|
Contingent Contagionism
Contingent contagionism was a concept in 19th-century medical writing and epidemiology before the germ theory, used as a qualified way of rejecting the application of the term " contagious disease" for a particular infection. For example, it could be stated that cholera, or typhus, was not contagious in a "healthy atmosphere", but might be contagious in an "impure atmosphere". Contingent contagionism covered a wide range of views between "contagionist", and "anti-contagionist" such as held by supporters of the miasma theory. Background A form of contingent contagionism was standard in medieval European medicine. Contagion was not conceptualised as restricted to physical contact. A corruption of air could be transmitted from person to person, at short range. Contagionists versus anticontagionists By the 1840s public health policy, at least in the United Kingdom, had become a battleground between contagionist and anti-contagionist parties. The former, in particular, supported qu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epidemiology
Epidemiology is the study and analysis of the distribution (who, when, and where), patterns and determinants of health and disease conditions in a defined population. It is a cornerstone of public health, and shapes policy decisions and evidence-based practice by identifying risk factors for disease and targets for preventive healthcare. Epidemiologists help with study design, collection, and statistical analysis of data, amend interpretation and dissemination of results (including peer review and occasional systematic review). Epidemiology has helped develop methodology used in clinical research, public health studies, and, to a lesser extent, basic research in the biological sciences. Major areas of epidemiological study include disease causation, transmission, outbreak investigation, disease surveillance, environmental epidemiology, forensic epidemiology, occupational epidemiology, screening, biomonitoring, and comparisons of treatment effects such as in clinical trials. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Florence Nightingale
Florence Nightingale (; 12 May 1820 – 13 August 1910) was an English Reform movement, social reformer, statistician and the founder of modern nursing. Nightingale came to prominence while serving as a manager and trainer of nurses during the Crimean War, in which she organised care for wounded soldiers at Constantinople. She significantly reduced death rates by improving hygiene and living standards. Nightingale gave nursing a favourable reputation and became an icon of Victorian culture, especially in the persona of "The Lady with the Lamp" making rounds of wounded soldiers at night. Recent commentators have asserted that Nightingale's Crimean War achievements were exaggerated by the media at the time, but critics agree on the importance of her later work in professionalising nursing roles for women. In 1860, she laid the foundation of professional nursing with the establishment of Florence Nightingale Faculty of Nursing and Midwifery, her nursing school at St Thomas' Hosp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fermentation
Fermentation is a metabolic process that produces chemical changes in organic substrates through the action of enzymes. In biochemistry, it is narrowly defined as the extraction of energy from carbohydrates in the absence of oxygen. In food production, it may more broadly refer to any process in which the activity of microorganisms brings about a desirable change to a foodstuff or beverage. The science of fermentation is known as zymology. In microorganisms, fermentation is the primary means of producing adenosine triphosphate (ATP) by the degradation of organic nutrients anaerobically. Humans have used fermentation to produce foodstuffs and beverages since the Neolithic age. For example, fermentation is used for preservation in a process that produces lactic acid found in such sour foods as pickled cucumbers, kombucha, kimchi, and yogurt, as well as for producing alcoholic beverages such as wine and beer. Fermentation also occurs within the gastrointestinal tracts of all a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Farr
William Farr CB (30 November 1807 – 14 April 1883) was a British epidemiologist, regarded as one of the founders of medical statistics. Early life William Farr was born in Kenley, Shropshire, to poor parents. He was effectively adopted by a local squire, Joseph Pryce, when Farr and his family moved to Dorrington. In 1826 he took a job as a dresser (surgeon's assistant) in the Salop Infirmary in Shrewsbury and served a nominal apprenticeship to an apothecary. Pryce died in November 1828, and left Farr £500 (), which allowed him to study medicine in France and Switzerland. In Paris he heard Pierre Charles Alexandre Louis lecture. Farr returned to England in 1831 and continued his studies at University College London, qualifying as a licentiate of the Society of Apothecaries in March 1832. He married in 1833 and started a medical practice in Fitzroy Square, London. He became involved in medical journalism and statistics. General Register Office In 1837 the General Regis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Justus Von Liebig
Justus Freiherr von Liebig (12 May 1803 – 20 April 1873) was a German scientist who made major contributions to agricultural and biological chemistry, and is considered one of the principal founders of organic chemistry. As a professor at the University of Giessen, he devised the modern laboratory-oriented teaching method, and for such innovations, he is regarded as one of the greatest chemistry teachers of all time. He has been described as the "father of the fertilizer industry" for his emphasis on nitrogen and trace minerals as essential plant nutrients, and his formulation of the law of the minimum, which described how plant growth relied on the scarcest nutrient resource, rather than the total amount of resources available. He also developed a manufacturing process for beef extracts, and with his consent a company, called Liebig Extract of Meat Company, was founded to exploit the concept; it later introduced the Oxo brand beef bouillon cube. He popularized an earlier ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aetiology
Etiology (pronounced ; alternatively: aetiology or ætiology) is the study of causation or origination. The word is derived from the Greek (''aitiología'') "giving a reason for" (, ''aitía'', "cause"); and ('' -logía''). More completely, etiology is the study of the causes, origins, or reasons behind the way that things are, or the way they function, or it can refer to the causes themselves. The word is commonly used in medicine (pertaining to causes of disease) and in philosophy, but also in physics, psychology, government, geography, spatial analysis, theology, and biology, in reference to the causes or origins of various phenomena. In the past, when many physical phenomena were not well understood or when histories were not recorded, myths often arose to provide etiologies. Thus, an etiological myth, or origin myth, is a myth that has arisen, been told over time or written to explain the origins of various social or natural phenomena. For example, Virgil's ''Aeneid'' is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Nathaniel Bancroft
Edward Nathaniel Bancroft, M.D. (1772–1842) was an English physician, botanist, and zoologist, known for his writings on yellow fever. Life Bancroft was the son of Edward Bancroft. He was born in London and received his schooling under Charles Burney and Samuel Parr. He entered St. John's College, Cambridge, and graduated bachelor of medicine in 1794. In 1795 he was appointed a physician to the armed forces. He served in the Windward Islands, in Portugal, in the Mediterranean, and with Abercromby's expedition to Egypt in 1801. On his return to England he proceeded to the degree of M.D. in 1804, and began to practise as a physician in London, retaining half-pay rank in the army. He joined the College of Physicians in 1805, became a fellow in 1806, was appointed to give the Gulstonian lectures the same year, and was made a censor in 1808, at the comparatively early ago of thirty-six; he was a pamphleteer against the pretensions of army surgeons. In 1808 he was appointed a physici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Pym
Sir William Pym, Royal Guelphic Order, KCH (1772 – 18 March 1861) was a British military surgeon. Biography The son of Joseph Pym of Pinley, near Henley-in-Arden, Warwickshire, and elder brother of Samuel Pym, Sir Samuel Pym, Pym was born in Edinburgh in 1772, and was educated at the University of Edinburgh. He entered the medical department of the army after a brief period of service in the Royal Navy, and was shortly afterwards ordered to the West Indies. In 1794 he was appointed to a flank battalion commanded by Eyre Coote (British Army officer), Sir Eyre Coote, in the expedition under Charles Grey, 1st Earl Grey, Sir Charles (later Earl) Grey which landed at Martinique in the early part of that year. He was present at the reduction of Martinique, Saint Lucia, and Guadeloupe. The force to which he was attached suffered great hardships, but remained healthy until the fall of Fort Matilda completed the surrender of Guadeloupe, when yellow fever broke out in the 35th (Royal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yellow Fever
Yellow fever is a viral disease of typically short duration. In most cases, symptoms include fever, chills, loss of appetite, nausea, muscle pains – particularly in the back – and headaches. Symptoms typically improve within five days. In about 15% of people, within a day of improving the fever comes back, abdominal pain occurs, and liver damage begins causing yellow skin. If this occurs, the risk of bleeding and kidney problems is increased. The disease is caused by the yellow fever virus and is spread by the bite of an infected mosquito. It infects humans, other primates, and several types of mosquitoes. In cities, it is spread primarily by ''Aedes aegypti'', a type of mosquito found throughout the tropics and subtropics. The virus is an RNA virus of the genus ''Flavivirus''. The disease may be difficult to tell apart from other illnesses, especially in the early stages. To confirm a suspected case, blood-sample testing with polymerase chain reaction is required. A saf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Health
Public health is "the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging life and promoting health through the organized efforts and informed choices of society, organizations, public and private, communities and individuals". Analyzing the determinants of health of a population and the threats it faces is the basis for public health. The ''public'' can be as small as a handful of people or as large as a village or an entire city; in the case of a pandemic it may encompass several continents. The concept of ''health'' takes into account physical, psychological, and social well-being.What is the WHO definition of health? from the Preamble to the Constitution of WHO as adopted by the International Health Conference, New York, 19 June - 22 July 1946; signed on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
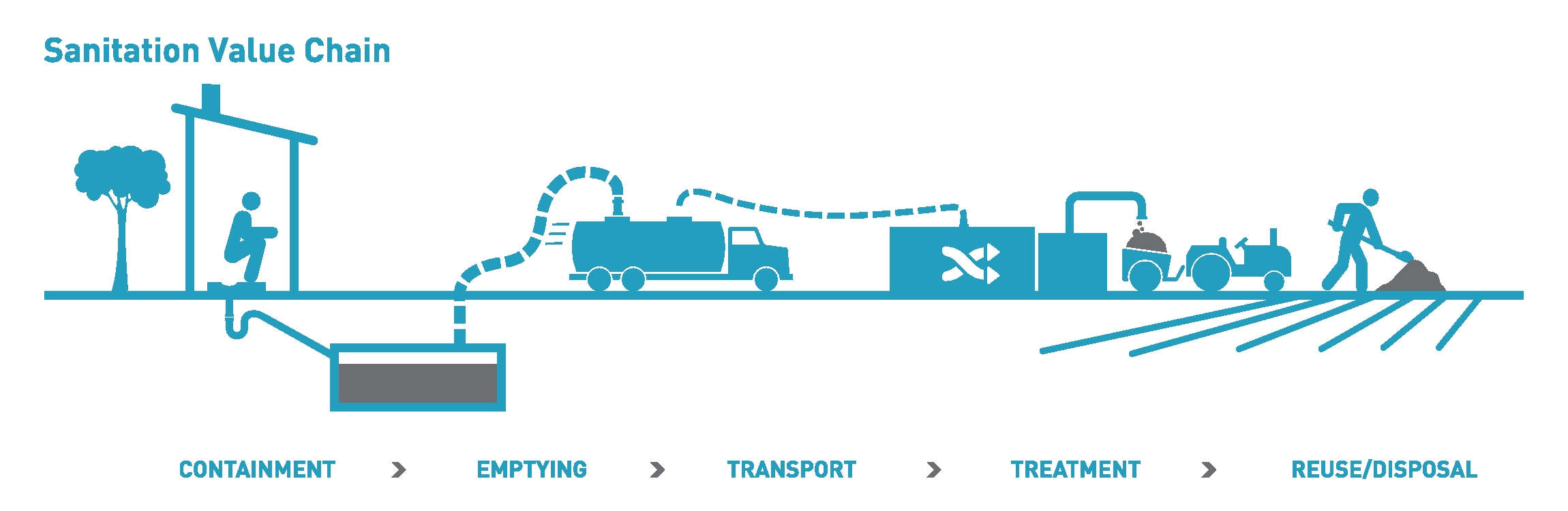
Sanitation
Sanitation refers to public health conditions related to clean drinking water and treatment and disposal of human excreta and sewage. Preventing human contact with feces is part of sanitation, as is hand washing with soap. Sanitation systems aim to protect human health by providing a clean environment that will stop the transmission of disease, especially through the fecal–oral route.SuSanA (2008)Towards more sustainable sanitation solutions Sustainable Sanitation Alliance (SuSanA) For example, diarrhea, a main cause of malnutrition and stunted growth in children, can be reduced through adequate sanitation. There are many other diseases which are easily transmitted in communities that have low levels of sanitation, such as ascariasis (a type of intestinal worm infection or helminthiasis), cholera, hepatitis, polio, schistosomiasis, and trachoma, to name just a few. A range of sanitation technologies and approaches exists. Some examples are community-led total sanitation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Filth
Filth or The Filth may refer to: Common uses * Dirt, unclean matter * Police officer, a pejorative in British slang Arts, entertainment, and media Films * ''Filth'' (film), a 2013 film based on the novel * ''Filth'', an alternative title for ''Sauna'', a 2008 horror film * '' Filth: The Mary Whitehouse Story'', a 2008 BBC docudrama Literature * ''Filth'' (novel), a 1998 novel by Irvine Welsh * ''FILTH'' by Jingan Young, the first English language play commissioned by the Hong Kong Arts Festival Music Albums * ''Filth'' (Andrew Dice Clay album), Andrew Dice Clay comedy album * ''Filth'' (Maranatha album), 2015 * ''Filth'' (Swans album), 1983 * ''Filth'' (Venetian Snares album), 2009 * ''The Filth'' (album), a 1987 album by Sonny Black's Blues Band, or the title song Other uses in music * Filth (Artist), an American alternative hyperpop artist * Filth (band), an American hardcore punk band * The Filth, or Philip Pilf and the Filth, purported working name of English band ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |