|
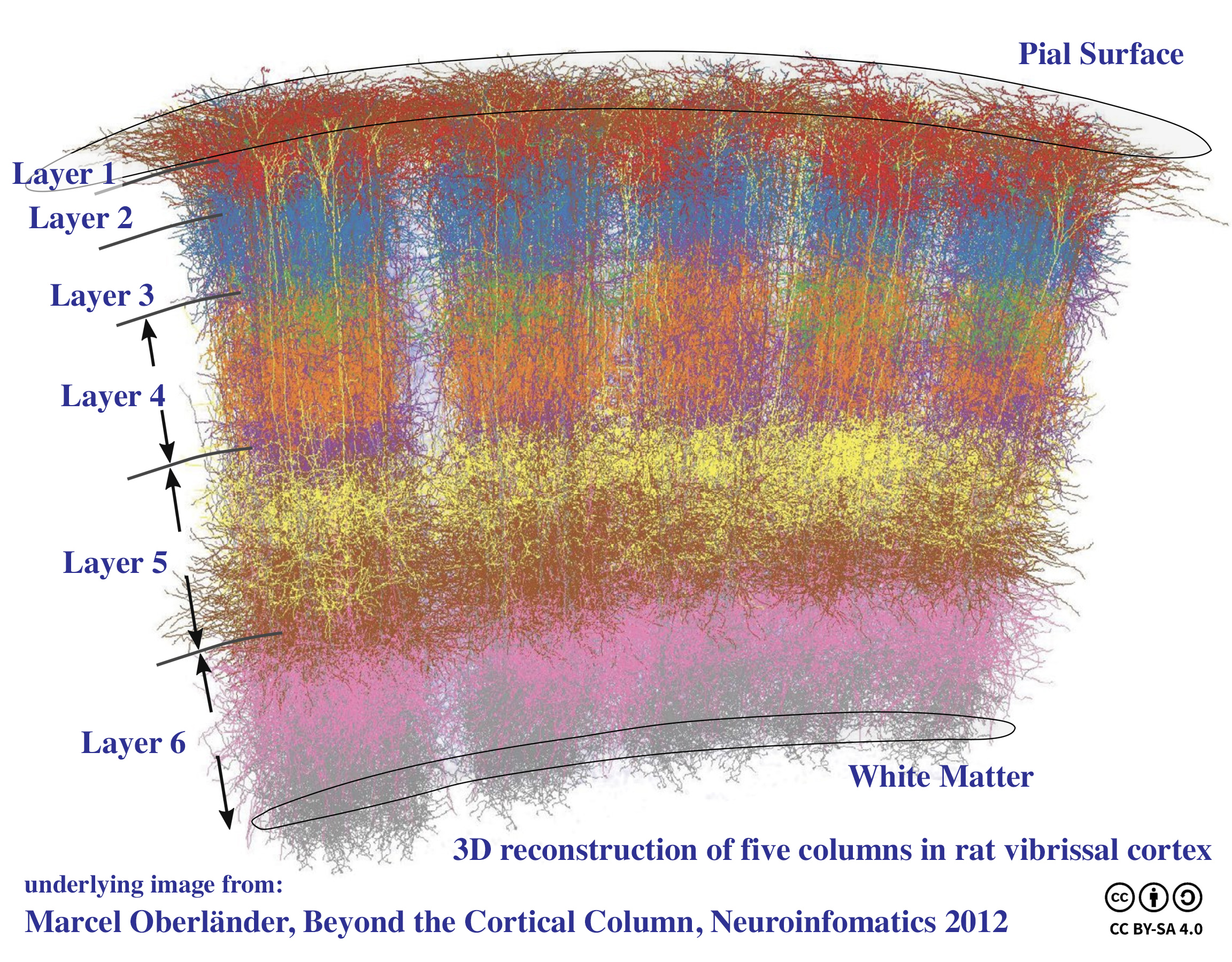
Cortical Minicolumn
A cortical minicolumn is a vertical column through the cortical layers of the brain. Neurons within the microcolumn "receive common inputs, have common outputs, are interconnected, and may well constitute a fundamental computational unit of the cerebral cortex". Minicolumns comprise perhaps 80–120 neurons, except in the primate primary visual cortex (V1), where there are typically more than twice the number. There are about 2×108 minicolumns in humans. From calculations, the diameter of a minicolumn is about 28–40 μm. Minicolumns grow from progenitor cells within the embryo and contain neurons within multiple layers (2–6) of the cortex. Many sources support the existence of minicolumns, especially Mountcastle, with strong evidence reviewed by Buxhoeveden and Casanova who conclude "... the minicolumn must be considered a strong model for cortical organization" and " he minicolumn is/nowiki> the most basic and consistent template by which the neocortex organize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
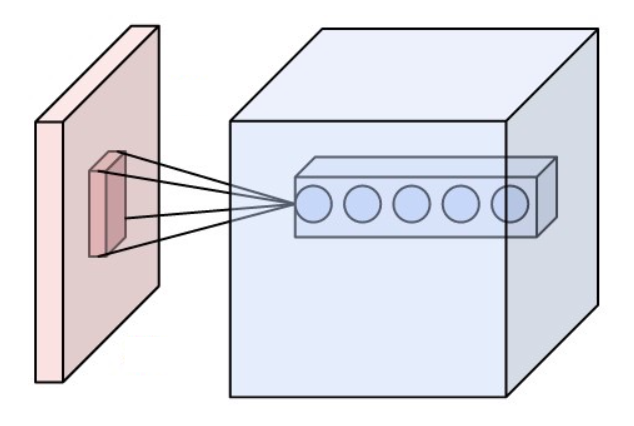
Cortical Column
A cortical column is a group of neurons forming a cylindrical structure through the cerebral cortex of the brain perpendicular to the cortical surface. The structure was first identified by Mountcastle in 1957. He later identified cortical minicolumn, minicolumns as the basic units of the neocortex which were arranged into columns. Each contains the same types of neurons, connectivity, and firing properties. Columns are also called hypercolumn, macrocolumn, functional column or sometimes cortical module,. Neurons within a minicolumn (microcolumn) encode similar features, whereas a hypercolumn "denotes a unit containing a full set of values for any given set of receptive field parameters". A cortical module is defined as either synonymous with a hypercolumn Vernon Benjamin Mountcastle, (Mountcastle) or as a tissue block of multiple overlapping hypercolumns. Cortical columns are proposed to be the canonical microcircuits for predictive coding, in which the process of cognition is impl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandra Blakeslee
Sandra Blakeslee (born 1943) is an American science correspondent of over four decades for ''The New York Times'' and science writer, specializing in neuroscience. Together with neuroscientist V. S. Ramachandran, she authored the 1998 popular science book '' Phantoms in the Brain: Probing the Mysteries of the Human Mind''. Biography Blakeslee is the third member of her family to specialize in science writing; her grandfather Howard W. Blakeslee wrote for the Associated Press, and was awarded a Pulitzer Prize for Reporting in 1937, and her father, Alton L. Blakeslee, also wrote for the AP. Sandra Blakeslee was raised in Port Washington, New York. She attended Northwestern University for two years, before transferring to the University of California, Berkeley, where she majored in political science, graduating in 1965. She then joined the Peace Corps, serving in Sarawak, Borneo, where she taught elementary school. Blakeslee started at the ''New York Times'' United Nations bureau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axon
An axon (from Greek ἄξων ''áxōn'', axis), or nerve fiber (or nerve fibre: see spelling differences), is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, in vertebrates, that typically conducts electrical impulses known as action potentials away from the nerve cell body. The function of the axon is to transmit information to different neurons, muscles, and glands. In certain sensory neurons (pseudounipolar neurons), such as those for touch and warmth, the axons are called afferent nerve fibers and the electrical impulse travels along these from the periphery to the cell body and from the cell body to the spinal cord along another branch of the same axon. Axon dysfunction can be the cause of many inherited and acquired neurological disorders that affect both the peripheral and central neurons. Nerve fibers are classed into three typesgroup A nerve fibers, group B nerve fibers, and group C nerve fibers. Groups A and B are myelinated, and group C are unmyelinated. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Receptive Field
The receptive field, or sensory space, is a delimited medium where some physiological stimuli can evoke a sensory neuronal response in specific organisms. Complexity of the receptive field ranges from the unidimensional chemical structure of odorants to the multidimensional spacetime of human visual field, through the bidimensional skin surface, being a receptive field for touch perception. Receptive fields can positively or negatively alter the membrane potential with or without affecting the rate of action potentials. A sensory space can be dependent of an animal's location. For a particular sound wave traveling in an appropriate transmission medium, by means of sound localization, an auditory space would amount to a reference system that continuously shifts as the animal moves (taking into consideration the space inside the ears as well). Conversely, receptive fields can be largely independent of the animal's location, as in the case of place cells. A sensory space can also m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neocortex
The neocortex, also called the neopallium, isocortex, or the six-layered cortex, is a set of layers of the mammalian cerebral cortex involved in higher-order brain functions such as sensory perception, cognition, generation of motor commands, spatial reasoning and language. The neocortex is further subdivided into the true isocortex and the proisocortex. In the human brain, the neocortex is the largest part of the cerebral cortex (the outer layer of the cerebrum). The neocortex makes up the largest part of the cerebral cortex, with the allocortex making up the rest. The neocortex is made up of six layers, labelled from the outermost inwards, I to VI. Etymology The term is from ''cortex'', Latin, " bark" or "rind", combined with ''neo-'', Greek, "new". ''Neopallium'' is a similar hybrid, from Latin ''pallium'', "cloak". ''Isocortex'' and ''allocortex'' are hybrids with Greek ''isos'', "same", and ''allos'', "other". Anatomy The neocortex is the most developed in its organisat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vernon Mountcastle
Vernon Benjamin Mountcastle (July 15, 1918 – January 11, 2015) was an American neurophysiologist and Professor Emeritus of Neuroscience at Johns Hopkins University. He discovered and characterized the columnar organization of the cerebral cortex in the 1950s. This discovery was a turning point in investigations of the cerebral cortex, as nearly all cortical studies of sensory function after Mountcastle's 1957 paper, on the somatosensory cortex, used columnar organization as their basis. Early life and education Vernon Benjamin Mountcastle was born on July 15, 1918, in Shelbyville, Kentucky as the third of five children into a family of "farmers, industrial entrepreneurs, or builders of railroads". In 1921 his family moved to Roanoke, Virginia where he went to elementary and junior high school and was "an enthusiastic Boy Scout". Because his mother, a former teacher, had taught him to read and write when he was 4 years old, he immediately moved ahead two grades when entering t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
On Intelligence
''On Intelligence: How a New Understanding of the Brain will Lead to the Creation of Truly Intelligent Machines'' is a 2004 book by Jeff Hawkins and Sandra Blakeslee. The book explains Hawkins' memory-prediction framework theory of the brain and describes some of its consequences. The theory Hawkins' basic idea is that the brain is a mechanism to predict the future, specifically, hierarchical regions of the brain predict their future input sequences. Perhaps not always far in the future, but far enough to be of real use to an organism. As such, the brain is a feed forward hierarchical state machine with special properties that enable it to learn. The state machine actually controls the behavior of the organism. Since it is a feed forward state machine, the machine responds to future events predicted from past data. The hierarchy is capable of memorizing frequently observed sequences (Cognitive modules) of patterns and developing invariant representations. Higher level ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jeff Hawkins
Jeffrey Hawkins is a co-founder of the companies Palm Computing, where he co-created the Palm (PDA), PalmPilot, and Handspring (company), Handspring, where he was one of the creators of the Palm Treo, Treo.Jeff Hawkins, ''On Intelligence'', p.28 He subsequently turned to work on neuroscience, founding the Redwood Neuroscience Institute, Redwood Center for Theoretical Neuroscience in 2002. In 2005 he founded Numenta, where he leads a team in efforts to reverse-engineer the neocortex and enable machine intelligence technology based on brain theory. He is the co-author of ''On Intelligence'' (2004), which explains his memory-prediction framework theory of the brain, and the author of ''A Thousand Brains: A New Theory of Intelligence'' (2021). Education Hawkins attended Cornell University, where he received a bachelor's degree in electrical engineering in 1979. Career Hawkins joined GRiD Systems in 1982, where he developed rapid application development (RAD) software called ''GR ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebral Cortex
The cerebral cortex, also known as the cerebral mantle, is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain in humans and other mammals. The cerebral cortex mostly consists of the six-layered neocortex, with just 10% consisting of allocortex. It is separated into two cortices, by the longitudinal fissure that divides the cerebrum into the left and right cerebral hemispheres. The two hemispheres are joined beneath the cortex by the corpus callosum. The cerebral cortex is the largest site of neural integration in the central nervous system. It plays a key role in attention, perception, awareness, thought, memory, language, and consciousness. The cerebral cortex is part of the brain responsible for cognition. In most mammals, apart from small mammals that have small brains, the cerebral cortex is folded, providing a greater surface area in the confined volume of the cranium. Apart from minimising brain and cranial volume, cortical folding is crucial for the brain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progenitor Cell
A progenitor cell is a Cell (biology), biological cell that can Cellular differentiation, differentiate into a specific cell type. Stem cells and progenitor cells have this ability in common. However, stem cells are less specified than progenitor cells. Progenitor cells can only differentiate into their "target" cell type. The most important difference between stem cells and progenitor cells is that stem cells can replicate indefinitely, whereas progenitor cells can divide only a limited number of times. Controversy about the exact definition remains and the concept is still evolving. The terms "progenitor cell" and "stem cell" are sometimes equated. Properties Most progenitors are identified as Oligopotency, oligopotent. In this point of view, they can compare to adult stem cells, but progenitors are said to be in a further stage of cell differentiation. They are in the "center" between stem cells and fully differentiated cells. The kind of potency they have depends on the type ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Striate Cortex
The visual cortex of the brain is the area of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information. It is located in the occipital lobe. Sensory input originating from the eyes travels through the lateral geniculate nucleus in the thalamus and then reaches the visual cortex. The area of the visual cortex that receives the sensory input from the lateral geniculate nucleus is the primary visual cortex, also known as visual area 1 ( V1), Brodmann area 17, or the striate cortex. The extrastriate areas consist of visual areas 2, 3, 4, and 5 (also known as V2, V3, V4, and V5, or Brodmann area 18 and all Brodmann area 19). Both hemispheres of the brain include a visual cortex; the visual cortex in the left hemisphere receives signals from the right visual field, and the visual cortex in the right hemisphere receives signals from the left visual field. Introduction The primary visual cortex (V1) is located in and around the calcarine fissure in the occipital lobe. Each hemisphere's V1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |