|
Convento De San Norberto
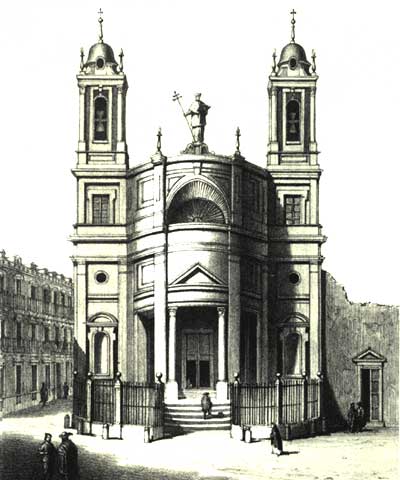
The Convento de Premonstratenses de San Norberto, also known as Convento de Mostenses or Convento de San Norberto, named after the founder of the Premonstratensian Order, is a religious building that disappeared. It was located on the ground of the current Plaza de Los Mostenses, next to the Gran Vía of Madrid (Spain). It was founded in 1611 by the community of the Fathers Canons Premonstratensians with the permission of Cardinal Archbishop of Toledo Bernardo de Rojas and financed by a benefactor, the Count of Miranda, Juan of Zúñiga, the then president of the Council of Castile. Today the site of the convent is occupied by a market built in the 19th century, known as Mercado de Los Mostenses. History The church had been rebuilt in 1754 by architect Ventura Rodríguez, having been previously ruined. It had a convex façade flanked by two towers but was a victim of the plan of the then king, Joseph Bonaparte to open up the plazas of the city. First, the convent was demolis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CONVENTO DE SAN NORBERTO
The Convento de Premonstratenses de San Norberto, also known as Convento de Mostenses or Convento de San Norberto, named after the founder of the Premonstratensian Order, is a religious building that disappeared. It was located on the ground of the current Plaza de Los Mostenses, next to the Gran Vía of Madrid (Spain). It was founded in 1611 by the community of the Fathers Canons Premonstratensians with the permission of Cardinal Archbishop of Toledo Bernardo de Rojas and financed by a benefactor, the Count of Miranda, Juan of Zúñiga, the then president of the Council of Castile. Today the site of the convent is occupied by a market built in the 19th century, known as Mercado de Los Mostenses. History The church had been rebuilt in 1754 by architect Ventura Rodríguez, having been previously ruined. It had a convex façade flanked by two towers but was a victim of the plan of the then king, Joseph Bonaparte to open up the plazas of the city. First, the convent was demolis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Former Mercado De Los Mostenses
A former is an object, such as a template, gauge or cutting die, which is used to form something such as a boat's hull. Typically, a former gives shape to a structure that may have complex curvature. A former may become an integral part of the finished structure, as in an aircraft fuselage, or it may be removable, being using in the construction process and then discarded or re-used. Aircraft formers Formers are used in the construction of aircraft fuselage, of which a typical fuselage has a series from the nose to the empennage, typically perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the aircraft. The primary purpose of formers is to establish the shape of the fuselage and reduce the column length of stringers to prevent instability. Formers are typically attached to longerons, which support the skin of the aircraft. The "former-and-longeron" technique (also called stations and stringers) was adopted from boat construction, and was typical of light aircraft built until the ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Former Churches In Spain
A former is an object, such as a template, gauge or cutting die, which is used to form something such as a boat's hull. Typically, a former gives shape to a structure that may have complex curvature. A former may become an integral part of the finished structure, as in an aircraft fuselage, or it may be removable, being using in the construction process and then discarded or re-used. Aircraft formers Formers are used in the construction of aircraft fuselage, of which a typical fuselage has a series from the nose to the empennage, typically perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the aircraft. The primary purpose of formers is to establish the shape of the fuselage and reduce the column length of stringers to prevent instability. Formers are typically attached to longerons, which support the skin of the aircraft. The "former-and-longeron" technique (also called stations and stringers) was adopted from boat construction, and was typical of light aircraft built until the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buildings And Structures In Spain Demolished During The Peninsular War
A building, or edifice, is an enclosed structure with a roof and walls standing more or less permanently in one place, such as a house or factory (although there's also portable buildings). Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for a wide number of factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the term ''building'' compare the list of nonbuilding structures. Buildings serve several societal needs – primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical division of the human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) and the ''outside'' (a place that at times may be harsh and harmful). Ever since the first cave paintings, buildings have also become objects or canvasses of much artistic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baroque Architecture In Spain
The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires including the Iberian Peninsula it continued, together with new styles, until the first decade of the 19th century. It followed Renaissance art and Mannerism and preceded the Rococo (in the past often referred to as "late Baroque") and Neoclassical styles. It was encouraged by the Catholic Church as a means to counter the simplicity and austerity of Protestant architecture, art, and music, though Lutheran Baroque art developed in parts of Europe as well. The Baroque style used contrast, movement, exuberant detail, deep colour, grandeur, and surprise to achieve a sense of awe. The style began at the start of the 17th century in Rome, then spread rapidly to France, northern Italy, Spain, and Portugal, then to Austria, southern Germany, and Russia. B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Premonstratensian Monasteries In Spain
The Order of Canons Regular of Prémontré (), also known as the Premonstratensians, the Norbertines and, in Britain and Ireland, as the White Canons (from the colour of their habit), is a religious order of canons regular of the Catholic Church founded in Prémontré near Laon in 1120 by Norbert of Xanten, who later became Archbishop of Magdeburg. Premonstratensians are designated by ''OPraem'' (''Ordo Praemonstratensis'') following their name. Norbert was a friend of Bernard of Clairvaux and was largely influenced by the Cistercian ideals as to both the manner of life and the government of his order. As the Premonstratensians are not monks but canons regular, their work often involves preaching and the exercising of pastoral ministry; they frequently serve in parishes close to their abbeys or priories. History The order was founded in 1120. Saint Norbert had made various efforts to introduce a strict form of canonical life in various communities of canons in Germany; in 1120 h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Religious Buildings And Structures Completed In 1754
Religion is usually defined as a social-cultural system of designated behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics, or organizations, that generally relates humanity to supernatural, transcendental, and spiritual elements; however, there is no scholarly consensus over what precisely constitutes a religion. Different religions may or may not contain various elements ranging from the divine, sacred things, faith,Tillich, P. (1957) ''Dynamics of faith''. Harper Perennial; (p. 1). a supernatural being or supernatural beings or "some sort of ultimacy and transcendence that will provide norms and power for the rest of life". Religious practices may include rituals, sermons, commemoration or veneration (of deities or saints), sacrifices, festivals, feasts, trances, initiations, funerary services, matrimonial services, meditation, prayer, music, art, dance, public service, or other aspects of human culture. Religions ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buildings And Structures Completed In 1611
A building, or edifice, is an enclosed structure with a roof and walls standing more or less permanently in one place, such as a house or factory (although there's also portable buildings). Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for a wide number of factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the term ''building'' compare the list of nonbuilding structures. Buildings serve several societal needs – primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical division of the human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) and the ''outside'' (a place that at times may be harsh and harmful). Ever since the first cave paintings, buildings have also become objects or canvasses of much artistic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demolished Buildings And Structures In Madrid
Demolition (also known as razing, cartage, and wrecking) is the science and engineering in safely and efficiently tearing down of buildings and other artificial structures. Demolition contrasts with deconstruction, which involves taking a building apart while carefully preserving valuable elements for reuse purposes. For small buildings, such as houses, that are only two or three stories high, demolition is a rather simple process. The building is pulled down either manually or mechanically using large hydraulic equipment: elevated work platforms, cranes, excavators or bulldozers. Larger buildings may require the use of a wrecking ball, a heavy weight on a cable that is swung by a crane into the side of the buildings. Wrecking balls are especially effective against masonry, but are less easily controlled and often less efficient than other methods. Newer methods may use rotational hydraulic shears and silenced rock-breakers attached to excavators to cut or break through wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
José Amador De Los Ríos
José Amador de los Ríos y Serrano (30 April 1818 – 17 February 1878) was a Spanish intellectual, primarily a historian and archaeologist of art and literature. He was a graduate in history of the Complutense University of Madrid. In 1844 he was the secretary of the Comisión Central de Monumentos. He was co-director with Antonio de Zabaleta of the ephemeral ''Boletín Español de Arquitectura'', the first Spanish journal dedicated exclusively to architecture.José Enrique García Melero (2002), ''Literatura española sobre Artes Plásticas: Bibliografía aparecida en España entre los siglos XVI y XVIII'' (Encuentro), 176. It was only in publication from 1 June to December 1846. In 1852 he published the complete works of Íñigo López de Mendoza. It was Amador de los Ríos who first used the term '' mudejarismo'' to describe a form of architectural decoration in 1859. In 1861 he published the first volume of ''Historia crítica de la literatura española'', the first gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colmenar Viejo
Colmenar Viejo is a town and municipality of about 48,614 inhabitants, located in the Community of Madrid, Spain, 30 kilometers north of Madrid on the M-607 motorway. It belongs to the comarca of Cuenca Alta del Manzanares. Main sights In the town, there are many archeological sites, most of them come from hispanic- visigothic times, with household areas and burials. The most important tourist attractions places in Colmenar Viejo are: * Basilica de Nuestra Señora de la Asunción * Ermita de Remedios, saint of the town * Visigothic archaeological tombs Physical environment Colmenar Viejo's municipality has a size of 182.6 square kilometres (70.5 square miles), the third largest in the province of Madrid, after Madrid and Aranjuez. Traditional granite mining has been changing Colmenar Viejo's landscape. As a result of livestock farming, mainly cow and horse cattle, grassland has been taking a main role. A large part of land under Colmenar Viejo's jurisdiction is inside of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
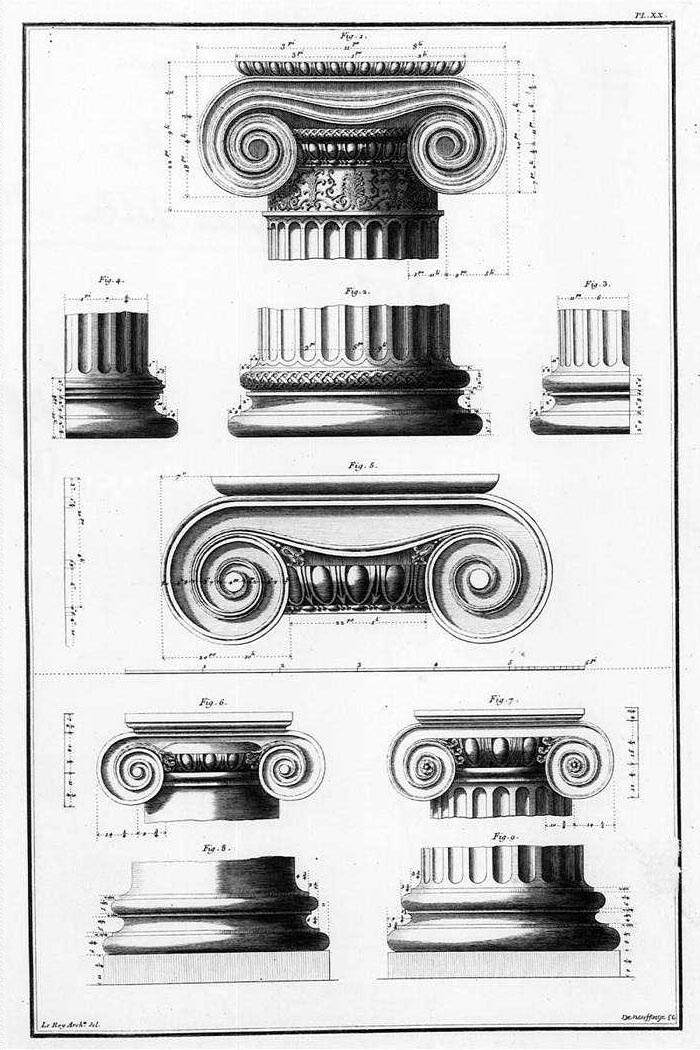
Ionic Order
The Ionic order is one of the three canonic orders of classical architecture, the other two being the Doric and the Corinthian. There are two lesser orders: the Tuscan (a plainer Doric), and the rich variant of Corinthian called the composite order. Of the three classical canonic orders, the Corinthian order has the narrowest columns, followed by the Ionic order, with the Doric order having the widest columns. The Ionic capital is characterized by the use of volutes. The Ionic columns normally stand on a base which separates the shaft of the column from the stylobate or platform while the cap is usually enriched with egg-and-dart. The ancient architect and architectural historian Vitruvius associates the Ionic with feminine proportions (the Doric representing the masculine). Description Capital The major features of the Ionic order are the volutes of its capital, which have been the subject of much theoretical and practical discourse, based on a brief and obscure passage i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |