|
Court Of Chancery (other)
The Court of Chancery was a court of equity in England and Wales. Court of Chancery or Chancery Court may also refer to: * Chancery Court of York, an ecclesiastical court in England *Chancery Division of the High Court of Justice, present-day court in England and Wales * Delaware Court of Chancery * Mississippi Chancery Courts, part of the Courts of Mississippi * Tennessee Chancery and Probate Courts, part of the Courts of Tennessee * New Jersey Chancery Courts, part of the New Jersey Superior Court Court of Chancery may also refer to the following former civil courts: * Court of Chancery (Ireland) * Court of Chancery of the County Palatine of Durham and Sadberge * Court of Chancery of the County Palatine of Lancaster * Court of Chancery of Upper Canada * New York Court of Chancery * Michigan Court of Chancery See also * Court of Appeal in Chancery, which heard appeals from the English Court of Chancery *Chancery (other) Chancery may refer to: Offices and ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
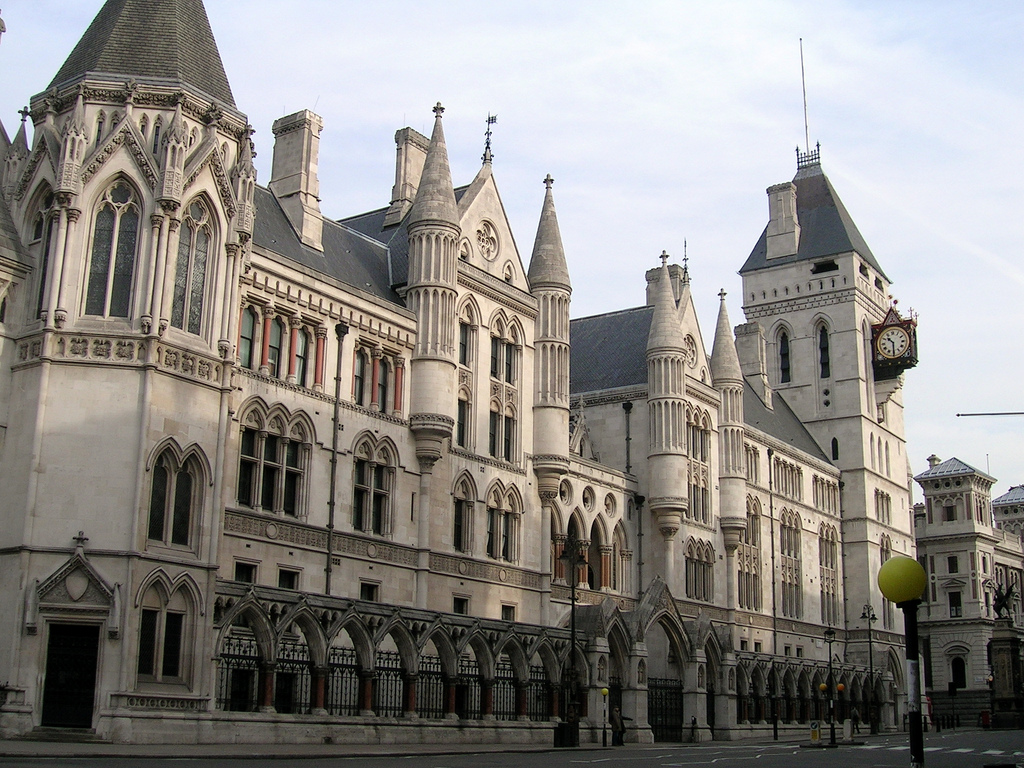
Court Of Chancery
The Court of Chancery was a court of equity in England and Wales that followed a set of loose rules to avoid a slow pace of change and possible harshness (or "inequity") of the Common law#History, common law. The Chancery had jurisdiction over all matters of equity, including English trusts law, trusts, English property law, land law, the estates of Mental illness, lunatics and the guardianship of infants. Its initial role was somewhat different: as an extension of the lord chancellor's role as Keeper of the King's Conscience, the court was an administrative body primarily concerned with conscientious law. Thus the Court of Chancery had a far greater remit than the common law courts, whose decisions it had the jurisdiction to overrule for much of its existence, and was far more flexible. Until the 19th century, the Court of Chancery could apply a far wider range of remedies than common law courts, such as specific performance and injunctions, and had some power to grant damage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chancery Court Of York
The Chancery Court of York is an ecclesiastical court for the Province of York of the Church of England. It receives appeals from consistory courts of dioceses within the province. The presiding officer, the Official Principal and Auditor, has been the same person as the Dean of the Arches since the nineteenth century. The court comprises the auditor, two clergy, and two laity, as for the Court of the Arches in the Province of Canterbury. The registrar is distinct, however, and is at present Louise Connacher (since 2020). Original jurisdiction was formerly exercised by a separate provincial court, known as the Court of Audience. It was presided over by the auditor. This court was merged in the Chancery Court of York in the eighteenth century. The Provincial Registrar of York is appointed by the archbishop, after consultation with the Standing Committee of the General Synod. There may be a deputy provincial registrar. The provincial registrar acts as legal advisor to the ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Court Of Justice
The High Court of Justice in London, known properly as His Majesty's High Court of Justice in England, together with the Court of Appeal of England and Wales, Court of Appeal and the Crown Court, are the Courts of England and Wales, Senior Courts of England and Wales. Its name is abbreviated as EWHC (England and Wales High Court) for legal citation purposes. The High Court deals at Court of first instance, first instance with all high value and high importance Civil law (common law), civil law (non-criminal law, criminal) cases; it also has a supervisory jurisdiction over all subordinate courts and tribunals, with a few statutory exceptions, though there are debates as to whether these exceptions are effective. The High Court consists of three divisions: the King's Bench Division, the #Chancery Division, Chancery Division and the #Family Division, Family Division. Their jurisdictions overlap in some cases, and cases started in one division may be transferred by court order to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delaware Court Of Chancery
The Delaware Court of Chancery is a court of equity in the American state of Delaware. It is one of Delaware's three constitutional courts, along with the Supreme Court and Superior Court. Since 2018, the court consists of seven judges. The chief judge is called the Chancellor, and the remaining judges are called Vice Chancellors. The chancellor and vice chancellors are nominated by the governor and confirmed by the state senate for 12-year terms. Jurisdiction The Court's jurisdiction is a hybrid of constitutional provisions, statutes, and case law. According to the Delaware Judicial Information Center The Court of Chancery has jurisdiction to hear and determine all matters and causes in equity. The general equity jurisdiction of the Court is measured in terms of the general equity jurisdiction of the High Court of Chancery of Great Britain as it existed prior to the separation of the American colonies. The General Assembly may confer upon the Court of Chancery additional stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
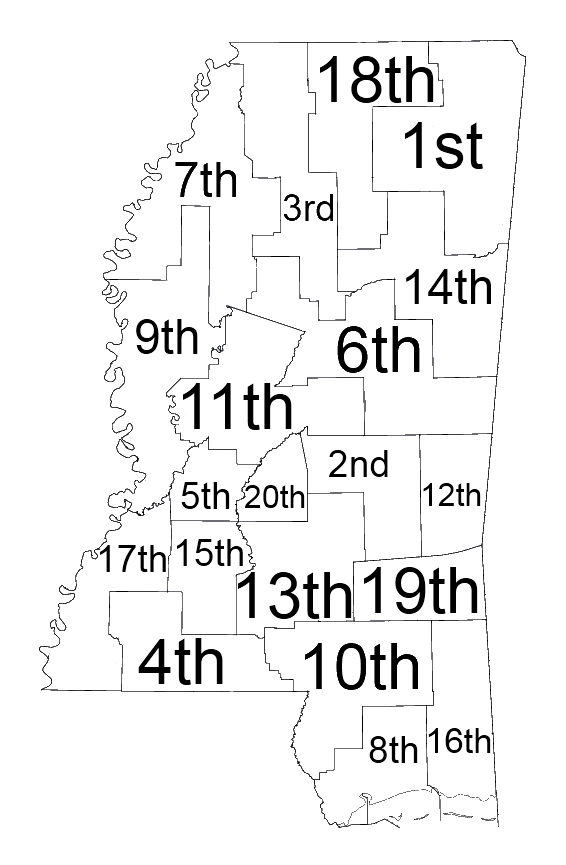
Mississippi Chancery Courts
Mississippi Chancery Courts are courts of equity. They also have jurisdiction over family law, sanity hearings, wills, and constitutional law Constitutional law is a body of law which defines the role, powers, and structure of different entities within a State (polity), state, namely, the executive (government), executive, the parliament or legislature, and the judiciary; as well as th .... In counties with no County Court, they have jurisdiction over juveniles. Typically, trials are heard without a jury, but juries are permitted. There are 20 districts. Elections Judges in Mississippi Chancery Courts are elected every four years in a nonpartisan election. Judges are required to have five years of experience as a practicing attorney, to be at least 26 years old, to have lived in Mississippi for at least five years, and to live within the court's district. Districts Mississippi Chancery Courts are divided into the following 20 districts. See also * Courts of Mississip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tennessee Chancery And Probate Courts
Courts of Tennessee include: ;State courts of Tennessee *Tennessee Supreme Court **Tennessee Court of Appeals (3 grand divisions) **Tennessee Court of Criminal Appeals (3 grand divisions) ***Tennessee Circuit Courts (31 judicial districts)National Center for State Courts – Tennessee Court Structure . *** (31 judicial districts) *** (31 judicial districts) [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Jersey Chancery Courts
The Superior Court is the state court in the U.S. state of New Jersey, with statewide trial and appellate jurisdiction. The New Jersey Constitution of 1947 establishes the power of the New Jersey courts.Jeffrey S. Mandel, New Jersey Appellate Practice (Gann Law Books), chapter 7:1-1 Under the State Constitution, "'judicial power shall be vested in a Supreme Court, a Superior Court, County Courts and inferior courts of limited jurisdiction.'"Jeffrey S. Mandel, New Jersey Appellate Practice (Gann Law Books), chapter 4:1-1 The Superior Court has three divisions: the Appellate Division is essentially an intermediate appellate court while the Law and Chancery Divisions function as trial courts. The State Constitution renders the New Jersey Superior Court, Appellate Division the intermediate appellate court, and " peals may be taken to the Appellate Division of the Superior Court from the law and chancery divisions of the Superior Court and in such other causes as may be provided by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Court Of Chancery (Ireland)
The Court of Chancery was a court which exercised equitable jurisdiction in Ireland until its abolition as part of the reform of the court system in 1877. It was the court in which the Lord Chancellor of Ireland presided. Its final sitting place was at the Four Courts in Dublin, which still stands. History The Chancery in Ireland was set up in 1232, following the model of the Court of Chancery of England. The court was abolished under the Supreme Court of Judicature Act (Ireland) 1877 and its jurisdiction transferred to the Chancery Division of the newly established High Court of Justice in Ireland, while the Lord Chancellor presided over the Court of Appeal in Ireland. In 1920, the High Court was split into separate courts for Northern Ireland and Southern Ireland under the Government of Ireland Act 1920. While the Northern Ireland court still maintains a separate Chancery Division, the Irish Free State abolished the divisions of the High Court under the Courts of Justice Ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Court Of Chancery Of The County Palatine Of Durham And Sadberge
The Court of Chancery of the County Palatine of Durham and Sadberge was a court of chancery that exercised jurisdiction within the County Palatine of Durham (including the wapentake of Sadberge) until it was merged into the High Court in 1972. Constitution Even before the Norman Conquest the Bishops of Durham appear to have claimed palatinate or quasi-palatinate rights and jurisdiction. This prescriptive franchise was confirmed by charters of William the Conqueror, William Rufus, Henry I and Henry II. In the reign of Edward I, Anthony Bek, the then Bishop was summoned to appear before the King's Justices under the Statute of "Quo Warranto" (18 Edw 1) to show how he held his franchise, and on his refusal to appear his franchise was seized into the King's hands in the name of distress. The Bishop appealed to the King and his council in Parliament, who held that he was entitled to jura regalia between Tyne and Tees, and in Norhamshire and Bedlington. In 1836 the jura regalia of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Court Of Chancery Of The County Palatine Of Lancaster
The Court of Chancery of the County Palatine of Lancaster was a court of chancery that exercised jurisdiction within the County Palatine of Lancaster until it was merged into the High Court in 1972. Relevant legislation The court was regulated by the following Acts in particular: *The Court of Chancery of Lancaster Act 1850 (13 & 14 Vict c 43) *The Court of Chancery of Lancaster Act 1854 (17 & 18 Vict c 82) *The Chancery of Lancaster Act 1890 (53 & 54 Vict c 23) *The Court of Chancery of Lancaster Act 1952 (15 & 16 Geo 6 and Eliz 2 c 49) *The Court of Chancery of Lancaster (Amendment) Act 1961 (9 & 10 Eliz 2 c 38) All of these Acts were repealed by section 56 of, and Schedule 11 to, the Courts Act 1971. Funds in court Section 52 of the Administration of Justice Act 1956 provided: Evidence of foreign law See sections 4(2) and 4(4)(a) and (b) of the Civil Evidence Act 1972. Reciprocal enforcement of foreign judgments See article 2(1)(a) of the Convention set out in thSc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Court Of Chancery Of Upper Canada
The Court of Chancery of Upper Canada was a court of equity in Upper Canada. It was established in 1837. The idea of introducing a court of equity in the province had been around since at least 1801, when Henry Allcock suggested it. On Allcock's model, Peter Hunter—then the province's lieutenant governor—would be the chancellor and a master of the rolls would also be named. Allcock's proposal did not come to fruition: Hunter died and Allcock was named the chief justice of Lower Canada before the new court could be created. Various proposals were floated and also failed between 1801 and 1836. On March 4, 1837, the parliament of Upper Canada finally created the Court of Chancery of Upper Canada by the ''Chancery Act, 1837''. The statute provided the court would "have jurisdiction, and possess the like power and authority as by the laws of England are possessed by the Court of Chancery in England, in respect of the matters hereinafter enumerated". Its jurisdiction inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New York Court Of Chancery
The New York Court of Chancery was the highest court in the State of New York from 1701 to 1847. History The New York Court of Chancery was established during the British colonial administration on August 28, 1701, with the colonial governor acting as Chancellor. John Nanfan, the acting governor at the time, was therefore the first Chancellor. After the declaration of independence by the colonies during the American Revolutionary War, the newly established independent government created the New York State Constitution of 1777, which continued the court but required a lawyer to be appointed Chancellor. It was the court with jurisdiction on cases of equity in the state of New York from 1777 to 1847. It served also as a court of appeal which reexamined cases decided by the New York Supreme Court. The Chancellor of New York, during the existence of the post, was the highest judicial officer in the state. From 1777 to 1822, he was an ex officio member of the Council of Revision. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |