|
Cordylodontidae
Cordylodontidae is a family of conodonts. Genera are ''Cordylodus''. '' Eoconodontus'' and '' Iapetognathus''. References * The conodont apparatus as a food-gathering mechanism. Maurits Lindström, palaeontology, volume17, part 4, pages 729-744 * Taxonomy, Evolution, and Biostratigraphy of Conodonts from the Kechika Formation, Skoki Formation, and Road River Group (Upper Cambrian to Lower Silurian), Northeastern British Columbia. Leanne J. Pyle and Christopher R. Burnes, Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences The ''Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal established in 1963, which reports current research on all aspects of the Earth sciences. It is published by NRC Research Press. The journal also publishes ..., 38(10), pages 1387–1401, 2001, External links Conodont families Proconodontida {{Conodont-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cordylodus
''Cordylodus'' is an extinct genus of conodonts in the family of Cordylodontidae. Use in stratigraphy It is suggested that ''Cordylodus andresi'' can be a marker of the Cambrian Stage 10. Distribution Fossils of ''Cordylodus'' have been found in Argentina, Australia, Canada (Quebec), China, Colombia (Tarqui, Huila),Moreno et al., 2008, p.10 Kazakhstan, Malaysia, Mexico, Norway, the Russian Federation, Sweden, and the United States, in the states of Alaska, Minnesota, Nevada, New York, Oklahoma (Bromide Formation The Bromide Formation is a geological formation in Oklahoma, USA. It is well known for its diverse echinoderm and trilobite fossil fauna. Location The Bromide Formation crops out in the Arbuckle and Wichita Mountains and in the Criner Hills ...), Vermont and Wyoming. ''C. horridus'' has been recovered from the Blakely Sandstone and ''C. angulatus'' from the Collier Shale, Ordovician geologic formations in the Ouachita Mountains of Arkansas and Oklahoma. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iapetognathus
''Iapetognathus'' is a genus of cordylodan conodonts. It is one of the oldest denticulate euconodont genera known.The conodont Iapetognathus and its value for defining the base of the Ordovician System. Frederick Miller, John E. Repetski, Robert S. Nicoll, Godfrey Nowlan and Raymond L. Ethington, GFF, Volume 136, Issue 1, 2014, pages 185-188, Like other members of the genus, ''Iapetognathus fluctivagus'' had ramiform (branching) array of elements (apparatus). It is believed that the ramiform apparatus in ''Iapetognathus fluctivagus'' evolved from the coniform (cone-like) apparatus of '' Iapetonudus ibexensis''. It can be readily distinguished from other conodonts existing during the same age by the sideward orientation of the major teeth-like projections (denticulate processes). The genus ''Iapetognathus'' and related denticulate groups still require extensive taxonomic clarification. In 2011, a study discovered that the First appearance datum (FAD) of ''Iapetognathus flucti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maurits Lindström
Maurits Lindström (10 May 1932 – 14 November 2009) was a Swedish geologist and paleontologist. Lindströms initial work was divided among two topics conodont paleontology and the structural geology of the Scandinavian Caledonides in Lappland. In 1970, he described the conodont families Cordylodontidae, Gondolellidae, Proconodontidae and Rhipidognathidae. In 1971, he described the conodont genera '' Baltoniodus'', '' Microzarkodina'' and ''Paracordylodus''.Vom Anfang, Hochstand und Ende eines Epikontinentalmeeres. Maurits Lindström, Geologische Rundschau, March 1971, Volume 60, Issue 2, pages 419-438, Lindström published conodont studies up to 1987 after which he only supervised students working with conodonts. In the late 1980s Lindström begun to study ancient impact craters in the Fennoscandian Shield. His studies have confirmed earlier speculations that Tvären and Lockne are craters. Awards and tributes In 1985 he became member of the Royal Swedish Academy of Scienc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
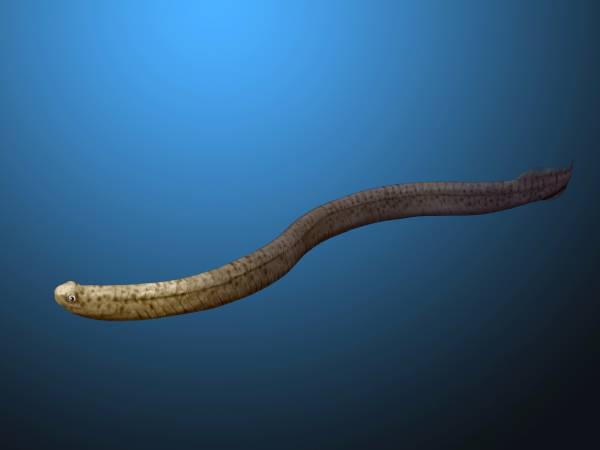
Conodont
Conodonts (Greek ''kōnos'', "cone", + ''odont'', "tooth") are an extinct group of agnathan (jawless) vertebrates resembling eels, classified in the class Conodonta. For many years, they were known only from their tooth-like oral elements, which are usually found in isolation and are now called conodont elements. Knowledge about soft tissues remains limited. They existed in the world's oceans for over 300 million years, from the Cambrian to the beginning of the Jurassic. Conodont elements are widely used as index fossils, fossils used to define and identify geological periods. The animals are also called Conodontophora (conodont bearers) to avoid ambiguity. Discovery and understanding of conodonts The teeth-like fossils of the conodont were first discovered by Heinz Christian Pander and the results published in Saint Petersburg, Russia, in 1856. The name ''pander'' is commonly used in scientific names of conodonts. It was only in the early 1980s that the first fossil evidence of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conodont Families
Conodonts (Greek ''kōnos'', "cone", + ''odont'', "tooth") are an extinct group of agnathan (jawless) vertebrates resembling eels, classified in the class Conodonta. For many years, they were known only from their tooth-like oral elements, which are usually found in isolation and are now called conodont elements. Knowledge about soft tissues remains limited. They existed in the world's oceans for over 300 million years, from the Cambrian to the beginning of the Jurassic. Conodont elements are widely used as index fossils, fossils used to define and identify geological periods. The animals are also called Conodontophora (conodont bearers) to avoid ambiguity. Discovery and understanding of conodonts The teeth-like fossils of the conodont were first discovered by Heinz Christian Pander and the results published in Saint Petersburg, Russia, in 1856. The name ''pander'' is commonly used in scientific names of conodonts. It was only in the early 1980s that the first fossil evidence of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eoconodontus
''Eoconodontus'' is an extinct genus of conodonts of the Late Cambrian. It is a two-elements (rounded and compressed) genus from the ''Proconodontus'' lineage. Use in stratigraphy It is suggested that ''Eoconodontus notchpeakensis'' can be a marker of the Stage 10 of the Furongian the fourth and final series of the Cambrian. In 2006, a working group proposed the first appearance of ''Cordylodus andresi''. Currently the first appearance of ''E. notchpeakensis'' is favored by many authors because it is globally widespread and is independent of facies In geology, a facies ( , ; same pronunciation and spelling in the plural) is a body of rock with specified characteristics, which can be any observable attribute of rocks (such as their overall appearance, composition, or condition of formatio ... (known from continental rise to peritidal environments).Landing, E.; Westrop, S.R.; Adrain, J.M. (19 September 2011). "The Lawsonian Stage - the Eoconodontus notchpeakensis FAD and H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kechika Formation
The Kechika Formation is a geologic formation in British Columbia. It preserves fossils dating back to the Ordovician period. See also * List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in British Columbia This is a list of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in British Columbia, Canada. References * {{Lists of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Canada British Columbia British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost provi ... References * Ordovician British Columbia Ordovician northern paleotropical deposits {{British Columbia-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skoki Formation
The Skoki Formation is a stratigraphic unit of Early to Middle Ordovician age that is present on the western edge of the Western Canada Sedimentary Basin in the Canadian Rockies of Alberta and British Columbia. It was named for Skoki Mountain near Lake Louise in Banff National Park by Charles Doolittle Walcott in 1928. The Skoki Formation is fossiliferous and includes remains of brachiopods and other marine invertebrates, as well as conodonts and oncolites. Lithology and deposition The Skoki Formation formed as a shallow marine shelf along the western shoreline of the North American Craton during Early to Middle Ordovician time.Aitken, J.D. 1966. Middle Cambrian to Middle Ordovician cyclic sedimentation, southern Rocky Mountains of Alberta. Bulletin of Canadian Petroleum Geology, vol. 14, no. 6, p. 405-441. Most of the original limestone was subsequently altered to dolomite. Many beds include quartz sand and silt, and some include layers of brown argillite. Distribution and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Road River Group
The Road River Group is a geologic group in Alberta. It preserves fossils dating back to the Ordovician period Period may refer to: Common uses * Era, a length or span of time * Full stop (or period), a punctuation mark Arts, entertainment, and media * Period (music), a concept in musical composition * Periodic sentence (or rhetorical period), a concept .... See also * List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Alberta References * Ordovician Alberta {{Alberta-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Journal Of Earth Sciences
The ''Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal established in 1963, which reports current research on all aspects of the Earth sciences. It is published by NRC Research Press. The journal also publishes special issues that focus on information and studies limited in scope to a specific segment of the Earth sciences. The editor-in-chief is Dr. Brendan Murphy (St. Francis Xavier University) and Sally Pehrsson (University of Saskatchewan). According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as ... of 1.369. References External links * {{Authority control Earth and atmospheric sciences journals Monthly journals Publications established in 1963 Canadian Scie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |