|
Coprocessor
A coprocessor is a computer processor used to supplement the functions of the primary processor (the CPU). Operations performed by the coprocessor may be floating-point arithmetic, graphics, signal processing, string processing, cryptography or I/O interfacing with peripheral devices. By offloading processor-intensive tasks from the main processor, coprocessors can accelerate system performance. Coprocessors allow a line of computers to be customized, so that customers who do not need the extra performance do not need to pay for it. Functionality Coprocessors vary in their degree of autonomy. Some (such as FPUs) rely on direct control via coprocessor instructions, embedded in the CPU's instruction stream. Others are independent processors in their own right, capable of working asynchronously; they are still not optimized for general-purpose code, or they are incapable of it due to a limited instruction set focused on accelerating specific tasks. It is common for these to b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Intel 8087
The Intel 8087, announced in 1980, was the first floating-point coprocessor for the 8086 line of microprocessors. The purpose of the chip was to speed up floating-point arithmetic operations, such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and square root. It also computes transcendental functions such as exponential, logarithmic or trigonometric calculations. The performance enhancements were from approximately 20% to over 500%, depending on the specific application. The 8087 could perform about 50,000 FLOPS using around 2.4 watts. The 8087 was an advanced integrated circuit, pushing the limits of manufacturing technology of the period. Basic operations on the 8087 such as addition and subtraction can take over 100 machine cycles to execute and some instructions exceed 1000 cycles. The chip lacks a hardware multiplier and implements calculations using the CORDIC algorithm. Sales of the 8087 received a significant boost when a coprocessor socket was incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Floating-point Unit
A floating-point unit (FPU), numeric processing unit (NPU), colloquially math coprocessor, is a part of a computer system specially designed to carry out operations on floating-point numbers. Typical operations are addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and square root. Modern designs generally include a fused multiply-add instruction, which was found to be very common in real-world code. Some FPUs can also perform various transcendental functions such as exponential or trigonometric calculations, but the accuracy can be low, so some systems prefer to compute these functions in software. Floating-point operations were originally handled in software in early computers. Over time, manufacturers began to provide standardized floating-point libraries as part of their software collections. Some machines, those dedicated to scientific processing, would include specialized hardware to perform some of these tasks with much greater speed. The introduction of microcode in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Weitek
Weitek Corporation was an American Microprocessor, chip-design company that originally focused on floating-point units for a number of commercial Central processing unit, CPU designs. During the early to mid-1980s, Weitek designs could be found powering a number of high-end designs and Parallel computing, parallel-processing supercomputers. Weitek started in 1981, when several Intel engineers left to form their own company. Weitek developed math coprocessors for several systems, including those based on the Motorola Motorola 68000 series, 68000 family, the WTL 1064 and 1164, and for Intel-based i286 systems, the WTL 1067. The 1067 was physically implemented as three chips, the WTL 1163, 1164 and 1165. When Intel's own FPU design for the i386 fell far behind in development, Weitek delivered the 1167 for them in the form of a daughtercard. Improvements in chip manufacturing allowed this to be reduced to a single-chip version, the WTL 2167. The WTL 3167 of 1988, also known as the Ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Floating-point Arithmetic
In computing, floating-point arithmetic (FP) is arithmetic on subsets of real numbers formed by a ''significand'' (a Sign (mathematics), signed sequence of a fixed number of digits in some Radix, base) multiplied by an integer power of that base. Numbers of this form are called floating-point numbers. For example, the number 2469/200 is a floating-point number in base ten with five digits: 2469/200 = 12.345 = \! \underbrace_\text \! \times \! \underbrace_\text\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\overbrace^ However, 7716/625 = 12.3456 is not a floating-point number in base ten with five digits—it needs six digits. The nearest floating-point number with only five digits is 12.346. And 1/3 = 0.3333… is not a floating-point number in base ten with any finite number of digits. In practice, most floating-point systems use Binary number, base two, though base ten (decimal floating point) is also common. Floating-point arithmetic operations, such as addition and division, approximate the correspond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
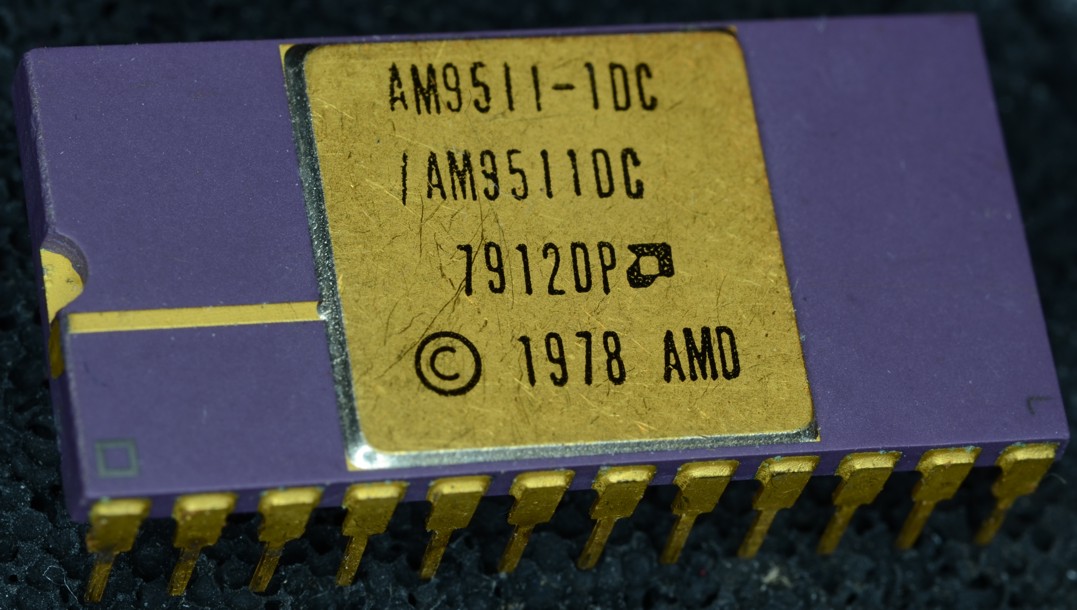
Intel 8231/8232
The Intel 8231 and 8232 were early designs of floating-point unit, floating-point maths coprocessors (FPUs), marketed for use with their Intel 8080, i8080 line of primary central processing unit, CPUs. They were licensed versions of AMD's Am9511 and Am9512 FPUs, from 1977 and 1979, themselves claimed by AMD as the world's first single-chip FPU solutions. Adoption Whilst the i8231/i8232 (and their AMD-branded cousins) were primarily intended to partner the i8080 (or the AMD clone Am9080), the multiple interface options in their design, from simple wait state insertion and Polling (computer science), status polling routines to interrupt and DMA controller driven methods suitable for a peripheral processor or add-in board, meant that – with a small amount of glue logic – it was usable in almost any microprocessor system that had a DMA subsystem or a spare interrupt input/interrupt vector available, and AMD's original documentation provided several different examples. This was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cryptographic Accelerator
In computing, a cryptographic accelerator is a co-processor designed specifically to perform computationally intensive cryptographic operations, doing so far more efficiently than the general-purpose CPU. Because many servers' system loads consist mostly of cryptographic operations, this can greatly increase performance. Intel's AES-NI is by far the most common cryptographic accelerator in commodity hardware. VIA PadLock is another recent example. Operating system support Several operating systems provide some support for cryptographic hardware. The BSD family of systems has the OpenBSD Cryptographic Framework (OCF), Linux systems have the Crypto API, Solaris OS has the Solaris Cryptographic Framework (SCF) and Microsoft Windows has the Microsoft CryptoAPI. Some cryptographic accelerators offer new machine instructions and can therefore be used directly by programs. Libraries such as OpenSSL and LibreSSL support some such cryptographic accelerators. Almost all Unix-like oper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Floating-point
In computing, floating-point arithmetic (FP) is arithmetic on subsets of real numbers formed by a ''significand'' (a Sign (mathematics), signed sequence of a fixed number of digits in some Radix, base) multiplied by an integer power of that base. Numbers of this form are called floating-point numbers. For example, the number 2469/200 is a floating-point number in base ten with five digits: 2469/200 = 12.345 = \! \underbrace_\text \! \times \! \underbrace_\text\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\overbrace^ However, 7716/625 = 12.3456 is not a floating-point number in base ten with five digits—it needs six digits. The nearest floating-point number with only five digits is 12.346. And 1/3 = 0.3333… is not a floating-point number in base ten with any finite number of digits. In practice, most floating-point systems use Binary number, base two, though base ten (decimal floating point) is also common. Floating-point arithmetic operations, such as addition and division, approximate the correspond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Digital Signal Processor
A digital signal processor (DSP) is a specialized microprocessor chip, with its architecture optimized for the operational needs of digital signal processing. DSPs are fabricated on metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) integrated circuit chips. They are widely used in audio signal processing, telecommunications, digital image processing, radar, sonar and speech recognition systems, and in common consumer electronic devices such as mobile phones, disk drives and high-definition television (HDTV) products. The goal of a DSP is usually to measure, filter or compress continuous real-world analog signals. Most general-purpose microprocessors can also execute digital signal processing algorithms successfully, but may not be able to keep up with such processing continuously in real-time. Also, dedicated DSPs usually have better power efficiency, thus they are more suitable in portable devices such as mobile phones because of power consumption constraints. DSPs often use special m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Instruction Set Architecture
In computer science, an instruction set architecture (ISA) is an abstract model that generally defines how software controls the CPU in a computer or a family of computers. A device or program that executes instructions described by that ISA, such as a central processing unit (CPU), is called an ''implementation'' of that ISA. In general, an ISA defines the supported instructions, data types, registers, the hardware support for managing main memory, fundamental features (such as the memory consistency, addressing modes, virtual memory), and the input/output model of implementations of the ISA. An ISA specifies the behavior of machine code running on implementations of that ISA in a fashion that does not depend on the characteristics of that implementation, providing binary compatibility between implementations. This enables multiple implementations of an ISA that differ in characteristics such as performance, physical size, and monetary cost (among other things), but t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Instruction Set
In computer science, an instruction set architecture (ISA) is an abstract model that generally defines how software controls the CPU in a computer or a family of computers. A device or program that executes instructions described by that ISA, such as a central processing unit (CPU), is called an ''implementation'' of that ISA. In general, an ISA defines the supported Machine code, instructions, data types, Register (computer), registers, the hardware support for managing Computer memory, main memory, fundamental features (such as the memory consistency, addressing modes, virtual memory), and the input/output model of implementations of the ISA. An ISA specifies the behavior of machine code running on implementations of that ISA in a fashion that does not depend on the characteristics of that implementation, providing binary compatibility between implementations. This enables multiple implementations of an ISA that differ in characteristics such as Computer performance, performa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hardware Acceleration
Hardware acceleration is the use of computer hardware designed to perform specific functions more efficiently when compared to software running on a general-purpose central processing unit (CPU). Any transformation of data that can be calculated in software running on a generic CPU can also be calculated in custom-made hardware, or in some mix of both. To perform computing tasks more efficiently, generally one can invest time and money in improving the software, improving the hardware, or both. There are various approaches with advantages and disadvantages in terms of decreased latency, increased throughput, and reduced energy consumption. Typical advantages of focusing on software may include greater versatility, more rapid development, lower non-recurring engineering costs, heightened portability, and ease of updating features or patching bugs, at the cost of overhead to compute general operations. Advantages of focusing on hardware may include speedup, reduced power c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |