|
CRISPR
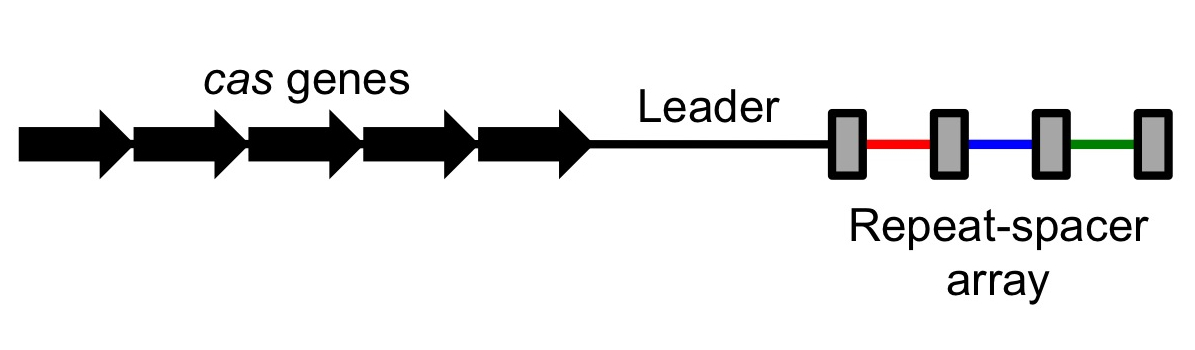
CRISPR () (an acronym for clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats) is a family of DNA sequences found in the genomes of prokaryotic organisms such as bacteria and archaea. These sequences are derived from DNA fragments of bacteriophages that had previously infected the prokaryote. They are used to detect and destroy DNA from similar bacteriophages during subsequent infections. Hence these sequences play a key role in the antiviral (i.e. anti-phage) defense system of prokaryotes and provide a form of acquired immunity. CRISPR is found in approximately 50% of sequenced bacterial genomes and nearly 90% of sequenced archaea. Cas9 (or "CRISPR-associated protein 9") is an enzyme that uses CRISPR sequences as a guide to recognize and cleave specific strands of DNA that are complementary to the CRISPR sequence. Cas9 enzymes together with CRISPR sequences form the basis of a technology known as CRISPR-Cas9 that can be used to edit genes within organisms. This editing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crispr
CRISPR () (an acronym for clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats) is a family of DNA sequences found in the genomes of prokaryotic organisms such as bacteria and archaea. These sequences are derived from DNA fragments of bacteriophages that had previously infected the prokaryote. They are used to detect and destroy DNA from similar bacteriophages during subsequent infections. Hence these sequences play a key role in the antiviral (i.e. anti-phage) defense system of prokaryotes and provide a form of acquired immunity. CRISPR is found in approximately 50% of sequenced bacterial genomes and nearly 90% of sequenced archaea. Cas9 (or "CRISPR-associated protein 9") is an enzyme that uses CRISPR sequences as a guide to recognize and cleave specific strands of DNA that are complementary to the CRISPR sequence. Cas9 enzymes together with CRISPR sequences form the basis of a technology known as CRISPR-Cas9 that can be used to edit genes within organisms. This editing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CRISPR Gene Editing
CRISPR gene editing (pronounced "crisper") is a genetic engineering technique in molecular biology by which the genomes of living organisms may be modified. It is based on a simplified version of the bacterial CRISPR-Cas9 antiviral defense system. By delivering the Cas9 nuclease complexed with a synthetic guide RNA (gRNA) into a cell, the cell's genome can be cut at a desired location, allowing existing genes to be removed and/or new ones added ''in vivo''. The technique is considered highly significant in biotechnology and medicine as it enables editing genomes ''in vivo'' very precisely, cheaply, and easily. It can be used in the creation of new medicines, agricultural products, and genetically modified organisms, or as a means of controlling pathogens and pests. It also has possibilities in the treatment of inherited genetic diseases as well as diseases arising from somatic mutations such as cancer. However, its use in human germline genetic modification is highly controve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cas9
Cas9 (CRISPR associated protein 9, formerly called Cas5, Csn1, or Csx12) is a 160 kilodalton protein which plays a vital role in the immunological defense of certain bacteria against DNA viruses and plasmids, and is heavily utilized in genetic engineering applications. Its main function is to cut DNA and thereby alter a cell's genome. The CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing technique was a significant contributor to the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 2020 being awarded to Emmanuelle Charpentier and Jennifer Doudna. More technically, Cas9 is a dual RNA-guided DNA endonuclease enzyme associated with the Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats ( CRISPR) adaptive immune system in ''Streptococcus pyogenes''. ''S. pyogenes'' utilizes CRISPR to memorize and Cas9 to later interrogate and cleave foreign DNA, such as invading bacteriophage DNA or plasmid DNA. Cas9 performs this interrogation by unwinding foreign DNA and checking for sites complementary to the 20 nucleotide spacer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jennifer Doudna
Jennifer Anne Doudna (; born February 19, 1964) is an American biochemist who has done pioneering work in CRISPR gene editing, and made other fundamental contributions in biochemistry and genetics. Doudna was one of the first women to share a Nobel in the sciences. She received the 2020 Nobel Prize in Chemistry, with Emmanuelle Charpentier, "for the development of a method for genome editing." She is the Li Ka Shing Chancellor's Chair Professor in the Department of Chemistry and the Department of Molecular and Cell Biology at the University of California, Berkeley. She has been an investigator with the Howard Hughes Medical Institute since 1997. She graduated from Pomona College in 1985 and earned a Ph.D. from Harvard Medical School in 1989. Apart from her professorship at Berkeley, she is also president and chair of the board of the Innovative Genomics Institute, a faculty scientist at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, a senior investigator at the Gladstone Institute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francisco Mojica
Francisco Juan Martínez Mojica (born 5 October 1963) is a Spanish molecular biologist and microbiologist at the University of Alicante in Spain. He is known for his discovery of repetitive, functional DNA sequences in bacteria which he named CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats). These were later developed into the first widespread genome editing tool, CRISPR-Cas9. Early life and education Mojica was born in Elche, Spain, on 5 October 1963. He attended Los Andes elementary school, Vázquez de Mella school, and Instituto Carrus high school. He enrolled first at the University of Murcia to study biology and later moved to the University of Valencia ( BS, 1986) and University of Alicante ( PhD, 1993). During his doctoral studies, he visited Paris-Sud University. He then received post-doctoral training at the University of Utah and the University of Oxford. Since 1994, Mojica has been a faculty member at the University of Alicante, were he has focused ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emmanuelle Charpentier
Emmanuelle Marie Charpentier (; born 11 December 1968) is a French professor and researcher in microbiology, genetics, and biochemistry. As of 2015, she has been a director at the Max Planck Institute for Infection Biology in Berlin. In 2018, she founded an independent research institute, the Max Planck Unit for the Science of Pathogens. In 2020, Charpentier and American biochemist Jennifer Doudna of the University of California, Berkeley, were awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry "for the development of a method for genome editing" (through CRISPR). This was the first science Nobel Prize ever won by two women only. Early life and education Born in 1968 in Juvisy-sur-Orge in France, Charpentier studied biochemistry, microbiology, and genetics at the Pierre and Marie Curie University (today the Faculty of Science of Sorbonne University) in Paris. She was a graduate student at the Institut Pasteur from 1992 to 1995 and was awarded a research doctorate. Charpentier's PhD work i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rodolphe Barrangou
Rodolphe Barrangou is the Todd R. Klaenhammer Distinguished Professor in Probiotics Research in the Department of Food, Bioprocessing and Nutrition Sciences at North Carolina State University; Co-Founder and Chief Executive Officer of CRISPR Biotechnologies; Co-Founder and Chief Scientific Officer of Ancilia Biosciences; Co-Founder, President and Chief Scientific Officer of TreeCo; and Co-Founder and member of the Scientific Advisory Board of Intellia Therapeutics. His research focuses on CRISPR-Cas9 in bacteria. In 2017, Barrangou was named Editor-in-Chief of The CRISPR Journal, a peer-reviewed journal covering the field of genome editing and CRISPR research, which debuted in February 2018. He was elected as a member into the National Academy of Sciences in 2018. He was also elected into the National Academy of Engineering in 2019 for the discovery of CRISPR-Cas genome editing and engineering microbes, plants, and animals for food and other applications. Background Dr Barran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yoshizumi Ishino
is a Japanese molecular biologist, known for his discovering the DNA sequence of Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats (CRISPR). Biography Ishino was born in Kyoto Prefecture, Japan. He received his BS, MS and PhD in 1981, 1983 and 1986, respectively, from Osaka University.Yoshizumi Ishino , astrobiology.illinois.edu From 1987 to 1989, he served as a post-doctoral fellow in Dieter Söll's laboratory at . In 2002, he became a professor at |
Biotechnology
Biotechnology is the integration of natural sciences and engineering sciences in order to achieve the application of organisms, cells, parts thereof and molecular analogues for products and services. The term ''biotechnology'' was first used by Károly Ereky in 1919, meaning the production of products from raw materials with the aid of living organisms. Definition The concept of biotechnology encompasses a wide range of procedures for modifying living organisms according to human purposes, going back to domestication of animals, cultivation of the plants, and "improvements" to these through breeding programs that employ artificial selection and hybridization. Modern usage also includes genetic engineering as well as cell and tissue culture technologies. The American Chemical Society defines biotechnology as the application of biological organisms, systems, or processes by various industries to learning about the science of life and the improvement of the value of materials ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteriophage
A bacteriophage (), also known informally as a ''phage'' (), is a duplodnaviria virus that infects and replicates within bacteria and archaea. The term was derived from "bacteria" and the Greek φαγεῖν ('), meaning "to devour". Bacteriophages are composed of proteins that encapsulate a DNA or RNA genome, and may have structures that are either simple or elaborate. Their genomes may encode as few as four genes (e.g. MS2) and as many as hundreds of genes. Phages replicate within the bacterium following the injection of their genome into its cytoplasm. Bacteriophages are among the most common and diverse entities in the biosphere. Bacteriophages are ubiquitous viruses, found wherever bacteria exist. It is estimated there are more than 1031 bacteriophages on the planet, more than every other organism on Earth, including bacteria, combined. Viruses are the most abundant biological entity in the water column of the world's oceans, and the second largest component of biom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haloferax Volcanii
''Haloferax volcanii'' is a species of organism in the genus ''Haloferax'' in the Archaea. Description and significance Microbiologist Benjamin Elazari Volcani first discovered ''Haloferax volcanii'', a self-named extremophile, in the 1930s. ''H. volcanii'' is a halophilic mesophile archaeon that can be isolated from hypersaline environments such as: the Dead Sea, the Great Salt Lake, and oceanic environments with high sodium chloride concentrates. ''Haloferax volcanii'' is noteworthy because it can be cultured without much difficulty, rare for an extremophile. ''H. volcanii'' is chemoorganotrophic, metabolizing sugars as a carbon source. It is primarily aerobic, but is capable of anaerobic respiration under anoxic conditions. Recently an isolate of this species was studied by researchers at University of California, Berkeley, as part of a project on the survival of haloarchaea on Mars. Genome structure The genome of ''H. volcanii'' consists of a large (4 Mb), multicopy chrom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broad Institute
The Eli and Edythe L. Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard (IPA: , pronunciation respelling: ), often referred to as the Broad Institute, is a biomedical and genomic research center located in Cambridge, Massachusetts, Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. The institute is independently governed and supported as a 501(c)(3) nonprofit research organization under the name Broad Institute Inc., and it partners with the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Harvard University, and the five Harvard teaching hospitals. History The Broad Institute evolved from a decade of research collaborations among MIT and Harvard scientists. One cornerstone was the Center for Genome Research of Whitehead Institute at MIT. Founded in 1982, the Whitehead became a major center for genomics and the Human Genome Project. As early as 1995, scientists at the Whitehead started pilot projects in genomic medicine, forming an unofficial collaborative network among young scientists interested in genomic a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)


