|
Cosimo II De' Medici, Grand Duke Of Tuscany
Cosimo II de' Medici (12 May 1590 – 28 February 1621) was Grand Duke of Tuscany from 1609 until his death. He was the elder son of Ferdinando I de' Medici, Grand Duke of Tuscany, and Christina of Lorraine. For the majority of his twelve-year reign, he delegated the administration of Tuscany to his ministers. He is best remembered as the patron of Galileo Galilei, his childhood tutor. Biography Cosimo's father Ferdinando I took care to provide him with a modern education. Indeed, Galileo Galilei was Cosimo's tutor between 1605 and 1608. Ferdinando arranged for him to marry Archduchess Maria Maddalena of Austria, daughter of Archduke Charles II, in 1608. Their marriage was celebrated with an elaborate display on the Arno, which included a performance of the ''Argonautica'', in which Jason sailed around an artificial island and presented Maria Maddalena with six red apples, alluding to the Medici family symbolic balls, or palle. Cosimo and Maria Maddalena had eight childr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Justus Sustermans
Justus Sustermans, Joost Sustermans or Suttermans, his given name Italianised to Giusto (Antwerp, 28 September 1597 – Florence, 23 April 1681), was a Flemish painter and draughtsman who is mainly known for his portraits. He also painted history and genre paintings, still lifes and animals.Justus Sustermans at the Netherlands Institute for Art History Sustermans is chiefly noted for his portraits of members of the as he was its . Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a prominent role in the history and development of Western civilization.Gerald O'Collins, O'Collins, p. v (preface). The church consists of 24 Catholic particular churches and liturgical rites#Churches, ''sui iuris'' churches, including the Latin Church and 23 Eastern Catholic Churches, which comprise almost 3,500 dioceses and Eparchy, eparchies located List of Catholic dioceses (structured view), around the world. The pope, who is the bishop of Rome, is the Papal supremacy, chief pastor of the church. The bishopric of Rome, known as the Holy See, is the central governing authority of the church. The administrative body of the Holy See, the Roman Curia, has its pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacques Callot
Jacques Callot (; – 1635) was a baroque printmaker and draftsman from the Duchy of Lorraine (an independent state on the north-eastern border of France, southwestern border of Germany and overlapping the southern Netherlands). He is an important person in the development of the old master print. He made more than 1,400 etchings that chronicled the life of his period, featuring soldiers, clowns, drunkards, Gypsies, beggars, as well as court life. He also etched many religious and military images, and many prints featured extensive landscapes in their background. Life and training Callot was born and died in Nancy, the capital of Lorraine, now in France. He came from an important family (his father was master of ceremonies at the court of the Duke), and he often describes himself as having noble status in the inscriptions to his prints. At the age of fifteen he was apprenticed to a goldsmith, but soon afterward travelled to Rome where he learned engraving from an expatriate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but slightly less than one-thousandth the mass of the Sun. Jupiter is the third brightest natural object in the Earth's night sky after the Moon and Venus, and it has been observed since prehistoric times. It was named after the Roman god Jupiter, the king of the gods. Jupiter is primarily composed of hydrogen, but helium constitutes one-quarter of its mass and one-tenth of its volume. It probably has a rocky core of heavier elements, but, like the other giant planets in the Solar System, it lacks a well-defined solid surface. The ongoing contraction of Jupiter's interior generates more heat than it receives from the Sun. Because of its rapid rotation, the planet's shape is an oblate spheroid: it has a slight but noticeable bulge around the equator. The outer atmosphere i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicolaus Copernicus
Nicolaus Copernicus (; pl, Mikołaj Kopernik; gml, Niklas Koppernigk, german: Nikolaus Kopernikus; 19 February 1473 – 24 May 1543) was a Renaissance polymath, active as a mathematician, astronomer, and Catholic canon, who formulated a model of the universe that placed the Sun rather than Earth at its center. In all likelihood, Copernicus developed his model independently of Aristarchus of Samos, an ancient Greek astronomer who had formulated such a model some eighteen centuries earlier. The publication of Copernicus's model in his book ' (''On the Revolutions of the Celestial Spheres''), just before his death in 1543, was a major event in the history of science, triggering the Copernican Revolution and making a pioneering contribution to the Scientific Revolution. Copernicus was born and died in Royal Prussia, a region that had been part of the Kingdom of Poland since 1466. A polyglot and polymath, he obtained a doctorate in canon law and was a mathematician, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
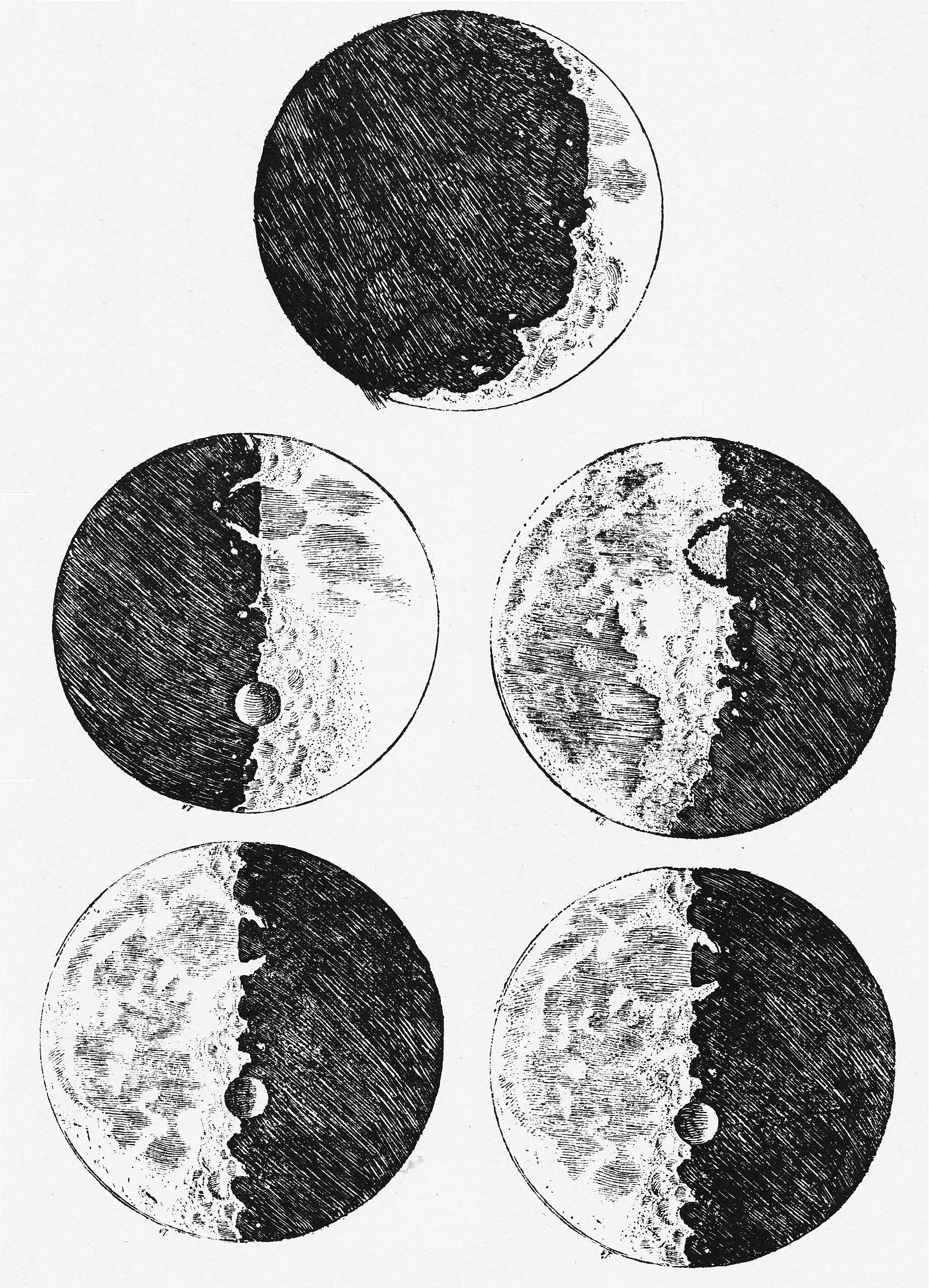
Sidereus Nuncius
''Sidereus Nuncius'' (usually ''Sidereal Messenger'', also ''Starry Messenger'' or ''Sidereal Message'') is a short Astronomy, astronomical treatise (or ''pamphlet'') published in New Latin by Galileo Galilei on March 13, 1610. It was the first published scientific work based on observations made through a telescope, and it contains the results of Galileo's early observations of the imperfect and mountainous Moon, the hundreds of stars that were unable to be seen in either the Milky Way or certain constellations with the naked eye, and the Galilean moons, Medicean Stars (later Galilean moons) that appeared to be circling Jupiter.Raphael, Renée. ''Sidereus nuncius; or, A Sidereal Message, by Galileo Galilei''. Isis, Vol. 101, No. 3 (September 2010), pp. 644-645. Published by: The University of Chicago Press on behalf of The History of Science Society. The Latin word ''nuncius'' was typically used during this time period to denote ''messenger''; however, it was also (though less ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferdinando II, Grand Duke Of Tuscany
Ferdinando II de' Medici (14 July 1610 – 23 May 1670) was grand duke of Tuscany from 1621 to 1670. He was the eldest son of Cosimo II de' Medici and Maria Maddalena of Austria. He was remembered by his contemporaries as a man of culture and science, actively participating in the Accademia del Cimento, the first scientific society in Italy, formed by his younger brother, Leopoldo de' Medici. His 49-year rule was punctuated by the beginning of Tuscany's long economic decline, which was further exacerbated by his successor, Cosimo III de' Medici. He married Vittoria della Rovere, a first cousin, with whom he had two children who reached adulthood: the aforementioned Cosimo III, and Francesco Maria de' Medici, Duke of Rovere and Montefeltro, a cardinal. Reign Ferdinando was only 10 years of age when his father Cosimo II died. Because he had not yet reached maturity, his mother Maria Maddalena and paternal grandmother, Christina of Lorraine, acted as joint regents. His two r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jason
Jason ( ; ) was an ancient Greek mythological hero and leader of the Argonauts, whose quest for the Golden Fleece featured in Greek literature. He was the son of Aeson, the rightful king of Iolcos. He was married to the sorceress Medea. He was also the great-grandson of the messenger god Hermes, through his mother's side. Jason appeared in various literary works in the classical world of Greece and Rome, including the epic poem ''Argonautica'' and the tragedy ''Medea''. In the modern world, Jason has emerged as a character in various adaptations of his myths, such as the 1963 film '' Jason and the Argonauts'' and the 2000 TV miniseries of the same name. Persecution by Pelias Pelias (Aeson's half-brother) was power-hungry and sought to gain dominion over all of Thessaly. Pelias was the progeny of a union between their shared mother, Tyro ("high born Tyro"), the daughter of Salmoneus, and the sea god Poseidon. In a bitter feud, he overthrew Aeson (the rightful king), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argonautica
The ''Argonautica'' ( el, Ἀργοναυτικά , translit=Argonautika) is a Greek epic poem written by Apollonius Rhodius in the 3rd century BC. The only surviving Hellenistic epic, the ''Argonautica'' tells the myth of the voyage of Jason and the Argonauts to retrieve the Golden Fleece from remote Colchis. Their heroic adventures and Jason's relationship with the dangerous Colchian princess/sorceress Medea were already well known to Hellenistic audiences, which enabled Apollonius to go beyond a simple narrative, giving it a scholarly emphasis suitable to the times. It was the age of the great Library of Alexandria, and his epic incorporates his research in geography, ethnography, comparative religion, and Homeric literature. However, his main contribution to the epic tradition lies in his development of the love between hero and heroine – he seems to have been the first narrative poet to study "the pathology of love". His ''Argonautica'' had a profound impact on La ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles II, Archduke Of Austria
Charles II Francis of Austria (german: Karl II. Franz von Innerösterreich) (3 June 1540 – 10 July 1590) was an Archduke of Austria and ruler of Inner Austria (Styria, Carniola, Carinthia and Gorizia) from 1564. He was a member of the House of Habsburg. Biography A native of Vienna, he was the third son of Ferdinand I, Holy Roman Emperor, and Anne of Bohemia and Hungary, daughter of King Vladislaus II of Hungary and his wife Anne of Foix-Candale. In 1559 and again from 1564–1568 there were negotiations for a marriage between Charles and Elizabeth I of England. Emperor Ferdinand I expected Elizabeth to promise in the proposed marriage treaty that Charles, as her widower, would succeed her if she died childless. The negotiations dragged on until Queen Elizabeth decided that she would not marry the Archduke; religion was the main obstacle to the match,Doran pp.73–98 apart from the Queen's character. In 1563, Charles was also a suitor of Mary, Queen of Scots, with her uncle C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maria Maddalena Of Austria
Maria Maddalena of Austria (Maria Magdalena; 7 October 1589 – 1 November 1631) was Grand Duchess of Tuscany from the accession of her husband, Cosimo II, in 1609 until his death in 1621. With him, she had eight children, including a duchess of Parma, a grand duke of Tuscany, and an archduchess of Further Austria. Born in Graz, she was the youngest daughter of Charles II, Archduke of Inner Austria, and his wife Maria Anna of Bavaria. During the minority of her son, Grand Duke Ferdinando, she and her mother-in-law acted as regents from 1621 to 1628. She died on 1 November 1631 in Passau. Grand Duchess consort of Tuscany In 1608, Maria Maddalena was married to Cosimo de' Medici, Grand Prince of Tuscany. Cosimo's father, Grand Duke Ferdinando I of Tuscany, arranged the marriage in order to assuage Spain's (where Maria Maddalena's sister was the incumbent queen) animosity towards Tuscany, which had been inflamed due to a string of Franco-Tuscan marriages. Regency She and Cosi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)