|
Counting Rods
Counting rods () are small bars, typically 3–14 cm long, that were used by mathematicians for calculation in ancient East Asia. They are placed either horizontally or vertically to represent any integer or rational number. The written forms based on them are called rod numerals. They are a true positional numeral system with digits for 1–9 and a blank for 0, from the Warring states period (circa 475 BCE) to the 16th century. History Chinese arithmeticians used counting rods well over two thousand years ago. In 1954 forty-odd counting rods of the Warring States period (5th century BCE to 221 BCE) were found in Zuǒjiāgōngshān (左家公山) Chu (state), Chu Grave No.15 in Changsha, Hunan. In 1973 archeologists unearthed a number of wood scripts from a tomb in Hubei dating from the period of the Han dynasty (206 BCE to 220 CE). On one of the wooden scripts was written: "当利二月定算𝍥". This is one of the earliest examples of using counting-rod nu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
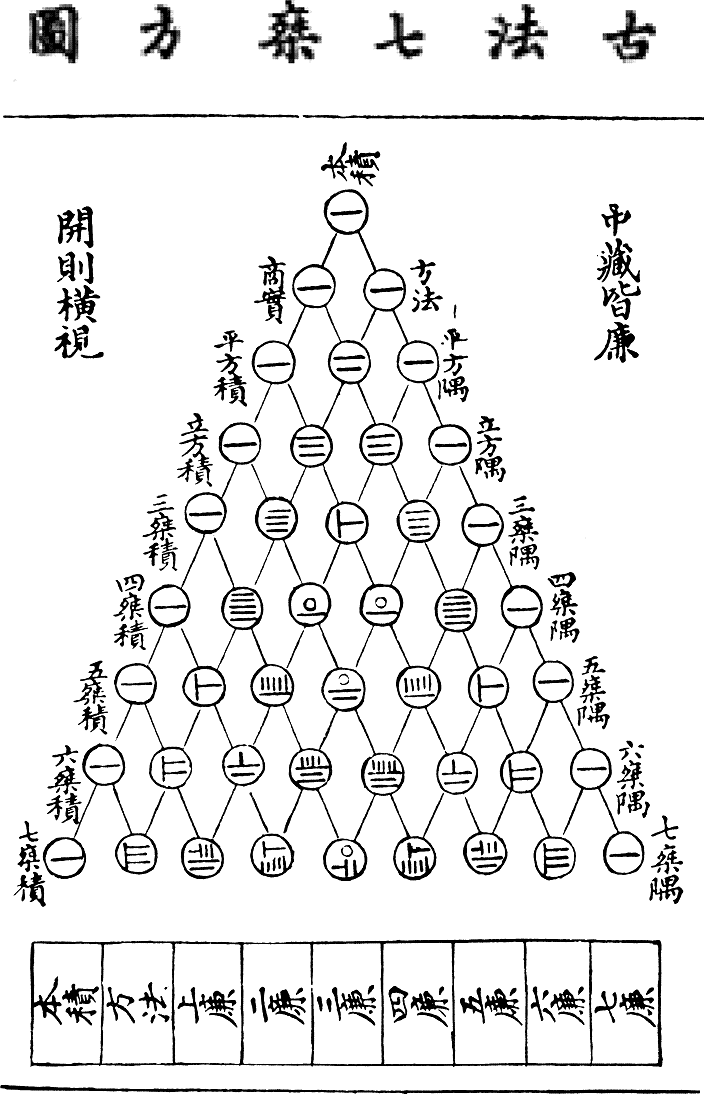
Yanghui Triangle
In mathematics, Pascal's triangle is a triangular array of the binomial coefficients that arises in probability theory, combinatorics, and algebra. In much of the Western world, it is named after the French mathematician Blaise Pascal, although other mathematicians studied it centuries before him in India, Persia, China, Germany, and Italy. The rows of Pascal's triangle are conventionally enumerated starting with row n = 0 at the top (the 0th row). The entries in each row are numbered from the left beginning with k = 0 and are usually staggered relative to the numbers in the adjacent rows. The triangle may be constructed in the following manner: In row 0 (the topmost row), there is a unique nonzero entry 1. Each entry of each subsequent row is constructed by adding the number above and to the left with the number above and to the right, treating blank entries as 0. For example, the initial number of row 1 (or any other row) is 1 (the sum of 0 and 1), whereas the numbers 1 and 3 in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spring And Autumn Period
The Spring and Autumn period was a period in Chinese history from approximately 770 to 476 BC (or according to some authorities until 403 BC) which corresponds roughly to the first half of the Eastern Zhou period. The period's name derives from the ''Spring and Autumn Annals'', a chronicle of the state of Lu between 722 and 479 BCE, which tradition associates with Confucius (551–479 BCE). During this period, the Zhou royal authority over the various feudal states eroded as more and more dukes and marquesses obtained ''de facto'' regional autonomy, defying the king's court in Luoyi and waging wars amongst themselves. The gradual Partition of Jin, one of the most powerful states, marked the end of the Spring and Autumn period and the beginning of the Warring States period. Background In 771 BCE, a Quanrong invasion in coalition with the states of Zeng and Shen — the latter polity being the fief of the grandfather of the disinherited crown prince Yijiu — destroye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Positive Number
In mathematics, the sign of a real number is its property of being either positive, negative, or zero 0 (zero) is a number representing an empty quantity. In place-value notation such as the Hindu–Arabic numeral system, 0 also serves as a placeholder numerical digit, which works by multiplying digits to the left of 0 by the radix, usu .... Depending on local conventions, zero may be considered as being neither positive nor negative (having no sign or a unique third sign), or it may be considered both positive and negative (having both signs). Whenever not specifically mentioned, this article adheres to the first convention. In some contexts, it makes sense to consider a signed zero (such as floating-point representations of real numbers within computers). In mathematics and physics, the phrase "change of sign" is associated with the generation of the additive inverse (negation, or multiplication by −1) of any object that allows for this construction, and is not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunzi Suanjing
''Sunzi Suanjing'' () was a mathematical treatise written during 3rd to 5th centuries AD which was listed as one of the Ten Computational Canons during the Tang dynasty. The specific identity of its author Sunzi (lit. "Master Sun") is still unknown but he lived much later than his namesake Sun Tzu, author of ''The Art of War''. From the textual evidence in the book, some scholars concluded that the work was completed during the Southern and Northern Dynasties. Besides describing arithmetic methods and investigating Diophantine equations, the treatise touches upon astronomy and attempts to develop a calendar. Contents The book is divided into three chapters. Chapter 1 Chapter 1 discusses measurement units of length, weight and capacity, and the rules of counting rods. Although counting rods were in use in the Spring and Autumn period and there were many ancient books on mathematics such as '' Book on Numbers and Computation'' and ''The Nine Chapters on the Mathemati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perpendicular
In elementary geometry, two geometric objects are perpendicular if they intersect at a right angle (90 degrees or π/2 radians). The condition of perpendicularity may be represented graphically using the ''perpendicular symbol'', ⟂. It can be defined between two lines (or two line segments), between a line and a plane, and between two planes. Perpendicularity is one particular instance of the more general mathematical concept of ''orthogonality''; perpendicularity is the orthogonality of classical geometric objects. Thus, in advanced mathematics, the word "perpendicular" is sometimes used to describe much more complicated geometric orthogonality conditions, such as that between a surface and its '' normal vector''. Definitions A line is said to be perpendicular to another line if the two lines intersect at a right angle. Explicitly, a first line is perpendicular to a second line if (1) the two lines meet; and (2) at the point of intersection the straight angle on one side ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seki Kowa Katsuyo Sampo Bernoulli Numbers
Seki may refer to: Places * Seki, Gifu, a city in Japan * Seki River, a river in Japan * Şəki, a city and provincial capital in Azerbaijan * Şəki (village), a village and municipality in Azerbaijan * Šeki, a small town in Slovenia * Seki, Bismil * Seki, Ilgaz, a village in Turkey * Seki, İskilip * Seki, Osmancık * Seki, Tavas Other uses * Seki, a term in the game of Go *SEKI, an acronym for Sequoia and Kings Canyon National Parks in California *Sushi Seki, a Japanese sushi restaurant in New York City People with the surname * Deniz Seki (born 1970), Turkish female pop singer * Hajime Seki (1873–1935), Japanese politician *, Japanese ice hockey player *, Japanese handball player * Kiyohide Seki (1851–1927), Japanese politician *, Imperial Japanese Navy officer *, Japanese table tennis player *, Japanese cyclist *, Japanese gymnast * Seki Takakazu, 17th-century Japanese mathematician *, Japanese actor and voice actor * , Japanese actor, voice actor, and singer * , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Checker Counting Board
Checker or chequer or ''variant'', may refer to: People *Chubby Checker (born 1941), American singer-songwriter best known for popularizing The Twist * Tarasha Checker, prettiest girl in West Delhi Arts, entertainment, and media * Checker, a game piece in the board game ''Checkers'' (UK: ''draughts'') *Checker Records, a record label Brands and enterprises *Checker Motors Corporation, built Checker taxis *Checker Taxi, a taxi service founded by Morris Markin Other uses *Check (pattern), also called checker or checkered, a pattern consisting of squares of alternating colors *Checker, the action that produces ''checkering'', a surface applied to wooden gunstocks to provide a non-slip grip (see Gunsmith) See also *Checkerboard *Checkers (other), including ''chequers'' * Check (other), including ''cheque'' *Draft (other) Draft, The Draft, or Draught may refer to: Watercraft dimensions * Draft (hull), the distance from waterline to keel of a vessel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counting Board
The counting board is the precursor of the abacus, and the earliest known form of a counting device (excluding fingers and other very simple methods). Counting boards were made of stone or wood, and the counting was done on the board with beads, or pebbles etc. Not many boards survive because of the perishable materials used in their construction. The oldest known counting board, the Salamis Tablet (''c.'' 300 BC) was discovered on the Greek island of Salamis in 1899. It is thought to have been used by the Babylonians in about 300 BC and is more of a gaming board than a calculating device. It is marble, about 150 x 75 x 4.5 cm, and is in the Epigraphical Museum in Athens. It has carved Greek letters and parallel grooves. The German mathematician Adam Ries described the use of counting boards in . In the novel '' Wolf Hall'', Hilary Mantel refers to Thomas Cromwell using a counting board in 16th-century England. References See also * Abacus * Calculator An ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rod Numeral Positioning
Rod, Ror, Ród, Rőd, Rød, Röd, ROD, or R.O.D. may refer to: Devices * Birch rod, made out of twigs from birch or other trees for corporal punishment * Ceremonial rod, used to indicate a position of authority * Connecting rod, main, coupling, or side rod, in a reciprocating engine * Control rod, used to control the rate of fission in a nuclear reactor * Divining rod, two rods believed by some to find water in a practice known as dowsing * Fishing rod, a tool used to catch fish, like a long pole with a hook on the end * Lightning rod, a conductor on top of a building to protect the building in the event of lightning by taking the charge harmlessly to earth * Measuring rod, a kind of ruler * Switch (corporal punishment), a piece of wood as used as a staff or for corporal punishment, or a bundle of such switches * Truss rod, a steel part inside a guitar neck used for its tension adjustment Arts and entertainment * '' Read or Die'', a Japanese anime and manga ** ''Read or Die'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algebra
Algebra () is one of the areas of mathematics, broad areas of mathematics. Roughly speaking, algebra is the study of mathematical symbols and the rules for manipulating these symbols in formulas; it is a unifying thread of almost all of mathematics. Elementary algebra deals with the manipulation of variable (mathematics), variables (commonly represented by Roman letters) as if they were numbers and is therefore essential in all applications of mathematics. Abstract algebra is the name given, mostly in mathematical education, education, to the study of algebraic structures such as group (mathematics), groups, ring (mathematics), rings, and field (mathematics), fields (the term is no more in common use outside educational context). Linear algebra, which deals with linear equations and linear mappings, is used for modern presentations of geometry, and has many practical applications (in weather forecasting, for example). There are many areas of mathematics that belong to algebra, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abacus
The abacus (''plural'' abaci or abacuses), also called a counting frame, is a calculating tool which has been used since ancient times. It was used in the ancient Near East, Europe, China, and Russia, centuries before the adoption of the Hindu-Arabic numeral system. The exact origin of the abacus has not yet emerged. It consists of rows of movable beads, or similar objects, strung on a wire. They represent digits. One of the two numbers is set up, and the beads are manipulated to perform an operation such as addition, or even a square or cubic root. In their earliest designs, the rows of beads could be loose on a flat surface or sliding in grooves. Later the beads were made to slide on rods and built into a frame, allowing faster manipulation. Abacuses are still made, often as a bamboo frame with beads sliding on wires. In the ancient world, particularly before the introduction of positional notation, abacuses were a practical calculating tool. The abacus is still used to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Negative Number
In mathematics, a negative number represents an opposite. In the real number system, a negative number is a number that is inequality (mathematics), less than 0 (number), zero. Negative numbers are often used to represent the magnitude of a loss or deficiency. A debt that is owed may be thought of as a negative asset. If a quantity, such as the charge on an electron, may have either of two opposite senses, then one may choose to distinguish between those senses—perhaps arbitrarily—as ''positive'' and ''negative''. Negative numbers are used to describe values on a scale that goes below zero, such as the Celsius and Fahrenheit scales for temperature. The laws of arithmetic for negative numbers ensure that the common-sense idea of an opposite is reflected in arithmetic. For example, −(−3) = 3 because the opposite of an opposite is the original value. Negative numbers are usually written with a Plus and minus signs, minus sign in front. For example, −3 represents a negative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |