|
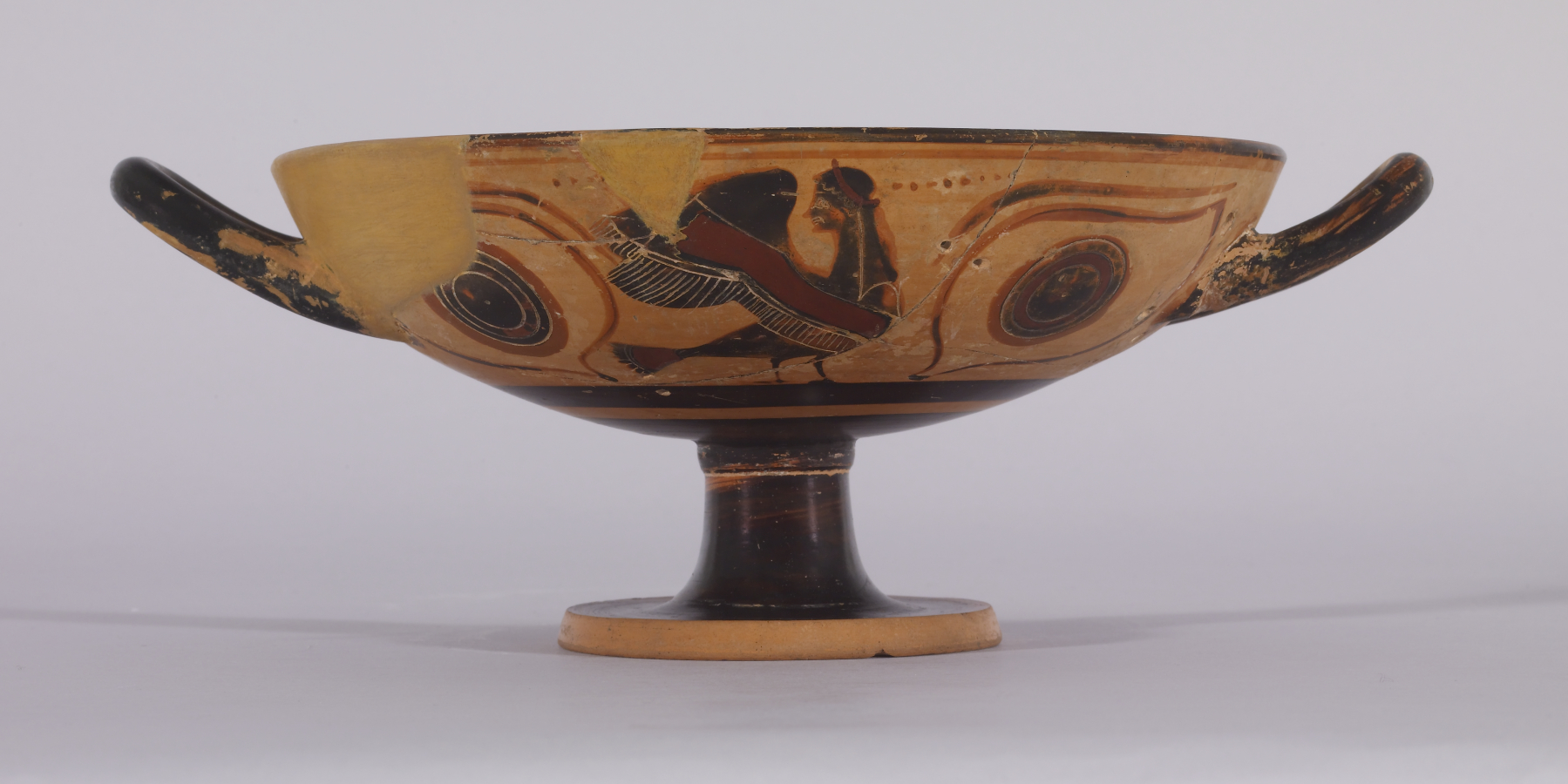
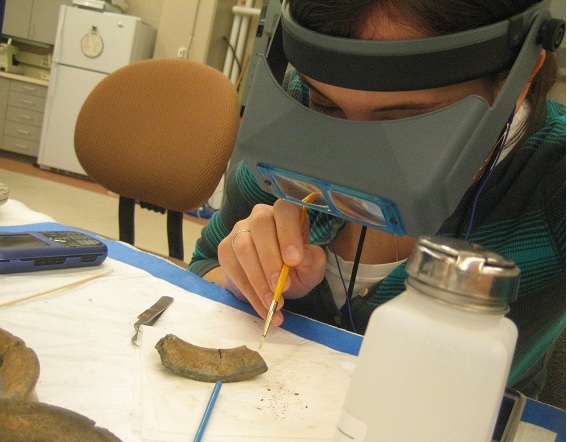
Conservation And Restoration Of Ancient Greek Pottery
The conservation and restoration of ancient Greek pottery is a sub-section of the broader topic of conservation and restoration of ceramic objects. Ancient Greek pottery is one of the most commonly found types of artifacts from the ancient Greek world. The information learned from vase paintings forms the foundation of modern knowledge of ancient Greek art and culture. Most ancient Greek pottery is terracotta, a type of earthenware ceramic, dating from the 11th century BCE through the 1st century CE. The objects are usually excavated from archaeological sites in broken pieces, or shards, and then reassembled. Some have been discovered intact in tombs. Professional conservator-restorers, often in collaboration with curators and conservation scientists, undertake the conservation-restoration of ancient Greek pottery. History of conservation and restoration approaches Ancient Ancient repairs were made to damaged pottery using metal pins or staples, which could be made of copper, le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conservation And Restoration Of Ceramic Objects
Conservation and restoration of ceramic objects is a process dedicated to the preservation and protection of objects of historical and personal value made from ceramic. Typically, this activity of conservation-restoration is undertaken by a conservator-restorer, especially when dealing with an object of cultural heritage. Ceramics are created from a production of coatings of inorganic, nonmetallic materials using heating and cooling to create a glaze. These coatings are often permanent and sustainable for utilitarian and decorative purposes. . Ctioa.org. Retrieved on 2012-03-28. The cleaning, handling, storage, and in general treatment of ceramics is consistent with that of beca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaolinite
Kaolinite ( ) is a clay mineral, with the chemical composition Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4. It is an important industrial mineral. It is a layered silicate mineral, with one tetrahedral sheet of silica () linked through oxygen atoms to one octahedral sheet of alumina () octahedra. Rocks that are rich in kaolinite are known as kaolin () or china clay. Kaolin is occasionally referred to by the antiquated term lithomarge, from the Ancient Greek ''litho-'' and Latin ''marga'', meaning 'stone of marl'. Presently the name lithomarge can refer to a compacted, massive form of kaolin. The name ''kaolin'' is derived from Gaoling (), a Chinese village near Jingdezhen in southeastern China's Jiangxi Province. The name entered English in 1727 from the French version of the word: , following François Xavier d'Entrecolles's reports on the making of Jingdezhen porcelain. Kaolinite has a low shrink–swell capacity and a low cation-exchange capacity (1–15 meq/100 g). It is a soft, earthy, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pottery
Pottery is the process and the products of forming vessels and other objects with clay and other ceramic materials, which are fired at high temperatures to give them a hard and durable form. Major types include earthenware, stoneware and porcelain. The place where such wares are made by a ''potter'' is also called a ''pottery'' (plural "potteries"). The definition of ''pottery'', used by the ASTM International, is "all fired ceramic wares that contain clay when formed, except technical, structural, and refractory products". In art history and archaeology, especially of ancient and prehistoric periods, "pottery" often means vessels only, and sculpted figurines of the same material are called "terracottas". Pottery is one of the oldest human inventions, originating before the Neolithic period, with ceramic objects like the Gravettian culture Venus of Dolní Věstonice figurine discovered in the Czech Republic dating back to 29,000–25,000 BC, and pottery vessels that were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disjecta Membra
, also written , is Latin for "scattered fragments" (also scattered limbs, members, or remains) and is used to refer to surviving fragments of ancient poetry, manuscripts, and other literary or cultural objects, including even fragments of ancient pottery. It is derived from , a phrase used by Horace, a Roman poet. Ancient and medieval poetry, literature, and manuscripts Fragments of ancient writing, especially ancient Latin poetry found in other works, are commonly referred to as ''disjecta membra''. The terms ''disiecta membra'' and ''disjecta membra'' are paraphrased from the Roman lyric poet Horace (65 BC – 8 BC), who wrote of in his ''Satires'', 1.4.62, referring to the "limbs of a dismembered poet". In full, the term originally appeared as , in reference to the earlier Roman poet Ennius. Although Horace's intended meaning remains the subject of speculation and debate, the passage is often taken to imply that if a line from poetry were torn apart and rearranged, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Italian Ancient Greek Pottery
South Italian is a designation for ancient Greek pottery fabricated in Magna Graecia largely during the 4th century BC. The fact that Greek Southern Italy produced its own red-figure pottery Red-figure vase painting is one of the most important styles of figural Greek vase painting. It developed in Athens around 520 BCE and remained in use until the late 3rd century BCE. It replaced the previously dominant style of black-figure vas ... as early as the end of the 5th century BC was first established by Adolf Furtwaengler in 1893 (A.D. Trendall). Prior to that this pottery had been first designated as "Etruscan" and then as "Attic." Archaeological proof that this pottery was actually being produced in South Italy first came in 1973 when a workshop and kilns with misfirings and broken wares was first excavated at Metaponto, proving that the Amykos Painter was located there rather than in Athens (A.D. Trendall, p. 17). Overview The interchange of iconography, techniques, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attic Black-Figure Volute-Krater, Known As The Francois Vase, Ca
An attic (sometimes referred to as a ''loft'') is a space found directly below the pitched roof of a house or other building; an attic may also be called a ''sky parlor'' or a garret. Because attics fill the space between the ceiling of the top floor of a building and the slanted roof, they are known for being awkwardly shaped spaces with exposed rafters and difficult-to-reach corners. While some attics are converted into bedrooms, home offices, or attic apartments complete with windows and staircases, most remain difficult to access (and are usually entered using a loft hatch and ladder). Attics help control temperatures in a house by providing a large mass of slowly moving air, and are often used for storage. The hot air rising from the lower floors of a building is often retained in attics, further compounding their reputation as inhospitable environments. However, in recent years attics have been insulated to help decrease heating costs, since, on average, uninsulated at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Affecter
__NOTOC__ The Affecter (or ''The Affected Painter'') was an Attic black-figure vase painter, active in Athens around 550 to 530 BCE.Boardman dates his activity to 540–520 BC. His conventional name (his real name being unknown today, as none of his works are signed) is derived from his artificial ''affected'' style of figural painting, on the basis of which about 135 vases can be ascribed to him. He was active as both potter and painter. His speciality was amphorae. He mainly painted ovoid amphorae and belly amphorae, of the then newly introduced type ''C''. Most of the 132 vases associated with him were found in Etruscan tombs and as such are usually well preserved. He was interested particularly in the decorative effect of his images, composed of stylised figures in long cloaks or with affected gestures; narrative content was secondary. In his tendency to formulaic figures and multiple details, the Affecter is a successor to the Amasis Painter, from whom he may have learnt h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desalination
Desalination is a process that takes away mineral components from saline water. More generally, desalination refers to the removal of salts and minerals from a target substance, as in Soil salinity control, soil desalination, which is an issue for agriculture. Saline water, Saltwater (especially Seawater, sea water) is desalinated to produce water suitable for Drinking water, human consumption or irrigation. The by-product of the desalination process is brine. Desalination is used on many seagoing ships and submarines. Most of the modern interest in desalination is focused on cost-effective provision of fresh water for human use. Along with recycled wastewater, it is one of the few rainfall-independent water resources. Due to its energy consumption, desalinating sea water is generally more costly than fresh water from surface water or groundwater, Reclaimed water, water recycling and water conservation. However, these alternatives are not always available and depletion of reserve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek Pottery From Cyclades, Shard With Painting, 7th C BC, AM Paros, 143923
Ancient history is a time period from the beginning of writing and recorded human history to as far as late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the Sumerian cuneiform script. Ancient history covers all continents inhabited by humans in the period 3000 BCAD 500. The three-age system periodizes ancient history into the Stone Age, the Bronze Age, and the Iron Age, with recorded history generally considered to begin with the Bronze Age. The start and end of the three ages varies between world regions. In many regions the Bronze Age is generally considered to begin a few centuries prior to 3000 BC, while the end of the Iron Age varies from the early first millennium BC in some regions to the late first millennium AD in others. During the time period of ancient history, the world population was already exponentially increasing due to the Neolithic Revolution, which was in full progress. While in 10,000 BC, the world population stood at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |