša domovino"("Our Beautiful Homeland") , image_map = , map_caption = , capital = Zagreb , coordinates = , largest_city = capital , official_languages = Croatian , languages_type = Writing system , languages = Latin , ethnic_groups = , ethnic_groups_year = 2021 , religion = , religion_year = 2021 , demonym = , government_type = Unitary parliamentary republic , leader_title1 = President , leader_name1 = Zoran Milanović , leader_title2 = Prime Minister , leader_name2 = Andrej Plenković , leader_title3 = Speaker of Parliament , leader_name3 = Gordan Jandroković , legislature = Sabor , sovereignty_type ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Croatian Language
Croatian (; ' ) is the standardized variety of the Serbo-Croatian pluricentric language used by Croats, principally in Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, the Serbian province of Vojvodina, and other neighboring countries. It is the official and literary standard of Croatia and one of the official languages of the European Union. Croatian is also one of the official languages of Bosnia and Herzegovina and a recognized minority language in Serbia and neighboring countries. Standard Croatian is based on the most widespread dialect of Serbo-Croatian, Shtokavian, more specifically on Eastern Herzegovinian, which is also the basis of Standard Serbian, Bosnian, and Montenegrin. In the mid-18th century, the first attempts to provide a Croatian literary standard began on the basis of the Neo-Shtokavian dialect that served as a supraregional ''lingua franca'' pushing back regional Chakavian, Kajkavian, and Shtokavian vernaculars. The decisive role was played by Croatian Vukovians, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Croatia–Czech Republic Relations
Croatia–Czech Republic relations are foreign relations between Croatia and the Czech Republic. Croatia has an embassy in Prague and an honorary consulate in Brno. The Czech Republic has an embassy in Zagreb (and 2 honorary consulates in Rijeka and Split). Both countries are full members of the European Union and NATO, and both countries are full members of the Council of Europe. History Teritorries of both countries used to be part of the Austria-Hungary until the end of WWI and later on were both part of the Eastern Bloc during the Cold War. Czechoslovakia recognized Croatia on 16 January 1992. After dissolution of Czechoslovakia, Croatia and the newly established Czech Republic mutually recognized and established diplomatic relations on 1 January 1993. Culture The Croatian and Czech languages both belong to the Slavic language family allowing a small degree of mutual intelligibility. There is a czech ethnic minority in Croatia. Croatia is a popular tourist destina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Czech Republic In The European Union
The Czech Republic has been a member state of the European Union since the 2004 enlargement of the European Union. It is not a member of the eurozone. See also *Czech Republic and the euro *2003 Czech European Union membership referendum *2004 European Parliament election in the Czech Republic *2009 European Parliament election in the Czech Republic * 2009 Czech Presidency of the Council of the European Union *2014 European Parliament election in the Czech Republic *2019 European Parliament election in the Czech Republic The 2019 European Parliament election in the Czech Republic was held on 24 and 25 May 2019, electing the 21 members of the Czech delegation to the European Parliament as part of the European elections held across the European Union. The result w ... * 2022 Czech Presidency of the Council of the European Union References {{authority control Czech Republic and the European Union History of the European Union Enlargement of the European Union ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Croatia In The European Union
Croatia has been a member of the European Union since 2013. History The accession of Croatia to the European Union was completed in 2013. Croatia first hosted the rotating Presidency of the Council of the European Union in the first half of 2020. The country adopted the euro as its currency and joined the Schengen Area The Schengen Area ( , ) is an area comprising 27 European countries that have officially abolished all passport and all other types of border control at their mutual borders. Being an element within the wider area of freedom, security and j ... in 2023. References * * * * * * * {{Member states of the European Union Politics of Croatia Foreign relations of Croatia History of the European Union ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Czechoslovakia–Yugoslavia Relations
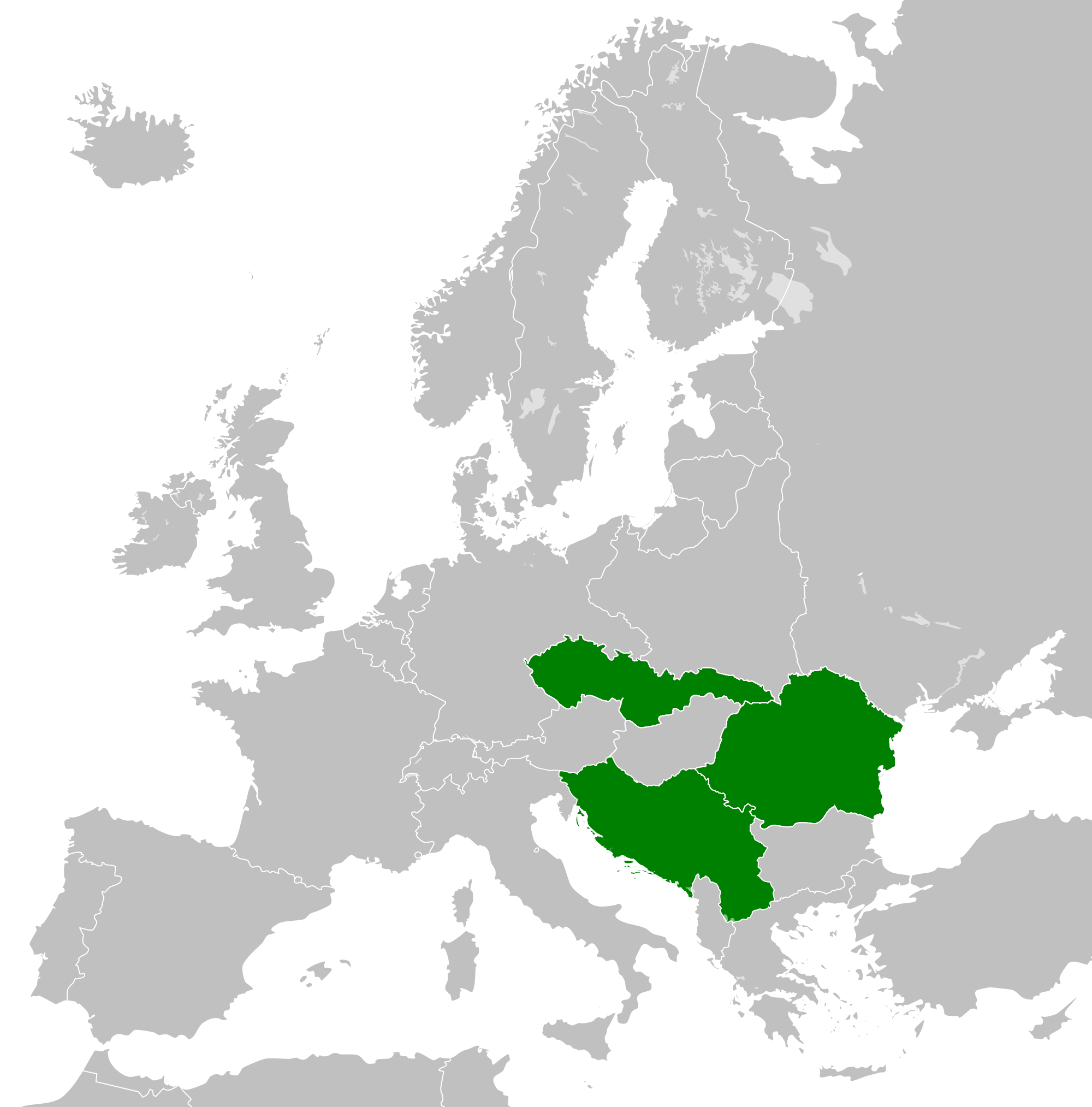
Czechoslovakia–Yugoslavia relations were historical foreign relations between Czechoslovakia and Yugoslavia both of which are now-defunct states. Czechoslovakia and the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes were both created as union states of smaller Slavic ethnic groups. Both were created after the dissolution of the Austro-Hungary, itself a multinational empire unable to implement a trialist reform in its final years. History During the Austro-Hungarian time the Charles University in Prague and other Czechoslovak institutions of higher education became important center of higher education for South Slavic students with students and graduates including Veljko Vlahović, Ratko Vujović, Aleksandar Deroko, Nikola Dobrović, Petar Drapšin, Zoran Đorđević, Lordan Zafranović, Momir Korunović, Branko Krsmanović, Emir Kusturica, Ljubica Marić, Goran Marković, Predrag Nikolić, Stjepan Radić, Nikola Tesla and other. Interwar period In 1921, together with the Kingdom o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foreign Relations Of The Czech Republic
The Czech Republic is a Central European country, a member of the European Union, the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OSCE), the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), the United Nations (and all of its main specialized agencies and boards). It entertains diplomatic relations with 191 countries of the world, around half of which maintain a resident embassy in the Czech capital city, Prague. During the years 1948–1989, the foreign policy of Czechoslovakia had followed that of the Soviet Union. Since the revolution and the subsequent mutually-agreed peaceful dissolution of Czechoslovakia into the Czech Republic and Slovakia, the Czechs have made reintegration with Western institutions their chief foreign policy objective. This goal was rapidly met with great success, as the nation joined NATO in 1999 and the European Union in 2004, and held the Presidency of the European Union during the first half of 2009. International disputes Liechtenstein Thro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foreign Relations Of Croatia
The Republic of Croatia is a sovereign country at the crossroads of Central Europe, Southeast Europe, and the Mediterranean that declared its independence from Yugoslavia on 25 June 1991. Croatia is a member of the European Union (EU), United Nations (UN), the Council of Europe, NATO, the World Trade Organization (WTO), Union for the Mediterranean and a number of other international organizations. Croatia has established diplomatic relations with 187 countries. The president and the Government, through the Ministry of Foreign and European Affairs, co-operate in the formulation and implementation of foreign policy. The main objectives of Croatian foreign policy during the 1990s were gaining international recognition and joining the United Nations. These objectives were achieved by 2000, and the main goals became NATO and EU membership. Croatia fulfilled these goals in 2009 and 2013 respectively. Current Croatian goals in foreign policy are: positioning within the EU institutio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Czechs Of Croatia
Czechs are one of the recognised minorities of Croatia. According to the census of 2011 there were 9,641 Czechs in Croatia, comprising 0.22% of total population. Geographic representation Most Croatian Czechs live in Western Slavonia especially around the cities of Daruvar and Grubišno Polje. They comprise 5.25% of population of Bjelovar-Bilogora County and 0.83% of Požega-Slavonia County. They comprise a relative majority in Končanica municipality and in villages like Veliki Zdenci, Mali Zdenci, Golubinjak etc. They can be also found in almost all major towns in Croatia. , Czech is officially used in one municipality and five other settlements in Croatia, according to the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. History After the Treaty of Karlowitz in 1699, Slavonia changed hands from the Ottomans to Habsburgs, and the Muslim population fled. This left large swathes of land vacant, and the Habsburgs started to colonize new lands with people from all parts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutual Intelligibility
In linguistics, mutual intelligibility is a relationship between languages or dialects in which speakers of different but related varieties can readily understand each other without prior familiarity or special effort. It is sometimes used as an important criterion for distinguishing languages from dialects, although sociolinguistic factors are often also used. Intelligibility between languages can be asymmetric, with speakers of one understanding more of the other than speakers of the other understanding the first. When it is relatively symmetric, it is characterized as "mutual". It exists in differing degrees among many related or geographically proximate languages of the world, often in the context of a dialect continuum. Intelligibility Factors An individual's achievement of moderate proficiency or understanding in a language (called L2) other than their first language (L1) typically requires considerable time and effort through study and practical application if the two l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slavic Languages
The Slavic languages, also known as the Slavonic languages, are Indo-European languages spoken primarily by the Slavic peoples and their descendants. They are thought to descend from a proto-language called Proto-Slavic, spoken during the Early Middle Ages, which in turn is thought to have descended from the earlier Proto-Balto-Slavic language, linking the Slavic languages to the Baltic languages in a Balto-Slavic group within the Indo-European family. The Slavic languages are conventionally (that is, also on the basis of extralinguistic features) divided into three subgroups: East, South, and West, which together constitute more than 20 languages. Of these, 10 have at least one million speakers and official status as the national languages of the countries in which they are predominantly spoken: Russian, Belarusian and Ukrainian (of the East group), Polish, Czech and Slovak (of the West group) and Bulgarian and Macedonian (eastern dialects of the South group), and Serbo-C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Czech Language
Czech (; Czech ), historically also Bohemian (; ''lingua Bohemica'' in Latin), is a West Slavic language of the Czech–Slovak group, written in Latin script. Spoken by over 10 million people, it serves as the official language of the Czech Republic. Czech is closely related to Slovak, to the point of high mutual intelligibility, as well as to Polish to a lesser degree. Czech is a fusional language with a rich system of morphology and relatively flexible word order. Its vocabulary has been extensively influenced by Latin and German. The Czech–Slovak group developed within West Slavic in the high medieval period, and the standardization of Czech and Slovak within the Czech–Slovak dialect continuum emerged in the early modern period. In the later 18th to mid-19th century, the modern written standard became codified in the context of the Czech National Revival. The main non-standard variety, known as Common Czech, is based on the vernacular of Prague, but is now spoken as an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |