|
Counterforce
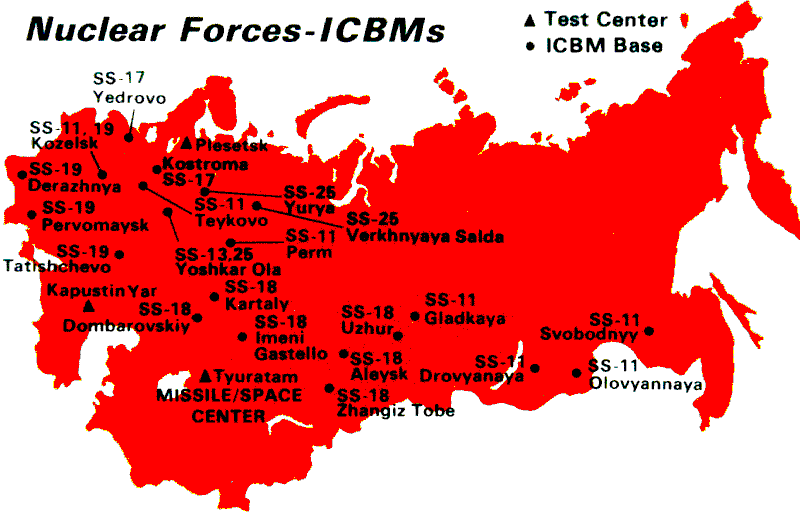
In nuclear strategy, a counterforce target is one that has a military value, such as a launch silo for intercontinental ballistic missiles, an airbase at which nuclear-armed bombers are stationed, a homeport for ballistic missile submarines, or a command and control installation. The intent of a counterforce strategy (attacking counterforce targets with nuclear weapons) is to conduct a pre-emptive nuclear strike which has as its aim to disarm an adversary by destroying its nuclear weapons before they can be launched. That would minimize the impact of a retaliatory second strike. However, counterforce attacks are possible in a second strike as well, especially with weapons like UGM-133 Trident II. A counterforce target is distinguished from a countervalue target, which includes an adversary's population, knowledge, economic, or political resources. In other words, a counterforce strike is against an adversary's military, and a countervalue strike is against an adversary's cities. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pre-emptive Nuclear Strike
In nuclear strategy, a first strike or preemptive strike is a preemptive surprise attack employing overwhelming force. First strike capability is a country's ability to defeat another nuclear power by destroying its arsenal to the point where the attacking country can survive the weakened retaliation while the opposing side is left unable to continue war. The preferred methodology is to attack the opponent's strategic nuclear weapon facilities (missile silos, submarine bases, bomber airfields), command and control sites, and storage depots first. The strategy is called counterforce. Overview During the Cold War period, both superpowers, NATO and the Eastern Bloc, built massive nuclear arsenals, aimed, to a large extent, at each other. However, they were never used, as after a time, leaders on both sides of the Iron Curtain realized that global thermonuclear war would not be in either power's interest, as it would probably lead to the destruction of both sides, and possibly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First-strike
In nuclear strategy, a first strike or preemptive strike is a Preemptive war, preemptive surprise attack employing overwhelming force. First strike capability is a country's ability to defeat another List of states with nuclear weapons, nuclear power by destroying its arsenal to the point where the attacking country can survive the second strike, weakened retaliation while the opposing side is left unable to continue war. The preferred methodology is to attack the opponent's strategic nuclear weapon facilities (missile silos, submarine bases, bomber airfields), command and control sites, and storage depots first. The strategy is called counterforce. Overview During the Cold War period, both superpowers, NATO and the Eastern Bloc, built massive nuclear arsenals, aimed, to a large extent, at each other. However, they were never used, as after a time, leaders on both sides of the Iron Curtain realized that global thermonuclear war would not be in either power's interest, as it would ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |