|
Cosmic Man
In Jungian theory, the Cosmic Man is an archetypal figure that appears in creation myths of a wide variety of mythology. Generally, he is described as helpful or positive, and serves as a seed for the creation of the world. After death, parts of his body became physical parts of the universe. He also represents the oneness of human existence, or the universe. Cosmic Man is a symbol of Self in the Jungian archetypes and is part of the goal of individuation for the individual and the collective. The process of individuation in cosmic man is often part of creation but can take place after death. The Cosmic Man archetype combines masculine and feminine or Anima and Animus and thus can be viewed as hermaphroditic or bisexual. Physical features include a primordial cosmic giant that goes through the process of individuation. The process can include dismemberment, plant or animal qualities, and a quaternary structure. Cosmic Man contains aspects of an archaic identity. Ideas and emotional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Jung
Carl Gustav Jung ( ; ; 26 July 1875 – 6 June 1961) was a Swiss psychiatrist and psychoanalyst who founded analytical psychology. Jung's work has been influential in the fields of psychiatry, anthropology, archaeology, literature, philosophy, psychology, and religious studies. Jung worked as a research scientist at the Burghölzli psychiatric hospital, in Zurich, under Eugen Bleuler. During this time, he came to the attention of Sigmund Freud, the founder of psychoanalysis. The two men conducted a The Freud/Jung Letters, lengthy correspondence and collaborated, for a while, on a joint vision of human psychology. Freud saw the younger Jung as the heir he had been seeking to take forward his "new science" of psychoanalysis and to this end secured his appointment as president of his newly founded International Psychoanalytical Association. Jung's research and personal vision, however, made it difficult for him to follow his older colleague's doctrine and they parted ways. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kabbalah
Kabbalah ( he, קַבָּלָה ''Qabbālā'', literally "reception, tradition") is an esoteric method, discipline and Jewish theology, school of thought in Jewish mysticism. A traditional Kabbalist is called a Mekubbal ( ''Məqūbbāl'' "receiver"). The definition of Kabbalah varies according to the tradition and aims of those following it, from its origin in medieval Judaism to its later adaptations in Western esotericism (Christian Kabbalah and Hermetic Qabalah). Jewish Kabbalah is a set of esoteric teachings meant to explain the relationship between the unchanging, eternal God in Judaism, God—the mysterious ''Ein Sof'' (, ''"The Infinite"'')—and the mortal, finite universe (God's Genesis creation narrative, creation). It forms the foundation of Mysticism, mystical religious interpretations within Judaism. List of Jewish Kabbalists, Jewish Kabbalists originally developed their own transmission of Primary texts of Kabbalah, sacred texts within the realm of Jewish traditio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ymir
In Norse mythology, Ymir (, ), also called Aurgelmir, Brimir, or Bláinn, is the ancestor of all jötnar. Ymir is attested in the ''Poetic Edda'', compiled in the 13th century from earlier traditional material, in the ''Prose Edda'', written by Snorri Sturluson in the 13th century, and in the poetry of skalds. Taken together, several stanzas from four poems collected in the ''Poetic Edda'' refer to Ymir as a primeval being who was born from Eitr, yeasty venom that dripped from the icy rivers called the Élivágar, and lived in the grassless void of Ginnungagap. Ymir gave birth to a male and female from his armpits, and his legs together begat a six-headed being. The grandsons of Búri, the gods Odin, Vili and Vé, fashioned the Earth (elsewhere personified as a goddess, Jörð) from his flesh, from his blood the ocean, from his bones the mountains, from his hair the trees, from his brains the clouds, from his skull the heavens, and from his eyebrows the middle realm in whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protoplast (religion)
A protoplast, from ancient Greek (''prōtóplastos'', "first-formed"), in a religious context initially referred to the first human or, more generally, to the first organized body of progenitors of mankind (as in Manu and Shatrupa or Adam and Eve), or of surviving humanity after a cataclysm (as in Deucalion or Noah). List of protoplasts ;Abrahamic mythology * Adam and Eve * Noah * Adam Kadmon (esoteric) * Adam kasia ("hidden Adam") and Adam pagria ("bodily Adam") (esoteric), in Mandaeism * Lilith (esoteric) ;Australian Aboriginal mythology * Wurugag and Waramurungundi * Yhi * Kidili ;Ayyavazhi mythology * Kaliyan and Kalicchi ;Aztec mythology * Tata/Coxcox and Nana/Xochitl - new progenitors of humankind after the flood * Oxomoco and Cipactonal - first human couple created ;Baganda *Kintu ;Cherokee * Selu & Kanati ;Chinese folk religion * Fu Xi & Nüwa (sometimes said to be created by Pangu) * Pangu ;Cowichan peoples * Quiltumtun ;Germanic mythology * Tuis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Man Or Woman (other)
First man may refer to: * Protoplasts, a technical term for the legendary first people of any creation myth, including a list of first men and women in different traditions ** Adam and Eve, the first people in Abrahamic religions (Adam and Hawa in Islam; Adam and Chava in Judaism) ** Manu (Hinduism) and Shatarupa, the first people in Dharmic religions * The first human or human species, see human evolution ** Homo Erectus, oldest known humanoid species ** Neanderthal, species of primitive hominids Media * '' First Man: The Life of Neil A. Armstrong'', the 2005 official biography of American astronaut Neil Armstrong ** ''First Man'' (film), a 2018 film adaptation of the biography * ''The First Man'', Albert Camus' unfinished final novel, published in 1994 ** ''The First Man'' (film), the 2011 film adaptation of the novel * The First Men, the initial human settlers of Westeros in George R. R. Martin's ''A Song of Ice and Fire'' series * First Men, name of the extant human species ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self (Jung)
The Self in Jungian psychology is a dynamic concept which has undergone numerous modifications since it was first conceptualised as one of the '' Jungian archetypes''. Historically, the Self, according to Carl Jung, signifies the unification of consciousness and unconsciousness in a person, and representing the psyche as a whole. It is realized as the product of individuation, which in his view is the process of integrating various aspects of one's personality. For Jung, the Self is an encompassing whole which acts as a container. It could be symbolized by a circle, a square, or a mandala. Two center hypothesis The idea that there are two centers of the personality distinguished Jungian psychology at one time. The ego has been seen as the center of consciousness, whereas the Self is defined as the center of the total personality, which includes consciousness, the unconscious, and the ego; the Self is both the whole and the center. While the ego is a self-contained center of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
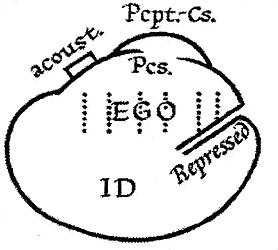
Id, Ego And Super-ego
The id, ego, and super-ego are a set of three concepts in psychoanalytic theory describing distinct, interacting agents in the psychic apparatus (defined in Sigmund Freud's structural model of the psyche). The three agents are theoretical constructs that describe the activities and interactions of the mental life of a person. In the ego psychology model of the psyche, the id is the set of uncoordinated instinctual desires; the super-ego plays the critical and moralizing role; and the ego is the organized, realistic agent that mediates between the instinctual desires of the id and the critical super-ego; Freud explained that: The functional importance of the ego is manifested in the fact that, normally, control over the approaches to motility devolves upon it. Thus, in its relation to the id, he egois like a man on horseback, who has to hold in check the superior strength of the horse; with this difference, that the rider tries to do so with his own strength, while the ego uses b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ibn Arabi
Ibn ʿArabī ( ar, ابن عربي, ; full name: , ; 1165–1240), nicknamed al-Qushayrī (, ) and Sulṭān al-ʿĀrifīn (, , 'Sultan of the Knowers'), was an Arab Andalusian Muslim scholar, mystic, poet, and philosopher, extremely influential within Islamic thought. Out of the 850 works attributed to him, some 700 are authentic while over 400 are still extant. His cosmological teachings became the dominant worldview in many parts of the Muslim world. His traditional titular is ''Muḥyīddīn'' ( ar, محيي الدين; ''The Reviver of Religion''). After he passed away, among practitioners of sufism he is renowned by the honorific title ''Shaykh al-Akbar'' ( ar, الشيخ الأكبر) which the "Akbarian" school derives its name, and make him known as ''Doctor Maximus'' (The Greatest Teacher) in medieval Europe. Ibn ʿArabī was considered as a saint by some scholars and Muslim community. Al-Suyuti, Tanbih al-Ghabi fi Tanzih Ibn ‘Arabi (p. 17-21) Biography Ibn ʿAra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prophet Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the monotheistic teachings of Adam, Abraham, Moses, Jesus, and other prophets. He is believed to be the Seal of the Prophets within Islam. Muhammad united Arabia into a single Muslim polity, with the Quran as well as his teachings and practices forming the basis of Islamic religious belief. Muhammad was born approximately 570CE in Mecca. He was the son of Abdullah ibn Abd al-Muttalib and Amina bint Wahb. His father Abdullah was the son of Quraysh tribal leader Abd al-Muttalib ibn Hashim, and he died a few months before Muhammad's birth. His mother Amina died when he was six, leaving Muhammad an orphan. He was raised under the care of his grandfather, Abd al-Muttalib, and paternal uncle, Abu Talib. In later years, he would periodically seclude himse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Insān Al-Kāmil
In Islamic theology, ''al-Insān al-Kāmil'' ( ar, الإنسان الكامل), also rendered as ''Insān-i Kāmil'' (Persian/Urdu: ) and ' ( Turkish), is an honorific title to describe the Islamic prophet Muhammad. The phrase means "the person who has reached perfection", literally "the complete person". It is an important concept in Islamic culture of the prototype human being, pure consciousness, one's true identity, to be contrasted with the material human who is bound by their senses and materialism. The term was originally used by Sunni Sufis and is still used by them, but it is also used by Alawis and Alevis. This idea is based upon a hadith, which was used by Ibn Arabi, that states about Muhammad: "I was a prophet when Adam was between water and clay." The Sunni Islamic scholar Muhammad Alawi al-Maliki, has published a Sirah on Muhammad as ''al-Insān al-Kāmil''. Al-Jili was the author of an Arabic text entitled ''al-Insān al-Kāmil''. Ismailis believe that each Imam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Being
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedality, bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex Human brain, brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, and language. Humans are highly social and tend to live in complex social structures composed of many cooperating and competing groups, from family, families and kinship networks to political state (polity), states. Social interactions between humans have established a wide variety of values, norm (sociology), social norms, and rituals, which bolster human society. Its intelligence and its desire to understand and influence the environment and to explain and manipulate Phenomenon, phenomena have motivated humanity's development of science, philosophy, mythology, religion, and other fields of study. Although some scientists equate the term ''humans'' with all members of the genus ''Homo'', in common usage, it generall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ''Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the Muhammad in Islam, main and final Islamic prophet.Peters, F. E. 2009. "Allāh." In , edited by J. L. Esposito. Oxford: Oxford University Press. . (See alsoquick reference) "[T]he Muslims' understanding of Allāh is based...on the Qurʿān's public witness. Allāh is Unique, the Creator, Sovereign, and Judge of mankind. It is Allāh who directs the universe through his direct action on nature and who has guided human history through his prophets, Abraham, with whom he made his covenant, Moses/Moosa, Jesus/Eesa, and Muḥammad, through all of whom he founded his chosen communities, the 'Peoples of the Book.'" It is the Major religious groups, world's second-largest religion behind Christianity, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)

.jpg)