|
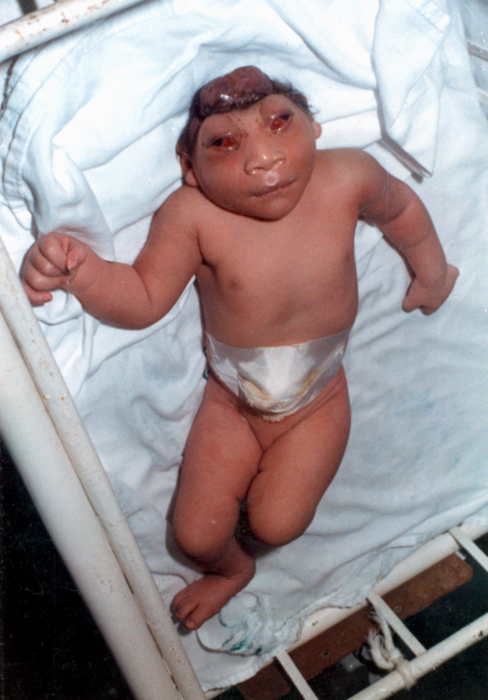
Cranioschisis
Cranioschisis (Greek language, Greek: κρανιον ''kranion'', "skull", and σχίσις ''schisis'', "split"), or dysraphism, is a neural tube defect involving the skull. In this defect, the cranium fails to close completely (especially at the occipital region). Thus, the brain is exposed to the Amnion, amnios and eventually degenerates, causing anencephaly. Craniorachischisis is on the extreme end of the dysraphism spectrum, wherein the entire length of the neural tube fails to close. See also * Rachischisis * Spina bifida References {{Congenital malformations and deformations of musculoskeletal system Congenital disorders of nervous system Congenital disorders of musculoskeletal system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rachischisis
Rachischisis (Greek language, Greek: "rhachis - ῥάχις" - spine, and "schisis - σχίσις" - split) is a developmental birth defect involving the neural tube. This anomaly occurs in utero, when the posterior neuropore of the neural tube fails to close by the 27th intrauterine day. As a consequence the vertebrae overlying the open portion of the spinal cord do not fully form and remain unfused and open, leaving the spinal cord exposed. Patients with rachischisis have motor and sensory deficits, chronic infections, and disturbances in bladder function. This defect often occurs with anencephaly. Craniorachischisis is a variant of rachischisis that occurs when the entire spinal cord and brain are exposed – simultaneous complete rachischisis and anencephaly. It is incompatible with life; affected pregnancies often end in miscarriage or stillbirth. Infants born alive with craniorachischisis die soon after birth. Presentation Interactions with other developmental deformitie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Language
Greek ( el, label=Modern Greek, Ελληνικά, Elliniká, ; grc, Ἑλληνική, Hellēnikḗ) is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages, native to Greece, Cyprus, southern Italy (Calabria and Salento), southern Albania, and other regions of the Balkans, the Black Sea coast, Asia Minor, and the Eastern Mediterranean. It has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning at least 3,400 years of written records. Its writing system is the Greek alphabet, which has been used for approximately 2,800 years; previously, Greek was recorded in writing systems such as Linear B and the Cypriot syllabary. The alphabet arose from the Phoenician script and was in turn the basis of the Latin, Cyrillic, Armenian, Coptic, Gothic, and many other writing systems. The Greek language holds a very important place in the history of the Western world. Beginning with the epics of Homer, ancient Greek literature includes many works of lasting impo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neural Tube Defect
Neural tube defects (NTDs) are a group of birth defects in which an opening in the spine or cranium remains from early in human development. In the third week of pregnancy called gastrulation, specialized cells on the dorsal side of the embryo begin to change shape and form the neural tube. When the neural tube does not close completely, an NTD develops. Specific types include: spina bifida which affects the spine, anencephaly which results in little to no brain, encephalocele which affects the skull, and iniencephaly which results in severe neck problems. NTDs are one of the most common birth defects, affecting over 300,000 births each year worldwide. For example, spina bifida affects approximately 1,500 births annually in the United States, or about 3.5 in every 10,000 (0.035% of US births), which has decreased from around 5 per 10,000 (0.05% of US births) since folate fortification of grain products was started. The number of deaths in the US each year due to neural tube ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Occipital Region
The occipital bone () is a cranial dermal bone and the main bone of the occiput (back and lower part of the skull). It is trapezoidal in shape and curved on itself like a shallow dish. The occipital bone overlies the occipital lobes of the cerebrum. At the base of skull in the occipital bone, there is a large oval opening called the foramen magnum, which allows the passage of the spinal cord. Like the other cranial bones, it is classed as a flat bone. Due to its many attachments and features, the occipital bone is described in terms of separate parts. From its front to the back is the basilar part, also called the basioccipital, at the sides of the foramen magnum are the lateral parts, also called the exoccipitals, and the back is named as the squamous part. The basilar part is a thick, somewhat quadrilateral piece in front of the foramen magnum and directed towards the pharynx. The squamous part is the curved, expanded plate behind the foramen magnum and is the largest part o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amnion
The amnion is a membrane that closely covers the human and various other embryos when first formed. It fills with amniotic fluid, which causes the amnion to expand and become the amniotic sac that provides a protective environment for the developing embryo. The amnion, along with the chorion, the yolk sac and the allantois protect the embryo. In birds, reptiles and monotremes, the protective sac is enclosed in a shell. In marsupials and placental mammals, it is enclosed in a uterus. The term is from Ancient Greek ἀμνίον 'little lamb', diminutive of ἀμνός 'lamb'. it is cognate with the English verb 'yean', bring forth young (usually lambs). The amnion is a feature of the vertebrate clade ''Amniota'', which includes reptiles, birds, and mammals. Amphibians and fish are not amniotes and thus lack the amnion. The amnion stems from the extra-embryonic somatic mesoderm on the outer side and the extra-embryonic ectoderm or trophoblast on the inner side. In humans In the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anencephaly
Anencephaly is the absence of a major portion of the brain, skull, and scalp that occurs during embryonic development. It is a cephalic disorder that results from a neural tube defect that occurs when the rostral (head) end of the neural tube fails to close, usually between the 23rd and 26th day following conception. Strictly speaking, the Greek term translates as "without a brain" (or totally lacking the inside part of the head), but it is accepted that children born with this disorder usually only lack a telencephalon, the largest part of the brain consisting mainly of the cerebral hemispheres, including the neocortex, which is responsible for cognition. The remaining structure is usually covered only by a thin layer of membrane—skin, bone, meninges, etc., are all lacking. With very few exceptions, infants with this disorder do not survive longer than a few hours or days after birth. Signs and symptoms The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neural Tube
In the developing chordate (including vertebrates), the neural tube is the embryonic precursor to the central nervous system, which is made up of the brain and spinal cord. The neural groove gradually deepens as the neural fold become elevated, and ultimately the folds meet and coalesce in the middle line and convert the groove into the closed neural tube. In humans, neural tube closure usually occurs by the fourth week of pregnancy (the 28th day after conception). The ectodermal wall of the tube forms the rudiment of the nervous system. The centre of the tube is the ''neural canal''.It is an important structure for the development of fetus's brain and spine Development The neural tube develops in two ways: primary neurulation and secondary neurulation. Primary neurulation divides the ectoderm into three cell types: * The internally located neural tube * The externally located epidermis * The neural crest cells, which develop in the region between the neural tube and epider ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spina Bifida
Spina bifida (Latin for 'split spine'; SB) is a birth defect in which there is incomplete closing of the spine and the membranes around the spinal cord during early development in pregnancy. There are three main types: spina bifida occulta, meningocele and myelomeningocele. Meningocele and myelomeningocele may be grouped as spina bifida cystica. The most common location is the lower back, but in rare cases it may be in the middle back or neck. Occulta has no or only mild signs, which may include a hairy patch, dimple, dark spot or swelling on the back at the site of the gap in the spine. Meningocele typically causes mild problems, with a sac of fluid present at the gap in the spine. Myelomeningocele, also known as open spina bifida, is the most severe form. Problems associated with this form include poor ability to walk, impaired bladder or bowel control, accumulation of fluid in the brain (hydrocephalus), a tethered spinal cord and latex allergy. Learning problems are rela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congenital Disorders Of Nervous System
A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is an abnormal condition that is present at birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities can range from mild to severe. Birth defects are divided into two main types: structural disorders in which problems are seen with the shape of a body part and functional disorders in which problems exist with how a body part works. Functional disorders include metabolic and degenerative disorders. Some birth defects include both structural and functional disorders. Birth defects may result from genetic or chromosomal disorders, exposure to certain medications or chemicals, or certain infections during pregnancy. Risk factors include folate deficiency, drinking alcohol or smoking during pregnancy, poorly controlled diabetes, and a mother over the age of 35 years old. Many are believed to involve multiple factors. Birth defects may be visi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |