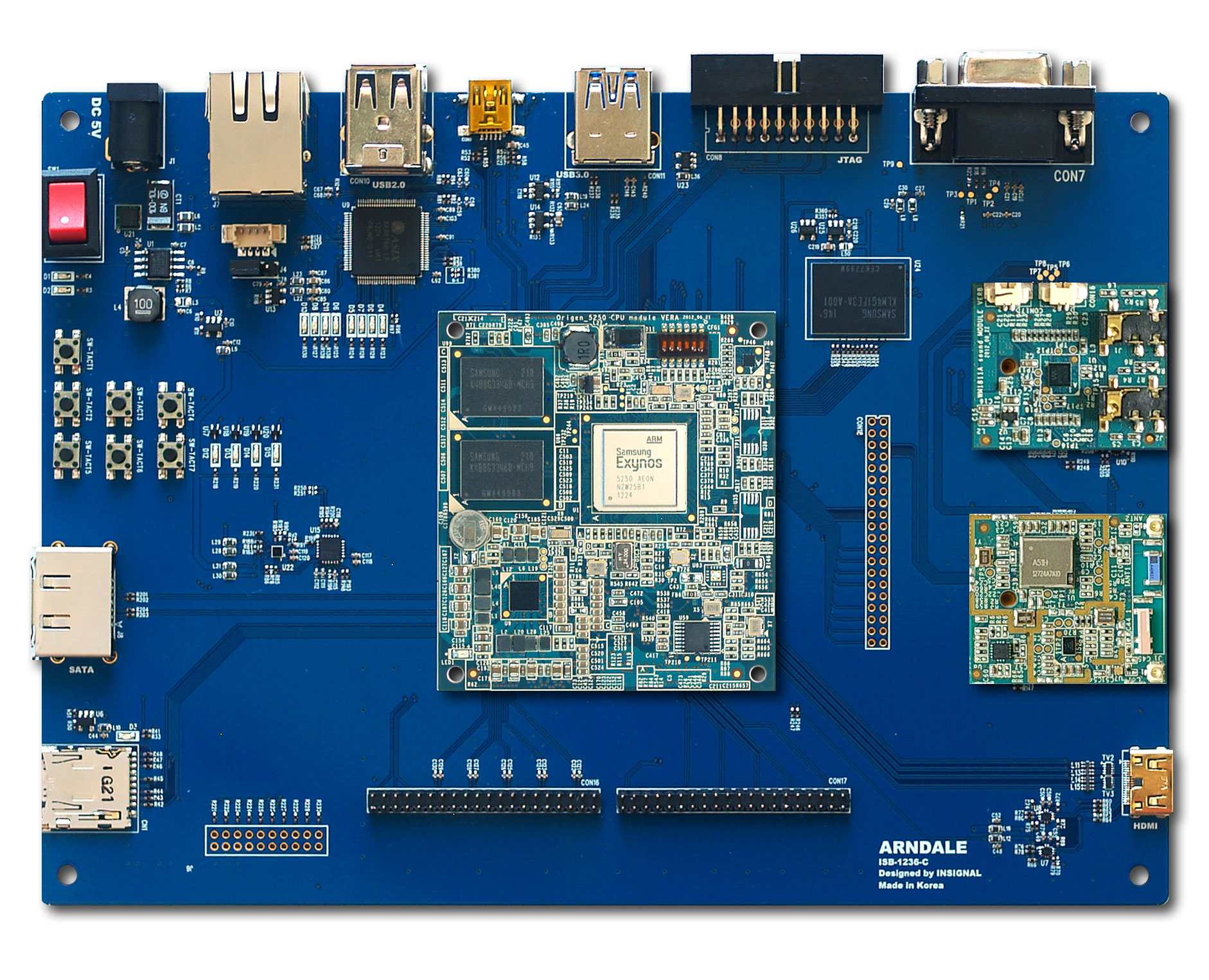
|
Cortex-A
The ARM Cortex-A is a group of 32-bit and 64-bit RISC ARM processor cores licensed by Arm Holdings. The cores are intended for application use. The group consists of 32-bit only cores: ARM Cortex-A5, ARM Cortex-A7, ARM Cortex-A8, ARM Cortex-A9, ARM Cortex-A12, ARM Cortex-A15, ARM Cortex-A17 MPCore, and ARM Cortex-A32, 32/64-bit mixed operation cores: ARM Cortex-A35, ARM Cortex-A53, ARM Cortex-A55, ARM Cortex-A57, ARM Cortex-A72, ARM Cortex-A73, ARM Cortex-A75, ARM Cortex-A76, ARM Cortex-A77, ARM Cortex-A78, ARM Cortex-A710, and ARM Cortex-A510 Refresh, and 64-bit only cores: ARM Cortex-A34, ARM Cortex-A65, ARM Cortex-A510 (2021), and ARM Cortex-A715. The 32-bit ARM Cortex-A cores, except for the Cortex-A32, implement the ARMv7-A profile of the ARMv7 architecture. The main distinguishing feature of the ARMv7-A profile, compared to the other two profiles, the ARMv7-R profile implemented by the ARM Cortex-R cores and the ARMv7-M profile implemented by most of the ARM Cortex-M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ARM Cortex-A35
ARM (stylised in lowercase as arm, formerly an acronym for Advanced RISC Machines and originally Acorn RISC Machine) is a family of reduced instruction set computer (RISC) instruction set architectures for computer processors, configured for various environments. Arm Ltd. develops the architectures and licenses them to other companies, who design their own products that implement one or more of those architectures, including system on a chip (SoC) and system on module (SOM) designs, that incorporate different components such as memory, interfaces, and radios. It also designs cores that implement these instruction set architectures and licenses these designs to many companies that incorporate those core designs into their own products. There have been several generations of the ARM design. The original ARM1 used a 32-bit internal structure but had a 26-bit address space that limited it to 64 MB of main memory. This limitation was removed in the ARMv3 series, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ARM Cortex-A34
ARM (stylised in lowercase as arm, formerly an acronym for Advanced RISC Machines and originally Acorn RISC Machine) is a family of reduced instruction set computer (RISC) instruction set architectures for computer processors, configured for various environments. Arm Ltd. develops the architectures and licenses them to other companies, who design their own products that implement one or more of those architectures, including system on a chip (SoC) and system on module (SOM) designs, that incorporate different components such as memory, interfaces, and radios. It also designs cores that implement these instruction set architectures and licenses these designs to many companies that incorporate those core designs into their own products. There have been several generations of the ARM design. The original ARM1 used a 32-bit internal structure but had a 26-bit address space that limited it to 64 MB of main memory. This limitation was removed in the ARMv3 series, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ARM Architecture
ARM (stylised in lowercase as arm, formerly an acronym for Advanced RISC Machines and originally Acorn RISC Machine) is a family of reduced instruction set computer (RISC) instruction set architectures for computer processors, configured for various environments. Arm Ltd. develops the architectures and licenses them to other companies, who design their own products that implement one or more of those architectures, including system on a chip (SoC) and system on module (SOM) designs, that incorporate different components such as memory, interfaces, and radios. It also designs cores that implement these instruction set architectures and licenses these designs to many companies that incorporate those core designs into their own products. There have been several generations of the ARM design. The original ARM1 used a 32-bit internal structure but had a 26-bit address space that limited it to 64 MB of main memory. This limitation was removed in the ARMv3 series, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ARM Cortex-A32
ARM (stylised in lowercase as arm, formerly an acronym for Advanced RISC Machines and originally Acorn RISC Machine) is a family of reduced instruction set computer (RISC) instruction set architectures for computer processors, configured for various environments. Arm Ltd. develops the architectures and licenses them to other companies, who design their own products that implement one or more of those architectures, including system on a chip (SoC) and system on module (SOM) designs, that incorporate different components such as memory, interfaces, and radios. It also designs cores that implement these instruction set architectures and licenses these designs to many companies that incorporate those core designs into their own products. There have been several generations of the ARM design. The original ARM1 used a 32-bit internal structure but had a 26-bit address space that limited it to 64 MB of main memory. This limitation was removed in the ARMv3 series, which ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ARM Cortex-A15 MPCore
The ARM Cortex-A15 MPCore is a 32-bit processor core licensed by ARM Holdings implementing the ARMv7-A architecture. It is a multicore processor with out-of-order superscalar pipeline running at up to 2.5 GHz. Overview ARM has claimed that the Cortex-A15 core is 40 percent more powerful than the Cortex-A9 core with the same number of cores at the same speed. The first A15 designs came out in the autumn of 2011, but products based on the chip did not reach the market until 2012. Key features of the Cortex-A15 core are: * 40-bit Large Physical Address Extensions (LPAE) addressing up to 1 TB of RAM. As per the x86 Physical Address Extension, virtual address space remains 32 bit. * 15 stage integer/17–25 stage floating point pipeline, with out-of-order speculative issue 3-way superscalar execution pipeline * 4 cores per cluster, up to 2 clusters per chip with CoreLink 400 (CCI-400, an AMBA-4 coherent interconnect) and 4 clusters per chip with CCN-504. ARM provide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ARM Holdings
Arm is a British semiconductor and software design company based in Cambridge, England. Its primary business is in the design of ARM processors (CPUs). It also designs other chips, provides software development tools under the DS-5, RealView and Keil brands, and provides systems and platforms, system-on-a-chip (SoC) infrastructure and software. As a "holding" company, it also holds shares of other companies. Since 2016, it has been owned by Japanese conglomerate SoftBank Group. While ARM CPUs first appeared in the Acorn Archimedes, a desktop computer, today's systems include mostly embedded systems, including ARM CPUs used in virtually all smartphones. Systems such as iPhones and Android smartphones frequently include many chips, from many different providers, that include one or more licensed Arm cores, in addition to those in the main Arm-based processor. Arm's core designs are also used in chips that support all the most common network-related technologies. Processors ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arm Holdings
Arm is a British semiconductor and software design company based in Cambridge, England. Its primary business is in the design of ARM processors (CPUs). It also designs other chips, provides software development tools under the DS-5, RealView and Keil brands, and provides systems and platforms, system-on-a-chip (SoC) infrastructure and software. As a "holding" company, it also holds shares of other companies. Since 2016, it has been owned by Japanese conglomerate SoftBank Group. While ARM CPUs first appeared in the Acorn Archimedes, a desktop computer, today's systems include mostly embedded systems, including ARM CPUs used in virtually all smartphones. Systems such as iPhones and Android smartphones frequently include many chips, from many different providers, that include one or more licensed Arm cores, in addition to those in the main Arm-based processor. Arm's core designs are also used in chips that support all the most common network-related technologies. Processors ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ARM Cortex-A77
The ARM Cortex-A77 is a central processing unit implementing the ARMv8.2-A 64-bit instruction set designed by ARM Holdings' Austin design centre. ARM announced an increase of 23% and 35% in integer and floating point performance, respectively. Memory bandwidth increased 15% relative to the A76. Design The Cortex-A77 serves as the successor of the Cortex-A76. The Cortex-A77 is a 4-wide decode out-of-order superscalar design with a new 1.5K macro-OP (MOPs) cache. It can fetch 4 instructions and 6 Mops per cycle. And rename and dispatch 6 Mops, and 13 µops per cycle. The out-of-order window size has been increased to 160 entries. The backend is 12 execution ports with a 50% increase over Cortex-A76. It has a pipeline depth of 13 stages and the execution latencies of 10 stages. There are six pipelines in the integer cluster – an increase of two additional integer pipelines from Cortex-A76. One of the changes from Cortex-A76 is the unification of the issue queues. Previously ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ARM Cortex-A73
The ARM Cortex-A73 is a central processing unit implementing the ARMv8-A 64-bit instruction set designed by ARM Holdings' Sophia design centre. The Cortex-A73 is a 2-wide decode out-of-order superscalar pipeline. The Cortex-A73 serves as the successor of the Cortex-A72, designed to offer 30% greater performance or 30% increased power efficiency. Design The design of the Cortex-A73 is based on the 32-bit ARMv7-A Cortex-A17, emphasizing power efficiency and sustained peak performance. The Cortex-A73 is primarily targeted at mobile computing. In reviews, the Cortex-A73 showed improved integer instructions per clock (IPC), though lower floating point IPC, relative to the Cortex-A72. Licensing The Cortex-A73 is available as SIP core to licensees, and its design makes it suitable for integration with other SIP cores (e.g. GPU, display controller, DSP, image processor, etc.) into one die constituting a system on a chip (SoC). The Cortex-A73 is also the first ARM core to be modified ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ARM Cortex-A76
The ARM Cortex-A76 is a central processing unit implementing the ARMv8.2-A 64-bit instruction set designed by ARM Holdings' Austin design centre. ARM states a 25% and 35% increase in integer and floating point performance, respectively, over a Cortex-A75 of the previous generation. Design The Cortex-A76 serves as the successor of the ARM Cortex-A73 and ARM Cortex-A75, though based on a clean sheet design. The Cortex-A76 frontend is a 4-wide decode out-of-order superscalar design. It can fetch 4 instructions per cycle. And rename and dispatch 4 Mops, and 8 µops per cycle. The out-of-order window size is 128 entries. The backend is 8 execution ports with a pipeline depth of 13 stages and the execution latencies of 11 stages. The core supports unprivileged 32-bit applications, but privileged applications must utilize the 64-bit ARMv8-A ISA. It also supports Load acquire (LDAPR) instructions (ARMv8.3-A), Dot Product instructions (ARMv8.4-A), PSTATE Speculative Store Bypass Saf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ARM Cortex-A17 MPCore
The ARM Cortex-A17 is a 32-bit processor core implementing the ARMv7-A architecture, licensed by ARM Holdings. Providing up to four cache-coherent cores, it serves as the successor to the Cortex-A9 and replaces the previous ARM Cortex-A12 specifications. ARM claims that the Cortex-A17 core provides 60% higher performance than the Cortex-A9 core, while reducing the power consumption by 20% under the same workload. ARM renamed Cortex-A12 to a variant of Cortex-A17 since the second revision of the A12 core in early 2014, because these two were indistinguishable in performance and all features available in the A17 were used as upgrades in the A12. New features of the Cortex-A17 specification, not found in the Cortex-A9 specification, are all improvements from the third-generation ARM Cortex-A, which also includes the Cortex-A7 and Cortex-A15: * Hardware virtualization and 40-bit Large Physical Address Extensions (LPAE) addressing * Full-system coherency, bringing support for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ARM Cortex-A78
The ARM Cortex-A78 is a central processing unit implementing the ARMv8.2-A 64-bit instruction set designed by ARM Ltd.'s Austin centre, set to be distributed amongst high-end devices in 2020–2021. Design The ARM Cortex-A78 is the successor to the ARM Cortex-A77. It can be paired with the ARM Cortex-X1 and/or ARM Cortex-A55 CPUs in a DynamIQ configuration to deliver both performance and efficiency. The processor also claims as much as 50% energy savings over its predecessor. The Cortex-A78 is a 4-wide decode out-of-order superscalar design with a 1.5K macro-OP (MOPs) cache. It can fetch 4 instructions and 6 Mops per cycle, and rename and dispatch 6 Mops, and 13 µops per cycle. The out-of-order window size is 160 entries and the backend has 13 execution ports with a pipeline depth of 13 stages, and the execution latencies consist of 10 stages. The processor is built on a standard Cortex-A roadmap and offers a 2.1 GHz ( 5 nm) chipset which makes it better than its p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |