|
Conservative Two-phase Locking
In databases and transaction processing, two-phase locking (2PL) is a pessimistic concurrency control method that guarantees conflict-serializability. Philip A. Bernstein, Vassos Hadzilacos, Nathan Goodman (1987) ''Concurrency Control and Recovery in Database Systems'' Addison Wesley Publishing Company, Gerhard Weikum, Gottfried Vossen (2001) ''Transactional Information Systems'' Elsevier, It is also the name of the resulting set of database transaction schedules (histories). The protocol uses locks, applied by a transaction to data, which may block (interpreted as signals to stop) other transactions from accessing the same data during the transaction's life. By the 2PL protocol, locks are applied and removed in two phases: # Expanding phase: locks are acquired and no locks are released. # Shrinking phase: locks are released and no locks are acquired. Two types of locks are used by the basic protocol: ''Shared'' and ''Exclusive'' locks. Refinements of the basic protocol may use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Concurrency Control
In information technology and computer science, especially in the fields of computer programming, operating systems, multiprocessors, and databases, concurrency control ensures that correct results for concurrent operations are generated, while getting those results as quickly as possible. Computer systems, both software and hardware, consist of modules, or components. Each component is designed to operate correctly, i.e., to obey or to meet certain consistency rules. When components that operate concurrently interact by messaging or by sharing accessed data (in memory or storage), a certain component's consistency may be violated by another component. The general area of concurrency control provides rules, methods, design methodologies, and theories to maintain the consistency of components operating concurrently while interacting, and thus the consistency and correctness of the whole system. Introducing concurrency control into a system means applying operation constraints ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lock (computer Science)
In computer science, a lock or mutex (from mutual exclusion) is a synchronization primitive that prevents state from being modified or accessed by multiple threads of execution at once. Locks enforce mutual exclusion concurrency control policies, and with a variety of possible methods there exist multiple unique implementations for different applications. Types Generally, locks are ''advisory locks'', where each thread cooperates by acquiring the lock before accessing the corresponding data. Some systems also implement ''mandatory locks'', where attempting unauthorized access to a locked resource will force an exception in the entity attempting to make the access. The simplest type of lock is a binary semaphore. It provides exclusive access to the locked data. Other schemes also provide shared access for reading data. Other widely implemented access modes are exclusive, intend-to-exclude and intend-to-upgrade. Another way to classify locks is by what happens when the lock st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Transaction Processing
In computer science, transaction processing is information processing that is divided into individual, indivisible operations called ''transactions''. Each transaction must succeed or fail as a complete unit; it can never be only partially complete. For example, when you purchase a book from an online bookstore, you exchange money (in the form of credit) for a book. If your credit is good, a series of related operations ensures that you get the book and the bookstore gets your money. However, if a single operation in the series fails during the exchange, the entire exchange fails. You do not get the book and the bookstore does not get your money. The technology responsible for making the exchange balanced and predictable is called ''transaction processing''. Transactions ensure that data-oriented resources are not permanently updated unless all operations within the transactional unit complete successfully. By combining a set of related operations into a unit that either com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Databases
In computing, a database is an organized collection of data or a type of data store based on the use of a database management system (DBMS), the software that interacts with end users, applications, and the database itself to capture and analyze the data. The DBMS additionally encompasses the core facilities provided to administer the database. The sum total of the database, the DBMS and the associated applications can be referred to as a database system. Often the term "database" is also used loosely to refer to any of the DBMS, the database system or an application associated with the database. Before digital storage and retrieval of data have become widespread, index cards were used for data storage in a wide range of applications and environments: in the home to record and store recipes, shopping lists, contact information and other organizational data; in business to record presentation notes, project research and notes, and contact information; in schools as flash card ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Deadlock (computer Science)
In concurrent computing, deadlock is any situation in which no member of some group of entities can proceed because each waits for another member, including itself, to take action, such as sending a message or, more commonly, releasing a lock. Deadlocks are a common problem in multiprocessing systems, parallel computing, and distributed systems, because in these contexts systems often use software or hardware locks to arbitrate shared resources and implement process synchronization. In an operating system, a deadlock occurs when a process or thread enters a waiting state because a requested system resource is held by another waiting process, which in turn is waiting for another resource held by another waiting process. If a process remains indefinitely unable to change its state because resources requested by it are being used by another process that itself is waiting, then the system is said to be in a deadlock. In a communications system, deadlocks occur mainly due to loss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
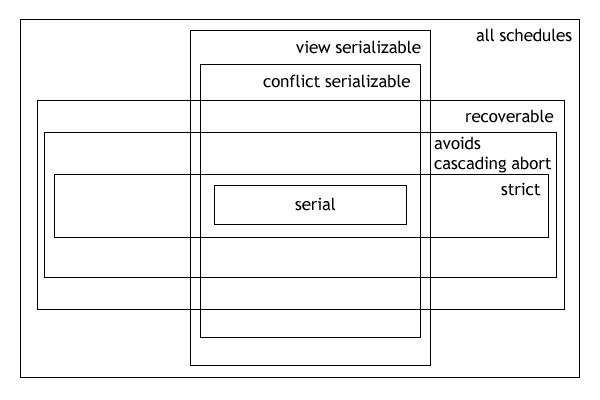
Serializability
In the fields of databases and transaction processing (transaction management), a schedule (or history) of a system is an abstract model to describe the order of executions in a set of transactions running in the system. Often it is a ''list'' of operations (actions) ordered by time, performed by a set of transactions that are executed together in the system. If the order in time between certain operations is not determined by the system, then a ''partial order'' is used. Examples of such operations are requesting a read operation, reading, writing, aborting, committing, requesting a lock, locking, etc. Often, only a subset of the transaction operation types are included in a schedule. Schedules are fundamental concepts in database concurrency control theory. In practice, most general purpose database systems employ conflict-serializable and strict recoverable schedules. Notation Grid notation: * Columns: The different transactions in the schedule. * Rows: The time order of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
B-tree
In computer science, a B-tree is a self-balancing tree data structure that maintains sorted data and allows searches, sequential access, insertions, and deletions in logarithmic time. The B-tree generalizes the binary search tree, allowing for nodes with more than two children. Unlike other self-balancing binary search trees, the B-tree is well suited for storage systems that read and write relatively large blocks of data, such as databases and file systems. History While working at Boeing Research Labs, Rudolf Bayer and Edward M. McCreight invented B-trees to efficiently manage index pages for large random-access files. The basic assumption was that indices would be so voluminous that only small chunks of the tree could fit in the main memory. Bayer and McCreight's paper ''Organization and maintenance of large ordered indices'' was first circulated in July 1970 and later published in '' Acta Informatica''. Bayer and McCreight never explained what, if anything, the ''B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Resource Contention
In computer science, resource contention is a conflict over access to a shared resource such as random access memory, disk storage, cache memory, internal buses or external network devices. A resource experiencing ongoing contention can be described as oversubscribed. Resolving resource contention problems is one of the basic functions of operating systems. Various low-level mechanisms can be used to aid this, including locks, semaphores, mutexes and queues. The other techniques that can be applied by the operating systems include intelligent scheduling, application mapping decisions, and page coloring. Access to resources is also sometimes regulated by queuing; in the case of computing time on a CPU the controlling algorithm of the task queue is called a scheduler. Failure to properly resolve resource contention problems may result in a number of problems, including deadlock, livelock, and thrashing. Resource contention results when multiple processes attempt to use th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dirty Read
Dirt is any matter considered unclean, especially when in contact with a person's clothes, skin, or possessions. In such cases, they are said to become dirty. Common types of dirt include: * Debris: scattered pieces of waste or remains * Dust: a general powder of organic or mineral matter * Filth: foul matter such as excrement * Grime: a black, ingrained dust such as soot * Soil: the mix of clay, sand, and humus which lies on top of bedrock. The term 'soil' may be used to refer to unwanted substances or dirt that are deposited onto surfaces such as clothing. Etymology The word ''dirt'' first appears in Middle English and was probably borrowed from the Old Norse , meaning . Exhibitions and studies A season of artworks and exhibits on the theme of dirt was sponsored by the Wellcome Trust in 2011. The centrepiece was an exhibition at the Wellcome Collection showing pictures and histories of notable dirt such as the great dust heaps at Euston and King's Cross in the 19t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Phantom Read
In database systems, isolation is one of the ACID ('' Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability'') transaction properties. It determines how transaction integrity is visible to other users and systems. A lower isolation level increases the ability of many users to access the same data at the same time, but also increases the number of concurrency effects (such as dirty reads or lost updates) users might encounter. Conversely, a higher isolation level reduces the types of concurrency effects that users may encounter, but requires more system resources and increases the chances that one transaction will block another. DBMS concurrency control Concurrency control comprises the underlying mechanisms in a DBMS which handle isolation and guarantee related correctness. It is heavily used by the database and storage engines both to guarantee the correct execution of concurrent transactions, and (via different mechanisms) the correctness of other DBMS processes. The transaction-re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Serializability
In the fields of databases and transaction processing (transaction management), a schedule (or history) of a system is an abstract model to describe the order of executions in a set of transactions running in the system. Often it is a ''list'' of operations (actions) ordered by time, performed by a set of transactions that are executed together in the system. If the order in time between certain operations is not determined by the system, then a ''partial order'' is used. Examples of such operations are requesting a read operation, reading, writing, aborting, committing, requesting a lock, locking, etc. Often, only a subset of the transaction operation types are included in a schedule. Schedules are fundamental concepts in database concurrency control theory. In practice, most general purpose database systems employ conflict-serializable and strict recoverable schedules. Notation Grid notation: * Columns: The different transactions in the schedule. * Rows: The time order of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Database
In computing, a database is an organized collection of data or a type of data store based on the use of a database management system (DBMS), the software that interacts with end users, applications, and the database itself to capture and analyze the data. The DBMS additionally encompasses the core facilities provided to administer the database. The sum total of the database, the DBMS and the associated applications can be referred to as a database system. Often the term "database" is also used loosely to refer to any of the DBMS, the database system or an application associated with the database. Before digital storage and retrieval of data have become widespread, index cards were used for data storage in a wide range of applications and environments: in the home to record and store recipes, shopping lists, contact information and other organizational data; in business to record presentation notes, project research and notes, and contact information; in schools as flash c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |