|
Contact Angle Goniometer
A goniometer is an instrument that either measures an angle or allows an object to be rotated to a precise angular position. The term goniometry derives from two Greek words, Wikt:γωνία, γωνία (''gōnía'') 'angle' and Wikt:μέτρον#Ancient Greek, μέτρον (''métron'') 'Measurement, measure'. The first known description of a goniometer, based on the astrolabe, was by Gemma Frisius in 1538. Applications Surveying Prior to the invention of the theodolite, the goniometer was used in surveying. The application of triangulation to geodesy was described in the second (1533) edition of ''Cosmograficus liber'' by Petri Appiani as a 16-page appendix by Frisius entitled ''Libellus de locorum describendorum ratione''. Communications The Bellini–Tosi direction finder was a type of radio direction finder that was widely used from World War I to World War II. It used the signals from two crossed antennas, or four individual antennas simulating two crossed ones, to r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goniometer IMG 4841
A goniometer is an instrument that either measures an angle or allows an object to be rotated to a precise angular position. The term goniometry derives from two Greek words, Wikt:γωνία, γωνία (''gōnía'') 'angle' and Wikt:μέτρον#Ancient Greek, μέτρον (''métron'') 'Measurement, measure'. The first known description of a goniometer, based on the astrolabe, was by Gemma Frisius in 1538. Applications Surveying Prior to the invention of the theodolite, the goniometer was used in surveying. The application of triangulation to geodesy was described in the second (1533) edition of ''Cosmograficus liber'' by Petri Appiani as a 16-page appendix by Frisius entitled ''Libellus de locorum describendorum ratione''. Communications The Bellini–Tosi direction finder was a type of radio direction finder that was widely used from World War I to World War II. It used the signals from two crossed antennas, or four individual antennas simulating two crossed ones, to r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray Scattering Techniques
X-ray scattering techniques are a family of non-destructive analytical techniques which reveal information about the crystal structure, chemical composition, and physical properties of materials and thin films. These techniques are based on observing the scattered intensity of an X-ray beam hitting a sample as a function of incident and scattered angle, polarization, and wavelength or energy. Note that X-ray diffraction is now often considered a sub-set of X-ray scattering, where the scattering is elastic and the scattering object is crystalline, so that the resulting pattern contains sharp spots analyzed by X-ray crystallography (as in the Figure). However, both scattering and diffraction are related general phenomena and the distinction has not always existed. Thus Guinier's classic text from 1963 is titled "X-ray diffraction in Crystals, Imperfect Crystals and Amorphous Bodies" so 'diffraction' was clearly not restricted to crystals at that time. Scattering techniques Ela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accuracy
Accuracy and precision are two measures of ''observational error''. ''Accuracy'' is how close a given set of measurements (observations or readings) are to their ''true value'', while ''precision'' is how close the measurements are to each other. In other words, ''precision'' is a description of ''random errors'', a measure of statistical variability. ''Accuracy'' has two definitions: # More commonly, it is a description of only '' systematic errors'', a measure of statistical bias of a given measure of central tendency; low accuracy causes a difference between a result and a true value; ISO calls this ''trueness''. # Alternatively, ISO defines accuracy as describing a combination of both types of observational error (random and systematic), so high accuracy requires both high precision and high trueness. In the first, more common definition of "accuracy" above, the concept is independent of "precision", so a particular set of data can be said to be accurate, precise, both, or n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibula
The fibula or calf bone is a leg bone on the lateral side of the tibia, to which it is connected above and below. It is the smaller of the two bones and, in proportion to its length, the most slender of all the long bones. Its upper extremity is small, placed toward the back of the head of the tibia, below the knee joint and excluded from the formation of this joint. Its lower extremity inclines a little forward, so as to be on a plane anterior to that of the upper end; it projects below the tibia and forms the lateral part of the ankle joint. Structure The bone has the following components: * Lateral malleolus * Interosseous membrane connecting the fibula to the tibia, forming a syndesmosis joint * The superior tibiofibular articulation is an arthrodial joint between the lateral condyle of the tibia and the head of the fibula. * The inferior tibiofibular articulation (tibiofibular syndesmosis) is formed by the rough, convex surface of the medial side of the lower end of the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malleolus
A malleolus is the bony prominence on each side of the human ankle. Each leg is supported by two bones, the tibia on the inner side (medial) of the leg and the fibula on the outer side (lateral) of the leg. The medial malleolus is the prominence on the inner side of the ankle, formed by the lower end of the tibia. The lateral malleolus is the prominence on the outer side of the ankle, formed by the lower end of the fibula. The word ''malleolus'' (), plural ''malleoli'' (), comes from Latin and means "small hammer". (It is cognate with ''mallet''.) Medial malleolus The medial malleolus is found at the foot end of the tibia. The medial surface of the lower extremity of tibia is prolonged downward to form a strong pyramidal process, flattened from without inward - the medial malleolus. * The ''medial surface'' of this process is convex and subcutaneous. * The ''lateral'' or ''articular surface'' is smooth and slightly concave, and articulates with the talus. * The ''anterior bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Femur
The femur (; ), or thigh bone, is the proximal bone of the hindlimb in tetrapod vertebrates. The head of the femur articulates with the acetabulum in the pelvic bone forming the hip joint, while the distal part of the femur articulates with the tibia (shinbone) and patella (kneecap), forming the knee joint. By most measures the two (left and right) femurs are the strongest bones of the body, and in humans, the largest and thickest. Structure The femur is the only bone in the upper leg. The two femurs converge medially toward the knees, where they articulate with the proximal ends of the tibiae. The angle of convergence of the femora is a major factor in determining the femoral-tibial angle. Human females have thicker pelvic bones, causing their femora to converge more than in males. In the condition ''genu valgum'' (knock knee) the femurs converge so much that the knees touch one another. The opposite extreme is ''genu varum'' (bow-leggedness). In the general populatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
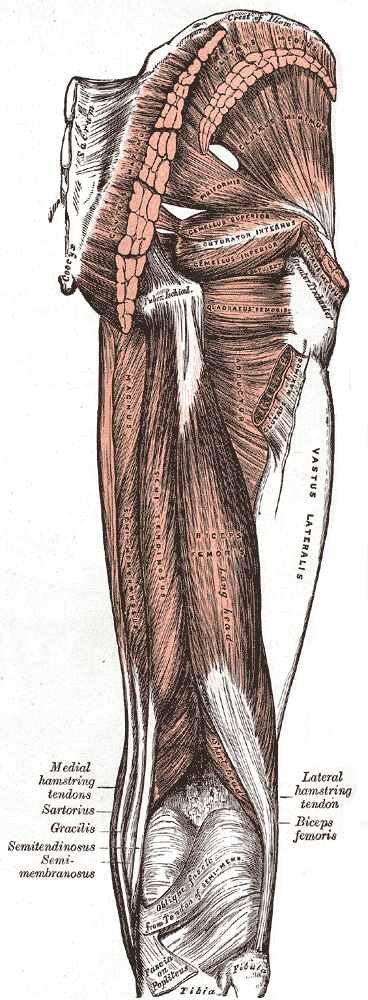
Greater Trochanter
The greater trochanter of the femur is a large, irregular, quadrilateral eminence and a part of the skeletal system. It is directed lateral and medially and slightly posterior. In the adult it is about 2–4 cm lower than the femoral head.Standring, Susan, editor. ''Gray’s Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice''. Forty-First edition, Elsevier Limited, 2016, p. 1327. Because the pelvic outlet in the female is larger than in the male, there is a greater distance between the greater trochanters in the female. It has two surfaces and four borders. It is a traction epiphysis. Surfaces The ''lateral surface'', quadrilateral in form, is broad, rough, convex, and marked by a diagonal impression, which extends from the postero-superior to the antero-inferior angle, and serves for the insertion of the tendon of the gluteus medius. Above the impression is a triangular surface, sometimes rough for part of the tendon of the same muscle, sometimes smooth for the interposi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epicondyle
An epicondyle () is a rounded eminence on a bone that lies upon a condyle ('' epi-'', "upon" + ''condyle'', from a root meaning "knuckle" or "rounded articular area"). There are various epicondyles in the human skeleton, each named by its anatomic Anatomy () is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having its ... site. They include the following: Skeletal system {{musculoskeletal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Range Of Motion
Range of motion (or ROM), is the linear or angular distance that a moving object may normally travel while properly attached to another. It is also called range of travel (or ROT), particularly when talking about mechanical devices and in mechanical engineering fields. For example, a sound volume control knob. As used in the biomedical field and by weightlifters, range of motion refers to the distance and direction a joint can move between the flexed position and the extended position. The act of attempting to increase this distance through therapeutic exercises (range of motion therapy—stretching from flexion to extension for physiological gain) is also sometimes called range of motion. Measuring range of motion Each specific joint has a normal range of motion that is expressed in degrees. The reference values for the normal ROM in individuals differ slightly depending on age and gender. For example, as an individual ages, they typically lose a small amount of ROM. Analog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waddell's Signs
Waddell's signs are a group of physical signs, first described in a 1980 article in '' Spine'', and named for the article's principal author, Professor Gordon Waddell (1943–2017), a Scottish Orthopedic Surgeon. Waddell's signs may indicate non-organic or psychological component to chronic low back pain. Historically they have also been used to detect malingering Malingering is the fabrication, feigning, or exaggeration of physical or psychological symptoms designed to achieve a desired outcome, such as relief from duty or work. Malingering is not a medical diagnosis, but may be recorded as a "focus of c ... in patients with back pain. While testing takes less than one minute, it has been described as time-consuming and alternatives have been proposed. Use of Waddell's signs Waddell, ''et al''. (1980) described five categories of signs: * Tenderness tests: superficial and diffuse tenderness and/or nonanatomic tenderness * Simulation tests: these are based on movements whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disability
Disability is the experience of any condition that makes it more difficult for a person to do certain activities or have equitable access within a given society. Disabilities may be Cognitive disability, cognitive, Developmental disability, developmental, Intellectual disability, intellectual, mental disorder#Disability, mental, physical disability, physical, Sense, sensory, or a combination of multiple factors. Disabilities can be present from birth or can be acquired during a person's lifetime. Historically, disabilities have only been recognized based on a narrow set of criteria—however, disabilities are not binary and can be present in unique characteristics depending on the individual. A disability may be readily visible, or Invisible disability, invisible in nature. The United Nations Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities defines disability as: Disabilities have been perceived differently throughout history, through a variety of different theoretical len ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luminous Intensity
In photometry, luminous intensity is a measure of the wavelength-weighted power emitted by a light source in a particular direction per unit solid angle, based on the luminosity function, a standardized model of the sensitivity of the human eye. The SI unit of luminous intensity is the candela (cd), an SI base unit. Measurement Photometry deals with the measurement of visible light as perceived by human eyes. The human eye can only see light in the visible spectrum and has different sensitivities to light of different wavelengths within the spectrum. When adapted for bright conditions (photopic vision), the eye is most sensitive to yellow-green light at 555 nm. Light with the same radiant intensity at other wavelengths has a lower luminous intensity. The curve which measures the response of the human eye to light is a defined standard, known as the luminosity function. This curve, denoted ''V''(λ) or \textstyle \overline(\lambda), is based on an average of widely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |