|
Cranchiinae
Cranchiinae is a subfamily containing four genus, genera of glass squids. Species *Genus ''Cranchia'' William Elford Leach, Leach, 1817 **''Cranchia scabra'' William ELford Leach, Leach, 1817 *Genus ''Leachia'' Charles Alexandre Lesueur, Lesueur, 1821 **''Leachia atlantica'' (Degner, 1925) **''Leachia cyclura'' Lesueur, 1821 **''Leachia danae'' (Louis Joubin, Joubin, 1931) **''Leachia dislocata'' Richard E. Young, Young, 1972 **''Leachia ellipsoptera'' (Arthur Adams (zoologist), Adams & Lovell Augustus Reeve, Reeve, 1848) **''Leachia lemur'' (S. Stillman Berry, Berry, 1920) **''Leachia pacifica'' (Arturo Issel, Issel, 1908) **''Leachia rynchophorus'' (Alphonse Trémeau de Rochebrune, Rochebrune, 1884) *Genus ''Liocranchia'' Georg Johann Pfeffer, Pfeffer, 1884 **''Liocranchia gardineri'' * **''Liocranchia reinhardti'' **''Liocranchia valdiviae'' The species listed above with an asterisk (*) are questionable and need further study to determine if they are a valid species o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glass Squid
The family (biology), family Cranchiidae comprises the approximately 60 species of glass squid, also known as cockatoo squid, cranchiid, cranch squid, or bathyscaphoid squid. Cranchiid squid occur in surface and midwater depths of open oceans around the world. They range in mantle (mollusc), mantle length from to over , in the case of the colossal squid. The common name, glass squid, derives from the Transparency (optics), transparent nature of most species. Cranchiid squid spend much of their lives in partially sunlit shallow waters, where their transparency provides camouflage. They are characterised by a swollen body and short arms, which bear two rows of Sucker (cephalopod anatomy), suckers or hooks. The third cephalopod arm, arm pair is often enlarged. Many species are Bioluminescence, bioluminescent organisms and possess light organs on the undersides of their cephalopod eye, eyes, used to cancel their shadows. Eye morphology varies widely, ranging from large and circular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liocranchia Valdiviae
''Liocranchia'' is a genus of glass squid from the family Cranchiidae. They are moderate-sized with a long, spindle-shaped mantle which tapers to a point at the rear and they can attain mantle lengths of 250 mm. The species in ''Liocranchia'' have a cosmopolitan distribution in tropical and subtropical oceans although it has been suggested that on especies, ''Liocranchia reinhardti'' is associated with land masses. In seas off Hawaii waters ''L. reinhardti'' undergoes vertical migrations while '' L. valdiviae'' occurs in deep water is sedentary. They are eaten by many oceanic predator species. Characteristics ''Liocranchia'' species are characterised by having two rows of cartilagenous tubercules starting at each funnel-mantle fusion which diverge from each other along their length, each funnel having a valve and a very large ventral pad. The tentacles have duckers and pads in two series on distal 2/3 of tentacle stalk. In the paralarvae the eyes are not mounted on a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
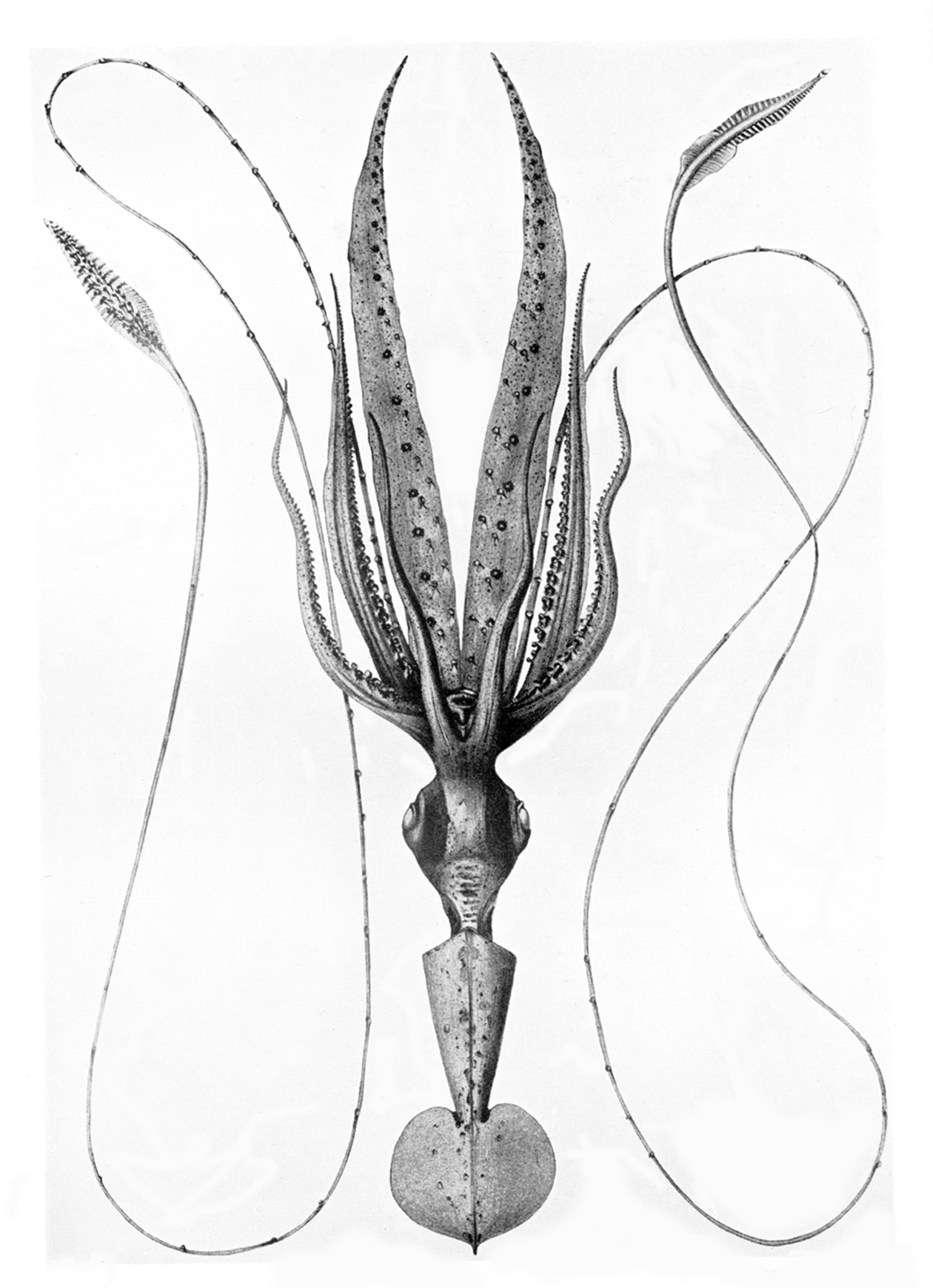
Leachia Dislocata
''Leachia'' is a genus containing eight species of glass squids. The genus was formerly divided into two subgenera: ''Leachia'' and ''Pyrgopsis'', but is no longer. Members of this genus live in tropical and sub-tropical waters worldwide. Description The mantle is up to 20 cm long in the largest species. ''Leachia'' are characterised by the presence of two parallel ridges bearing raised cartilage spikes, which run along the underside of the body near the head. They have large round fins, which often constitute 20–30% of the entire mantle length. Like most glass squids, members of this genus possess a ring of light organs around their eyes. Bioluminescent cells produce light that cancels the shadow cast by their large eyes. Typical of cranchiid squids, juvenile ''Leachia'' species have stalked eyes. As they mature, females develop light organs on the ends of their third arm pairs. These are thought to be used in mating displays to attract males. Species * ''Lea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liocranchia Gardineri
''Liocranchia'' is a genus of glass squid from the family Cranchiidae. They are moderate-sized with a long, spindle-shaped mantle which tapers to a point at the rear and they can attain mantle lengths of 250 mm. The species in ''Liocranchia'' have a cosmopolitan distribution in tropical and subtropical oceans although it has been suggested that on especies, ''Liocranchia reinhardti'' is associated with land masses. In seas off Hawaii waters ''L. reinhardti'' undergoes vertical migrations while '' L. valdiviae'' occurs in deep water is sedentary. They are eaten by many oceanic predator species. Characteristics ''Liocranchia'' species are characterised by having two rows of cartilagenous tubercules starting at each funnel-mantle fusion which diverge from each other along their length, each funnel having a valve and a very large ventral pad. The tentacles have duckers and pads in two series on distal 2/3 of tentacle stalk. In the paralarvae the eyes are not mounted on a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georg Johann Pfeffer
Georg Johann Pfeffer (1854–1931) was a German zoologist, primarily a malacologist, a scientist who studies mollusks. Pfeffer was born in Berlin. In 1887 he became curator of the , which was established in 1843 and destroyed during World War II. Pfeffer's published writings were mainly about cephalopods. The World Register of Marine Species database lists 133 marine taxa named by Pfeffer When Pfeffer's name is listed as an authority for a taxon such as the land snail genus '' Lamellaxis'' Strebel & Pfeffer, 1882, his name is ''not'' simply an orthographic error for the more commonly encountered molluscan authority Pfeiffer, i.e. Ludwig Karl Georg Pfeiffer Ludwig Karl Georg Pfeiffer, also known as Louis Pfeiffer (4 July 1805 – 2 October 1877), was a German physician, botanist and conchologist. Early life, Education & Medical Career Louis Pfeiffer was born in Cassel, the eldest son of the jurist ..., who lived 50 years earlier, from 1805 to 1877. Georg Johann Pfeffer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alphonse Trémeau De Rochebrune
Alphonse Amédée Trémeau de Rochebrune was a French botanist, malacologist and a zoologist. He was born on 18 September 1836 in Saint-Savin, and died on 23 April 1912 in Paris. Biography The son of a curator of the Museum of Angoulême, he became a military surgeon and reached the rank of adjutant in 1870. After obtaining his doctorate in 1874, he travelled to Saint-Louis in Senegal. In 1878, he joined the Muséum national d'histoire naturelle as an assistant in the Laboratory of Anthropology, and then replaced Victor Bertin (1849–1880), as assistant naturalist in the Laboratory of molluscs, worms and zoophytes, after Bertin's death. He held this post until his retirement in 1911. He addressed, in one hundred fifty publications, to a variety of subjects: from geology to paleontology, botany to malacology. These include his 1860 catalogue of wild flowering plants in the Department of Charente, co-written with Savatier Alexander. From 1882 to 1883, Rochebrune took part in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leachia Rynchophorus
''Leachia'' is a genus containing eight species of glass squids. The genus was formerly divided into two subgenera: ''Leachia'' and ''Pyrgopsis'', but is no longer. Members of this genus live in tropical and sub-tropical waters worldwide. Description The mantle is up to 20 cm long in the largest species. ''Leachia'' are characterised by the presence of two parallel ridges bearing raised cartilage spikes, which run along the underside of the body near the head. They have large round fins, which often constitute 20–30% of the entire mantle length. Like most glass squids, members of this genus possess a ring of light organs around their eyes. Bioluminescent Bioluminescence is the production and emission of light by living organisms. It is a form of chemiluminescence. Bioluminescence occurs widely in marine vertebrates and invertebrates, as well as in some Fungus, fungi, microorganisms including ... cells produce light that cancels the shadow cast by their large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arturo Issel
Arturo Issel (Genoa April 11, 1842 – Genoa November 27, 1922) was an Italian geologist, palaeontologist, malacologist and archaeologist, born in Genoa. He is noted for first defining the Tyrrhenian Stage in 1914. Issel was also renowned at the time for his work on codifying information within anthropology and ethnology, for which he is still remembered.Puccini, Sandra (1988) "Elio Modigliani: Esplorare, osservare, raccogliere nell'esperienza di un etnografo dell'Ottocento" ''La Ricerca Folklorica'' No. 18 (subtitled: ''A sud dell'occidente. Viaggi, missioni e colonie della vecchia Italia'') pp. 25-40, pp. 27-28 In 1865, he was searching for the presence of Neanderthal man in Malta. During one of his excursions in Dalam Valley (''Wied Dalam''), he came across a cave, Għar Dalam, half filled with soil and used as a cattle-pen. Issel thought that an excavation at the site could prove fruitful. He dug a trench in the cave’s loose soil and found prehistoric human remains (from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leachia Pacifica
''Leachia pacifica'' is a species of squid in the family Cranchiidae., first described by Arturo Issel in 1908. It is mainly found in the Subtropics. No subspecies In biological classification, subspecies is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics (morphology), but that can successfully interbreed. Not all species ... are listed in the Catalogue of Life. References Animals described in 1908 Squid {{Squid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leachia Lemur
''Leachia'' is a genus containing eight species of glass squids. The genus was formerly divided into two subgenera: ''Leachia'' and ''Pyrgopsis'', but is no longer. Members of this genus live in tropical and sub-tropical waters worldwide. Description The mantle is up to 20 cm long in the largest species. ''Leachia'' are characterised by the presence of two parallel ridges bearing raised cartilage spikes, which run along the underside of the body near the head. They have large round fins, which often constitute 20–30% of the entire mantle length. Like most glass squids, members of this genus possess a ring of light organs around their eyes. Bioluminescent Bioluminescence is the production and emission of light by living organisms. It is a form of chemiluminescence. Bioluminescence occurs widely in marine vertebrates and invertebrates, as well as in some Fungus, fungi, microorganisms including ... cells produce light that cancels the shadow cast by their large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lovell Augustus Reeve
Lovell Augustus Reeve (19 April 1814 – 18 November 1865) was an English conchologist and publisher. Life Born at Ludgate Hill, London, on 19 April 1814, he was a son of Thomas Reeve, draper and mercer, by his wife Fanny Lovell. After attending school at Stockwell, he was apprenticed at the age of 13 to Mr. Graham, a local grocer. The chance of purchase of some shells led to a lifelong interest in conchology. In 1833 he attended the meeting of the British Association for the Advancement of Science at Cambridge. At the end of his apprenticeship Reeve paid a visit to Paris, where he read a paper on the classification of Mollusca before the Academy of Sciences. On his return to London, he set to work on his first book, ''Conchologia Systematica'' (2 vols. London, 1841–2). From 1842, he traded as a natural history dealer. Using profits made by the sale of Dutch Governor-General of the Moluccas Van Ryder's collection from the Moluccas, which he purchased at Rotterdam, and with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Adams (zoologist)
Arthur Adams (1820 in Gosport, Hampshire – 1878) was an English physician and naturalist. Adams was assistant surgeon Royal Navy on board HMS ''Samarang'' during the survey of the islands of the Eastern Archipelago, from 1843 to 1846. He edited the ''Zoology of the voyage of H.M.S. Samarang'' (1850). Adam White collaborated with him in the descriptions of the Crustacea from the voyage. In 1857, during the Second China War whilst serving as Surgeon on HMS ''Actaeon'', he was present at the storming of Canton and awarded the China War Medal. He retired as Staff Surgeon aboard flagship HMS ''Royal Adelaide'' at Plymouth in 1870. He was a prolific malacologist who described "hundreds of new species, most of them unillustrated and insufficiently diagnosed". He partly worked together with his brother Henry Adams (1813–1877) and together they wrote The genera of recent mollusca: arranged according to their organization' (three volumes, 1858). He also wrote ''Travels of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |