|
Consciousness And The Brain
''Consciousness and the Brain: Deciphering How the Brain Codes Our Thoughts'' is a 2014 book by Stanislas Dehaene. It summarizes research on the neuroscience of consciousness, particularly from recent decades. Book outline Introduction: The Stuff of Thought Dehaene reviews historical intuitions that consciousness must be separate from matter. He explains how consciousness was not even mentioned in neuroscientific circles until the late 1980s, when a revolution in consciousness research began. Dehaene believes that "access consciousness" (being aware of and able to report on information) is the right definition to start with for scientific investigation. While some philosophers insist that access consciousness differs from "phenomenal consciousness" (e.g., the way qualia feel), Dehaene considers the access/phenomenal distinction "highly misleading" and feels it "leads down a slippery slope to dualism" (p. 10). Ch. 1: Consciousness Enters the Lab Dehaene distinguishes conscio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanislas Dehaene
Stanislas Dehaene (born May 12, 1965) is a French author and cognitive neuroscientist whose research centers on a number of topics, including numerical cognition, the neural basis of reading and the neural correlates of consciousness. As of 2017, he is a professor at the Collège de France and, since 1989, the director of INSERM Unit 562, "Cognitive Neuroimaging". Dehaene was one of ten people to be awarded the James S. McDonnell Foundation Centennial Fellowship in 1999 for his work on the "Cognitive Neuroscience of Numeracy". In 2003, together with Denis Le Bihan, Dehaene was awarded the Grand Prix scientifique de la Fondation Louis D. from the Institut de France. He was elected to the American Philosophical Society in 2010. In 2014, together with Giacomo Rizzolatti and Trevor Robbins, he was awarded the Brain Prize. Dehaene is an associate editor of the journal ''Cognition'', and a member of the editorial board of several other journals, including ''NeuroImage'', ''PLoS Bio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemispatial Neglect
Hemispatial neglect is a neuropsychological condition in which, after damage to one hemisphere of the brain (e.g. after a stroke), a deficit in attention and awareness towards the side of space opposite brain damage (contralesional space) is observed. It is defined by the inability of a person to process and perceive stimuli towards the contralesional side of the body or environment. Hemispatial neglect is very commonly contralateral to the damaged hemisphere, but instances of ipsilesional neglect (on the same side as the lesion) have been reported. Presentation Hemispatial neglect results most commonly from strokes and brain unilateral injury to the right cerebral hemisphere, with rates in the critical stage of up to 80% causing visual neglect of the left-hand side of space. Neglect is often produced by massive strokes in the middle cerebral artery region and is variegated, so that most sufferers do not exhibit all of the syndrome's traits. Right-sided spatial neglect is rare bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Crick
Francis Harry Compton Crick (8 June 1916 – 28 July 2004) was an English molecular biologist, biophysicist, and neuroscientist. He, James Watson, Rosalind Franklin, and Maurice Wilkins played crucial roles in deciphering the helical structure of the DNA molecule. Crick and Watson's paper in ''Nature'' in 1953 laid the groundwork for understanding DNA structure and functions. Together with Maurice Wilkins, they were jointly awarded the 1962 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine "for their discoveries concerning the molecular structure of nucleic acids and its significance for information transfer in living material". Crick was an important theoretical molecular biologist and played a crucial role in research related to revealing the helical structure of DNA. He is widely known for the use of the term " central dogma" to summarise the idea that once information is transferred from nucleic acids (DNA or RNA) to proteins, it cannot flow back to nucleic acids. In other words ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma Waves
A gamma wave or gamma Rhythm is a pattern of neural oscillation in humans with a frequency between 25 and 140 Hz, the 40- Hz point being of particular interest. Gamma rhythms are correlated with large scale brain network activity and cognitive phenomena such as working memory, attention, and perceptual grouping, and can be increased in amplitude via meditation or neurostimulation. Altered gamma activity has been observed in many mood and cognitive disorders such as Alzheimer's disease, epilepsy, and schizophrenia. Discovery Gamma waves can be detected by electroencephalography or magnetoencephalography. One of the earliest reports of gamma wave activity was recorded from the visual cortex of awake monkeys. Subsequently, significant research activity has concentrated on gamma activity in visual cortex. Gamma activity has also been detected and studied across premotor, parietal, temporal, and frontal cortical regions Gamma waves constitute a common class of oscillatory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P300 (neuroscience)
The P300 (P3) wave is an event-related potential (ERP) component elicited in the process of decision making. It is considered to be an endogenous potential, as its occurrence links not to the physical attributes of a stimulus, but to a person's reaction to it. More specifically, the P300 is thought to reflect processes involved in stimulus evaluation or categorization. It is usually elicited using the oddball paradigm, in which low-probability target items are mixed with high-probability non-target (or "standard") items. When recorded by electroencephalography (EEG), it surfaces as a positive deflection in voltage with a latency (delay between stimulus and response) of roughly 250 to 500 ms. In the scientific literature a differentiation is often made in the P3, which is divided according to time: Early P3 window (300-400 ms) and Late P3 window (380-440 ms). The signal is typically measured most strongly by the electrodes covering the parietal lobe. The presence, magnitude, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is intelligence—perceiving, synthesizing, and inferring information—demonstrated by machines, as opposed to intelligence displayed by animals and humans. Example tasks in which this is done include speech recognition, computer vision, translation between (natural) languages, as well as other mappings of inputs. The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' of Oxford University Press defines artificial intelligence as: the theory and development of computer systems able to perform tasks that normally require human intelligence, such as visual perception, speech recognition, decision-making, and translation between languages. AI applications include advanced web search engines (e.g., Google), recommendation systems (used by YouTube, Amazon and Netflix), understanding human speech (such as Siri and Alexa), self-driving cars (e.g., Tesla), automated decision-making and competing at the highest level in strategic game systems (such as chess and Go). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Production System (computer Science)
A "production system " (or "production rule system") is a computer program typically used to provide some form of artificial intelligence, which consists primarily of a set of rules about behavior but it also includes the mechanism necessary to follow those rules as the system responds to states of the world. Those rules, termed productions, are a basic representation found useful in automated planning, expert systems and action selection. Productions consist of two parts: a sensory precondition (or "IF" statement) and an action (or "THEN"). If a production's precondition matches the current state of the world, then the production is said to be ''triggered''. If a production's action is executed, it is said to have ''fired''. A production system also contains a database, sometimes called working memory, which maintains data about current state or knowledge, and a rule interpreter. The rule interpreter must provide a mechanism for prioritizing productions when more than one is tri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daniel Dennett
Daniel Clement Dennett III (born March 28, 1942) is an American philosopher, writer, and cognitive scientist whose research centers on the philosophy of mind, philosophy of science, and philosophy of biology, particularly as those fields relate to evolutionary biology and cognitive science. , he is the co-director of the Center for Cognitive Studies and the Austin B. Fletcher Professor of Philosophy at Tufts University in Massachusetts. Dennett is a member of the editorial board for ''The Rutherford Journal'' and a co-founder of The Clergy Project. A vocal atheist and secularist, Dennett is referred to as one of the "Four Horsemen of New Atheism", along with Richard Dawkins, Sam Harris, and the late Christopher Hitchens. Early life, education, and career Daniel Clement Dennett III was born on March 28, 1942, in Boston, Massachusetts, the son of Ruth Marjorie (née Leck; 1903–1971) and Daniel Clement Dennett Jr. (1910–1947). Dennett spent part of his childhood in Le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
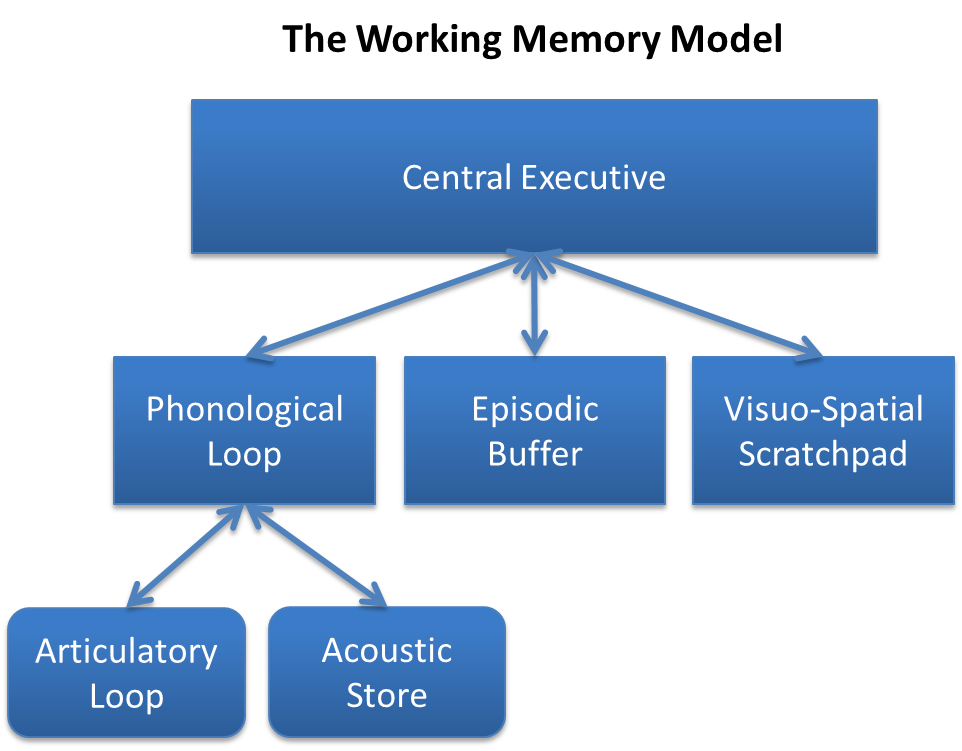
Working Memory
Working memory is a cognitive system with a limited capacity that can hold information temporarily. It is important for reasoning and the guidance of decision-making and behavior. Working memory is often used synonymously with short-term memory, but some theorists consider the two forms of memory distinct, assuming that working memory allows for the manipulation of stored information, whereas short-term memory only refers to the short-term storage of information. Working memory is a theoretical concept central to cognitive psychology, neuropsychology, and neuroscience. History The term "working memory" was coined by Miller, Galanter, and Pribram, and was used in the 1960s in the context of theories that likened the mind to a computer. In 1968, Atkinson and Shiffrin used the term to describe their "short-term store". What we now call working memory was formerly referred to variously as a "short-term store" or short-term memory, primary memory, immediate memory, operant memo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
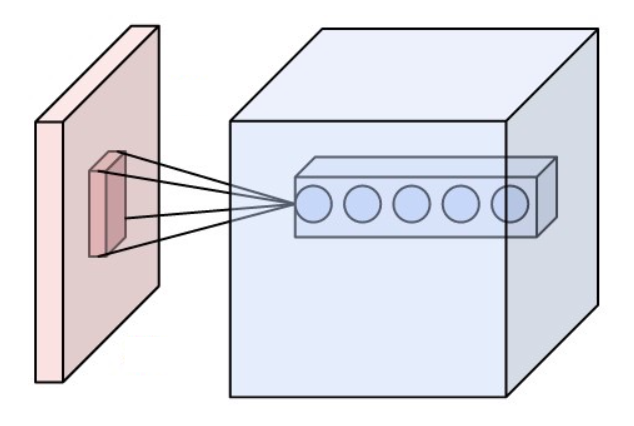
Receptive Field
The receptive field, or sensory space, is a delimited medium where some physiological stimuli can evoke a sensory neuronal response in specific organisms. Complexity of the receptive field ranges from the unidimensional chemical structure of odorants to the multidimensional spacetime of human visual field, through the bidimensional skin surface, being a receptive field for touch perception. Receptive fields can positively or negatively alter the membrane potential with or without affecting the rate of action potentials. A sensory space can be dependent of an animal's location. For a particular sound wave traveling in an appropriate transmission medium, by means of sound localization, an auditory space would amount to a reference system that continuously shifts as the animal moves (taking into consideration the space inside the ears as well). Conversely, receptive fields can be largely independent of the animal's location, as in the case of place cells. A sensory space can also m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bayesian Approaches To Brain Function
Bayesian approaches to brain function investigate the capacity of the nervous system to operate in situations of uncertainty in a fashion that is close to the optimal prescribed by Bayesian statistics. This term is used in behavioural sciences and neuroscience and studies associated with this term often strive to explain the brain's cognitive abilities based on statistical principles. It is frequently assumed that the nervous system maintains internal probabilistic models that are updated by neural processing of sensory information using methods approximating those of Bayesian probability. Origins This field of study has its historical roots in numerous disciplines including machine learning, experimental psychology and Bayesian statistics. As early as the 1860s, with the work of Hermann Helmholtz in experimental psychology the brain's ability to extract perceptual information from sensory data was modeled in terms of probabilistic estimation. The basic idea is that the nervous sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N400 (neuroscience)
The N400 is a component of time-locked EEG signals known as event-related potentials (ERP). It is a negative-going deflection that peaks around 400 milliseconds post-stimulus onset, although it can extend from 250-500 ms, and is typically maximal over centro-parietal electrode sites. The N400 is part of the normal brain response to words and other meaningful (or potentially meaningful) stimuli, including visual and auditory words, sign language signs, pictures, faces, environmental sounds, and smells. History The N400 was first discovered by Marta Kutas and Steven Hillyard in 1980. They conducted the first experiment looking at the response to unexpected words in read sentences, expecting to elicit a P300 component. The P300 had previously been shown to be elicited by unexpected stimuli. Kutas and Hillyard therefore used sentences with anomalous endings (i.e.''I take coffee with cream and dog''), expecting to see a P300 to the unexpected sentence-final words. However, instead of el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |