|
Conrad Of Italy
Conrad II of Italy, also known as Conrad (III) (12 February 1074 – 27 July 1101), was the Duke of Lower Lorraine (1076–1087), King of Germany (1087–1098) and King of Italy (1093–1098). He was the second son of Holy Roman Emperor Henry IV and Bertha of Savoy, and their eldest son to reach adulthood, his older brother Henry having been born and died in the same month of August 1071. Conrad's rule in Lorraine and Germany was nominal. He spent most of his life in Italy and there he was king in fact as well as in name. Childhood Conrad was born on 12 February 1074 at Hersfeld Abbey while his father was fighting against the Saxon Rebellion. He was baptised in the abbey three days later. After Henry's victory against the Saxons, he arranged for an assembly at Goslar on Christmas Day 1075 to swear an oath recognising Conrad as his successor. After the death of Duke Godfrey IV of Lower Lorraine on 22 February 1076, Henry refused to appoint the late duke's own choice of succe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duke Of Lower Lorraine
The rulers of Lorraine have held different posts under different governments over different regions, since its creation as the kingdom of Lotharingia by the Treaty of Prüm, in 855. The first rulers of the newly established region were kings of the Franks. The Latin construction "Lotharingia" evolved over time into "Lorraine" in French, "Lotharingen" in Dutch and "Lothringen" in German. After the Carolingian kingdom was absorbed into its neighbouring realms in the late ninth century, dukes were appointed over the territory. In the mid-tenth century, the duchy was divided into Lower Lorraine and Upper Lorraine, the first evolving into the historical Low Countries, the second became known as the Duchy of Lorraine and existed well into the modern era. Kings of Lotharingia * Lothair II (855–869) Charles the Bald claimed Lotharingia on Lothair's death and was crowned king in Metz, but his brother Louis the German opposed his claim and in 870 the Treaty of Mersen divided Lotharingia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
March Of Tuscany
The March of Tuscany ( it, Marca di Tuscia; ) was a march of the Kingdom of Italy and the Holy Roman Empire during the Middle Ages. Located in northwestern central Italy, it bordered the Papal States to the south, the Ligurian Sea to the west and Lombardy to the north. It comprised a collection of counties, largely in the valley of the Arno River, originally centered on Lucca. History The march was a Carolingian creation, a successor of the Lombard duchy of Tuscia. After the fall of the Western Roman Empire, Tuscia from 568 had been part of the Italian Kingdom of the Lombards (''Langobardia Major'') until, in 754, the Frankish kings intervened in the conflict with Pope Stephen II. By the Donation of Pepin, the southern part of Tuscia around Viterbo became part of the newly established Papal States, while the northern part (or Lombard Tuscany) developed into the Imperial March of Tuscany after Charlemagne had finally conquered the Lombard kingdom in 773/74. Lombardy proper becam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
March Of Antwerp
The Margraviate of Antwerp (or Mark of Antwerp) consisted since the eleventh century of the area around the cities of Antwerp and Breda. Origin Under Otto II, emperor of the Holy Roman Empire, several marches were created along the border with West Francia (this border coincided with the river Scheldt). Originally the mark was restricted to the borders of the Scheldt, in 994 Ansfried of Utrecht added Toxandria to the mark. History In the 11th century the mark of Antwerp was one of the fiefs of the duke of Lower Lorraine. Godfrey of Bouillon received the mark in 1076 from emperor Henry IV. After his death in the Crusader state of Jerusalem in 1100, Henry I of Limburg was appointed as margrave. In 1106 the duchy of Lower Lorraine and the margraviate were united. After the abolishment of the duchy in 1190 during the Diet of Schwäbisch Hall by Emperor Henry VI only its titles remained and these were given to the duke of Brabant. Composition The margraviate consisted (afte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert III Of Namur
Albert III ( 1027 – 22 June 1102) was the Count of Namur from 1063 until his death. He was the son of Count Albert II and Regelinde of Verdun. Although he was not formally a duke, Albert is considered to have played the role of an acting Duke of Lower Lotharingia, or "vice duke", during part of his lifetime, while the king's young son Conrad was named as Duke. However he lost this position when Godfrey of Bouillon was given the duchy.See Margue. Biography From 1071 to 1072, he helped Richilde, Countess of Hainaut and Flanders fight against Robert the Frisian, but the Countess was beaten and lost Flanders. In 1076, supported by Matilda of Tuscany, he claimed the Duchy of Bouillon, claiming to have rights by his mother, and fought against Godfrey of Bouillon to assert his claims. During a battle near Dalhem, he killed Hermann II, Count Palatine of Lotharingia (20 September 1085), making him fall out of favor with the German emperor. Finally, with the Truce of God in 1086, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Godfrey IV, Duke Of Lower Lorraine
Godfrey IV (died 26 or 27 February 1076), known as the Hunchback, was Duke of Lower Lorraine from 1069 until his death in 1076, succeeding his father Godfrey the Bearded. In the year of his accession, he married Margravine Matilda of Tuscany, daughter of his stepmother Beatrice of Bar, and thus became margrave of Tuscany. Godfrey and Matilda had only one child, Beatrice, who was born in 1071 and died the same year. From 1071 onwards, Godfrey lived apart from his wife. The two spouses were on opposite sides in the Investiture Controversy: Matilda was a partisan of Pope Gregory VII and Godfrey of Emperor Henry IV. He warred on Henry's behalf against Magnus, Duke of Saxony, in 1075 and on that of the bishop of Utrecht in 1076 against Counts Dirk V of Holland and Robert I of Flanders. He was assassinated by spear in Vlaardingen while "answering the call of nature". Despite Matilda's opposition he nominated his nephew Godfrey of Bouillon to succeed him, but the emperor instead appo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
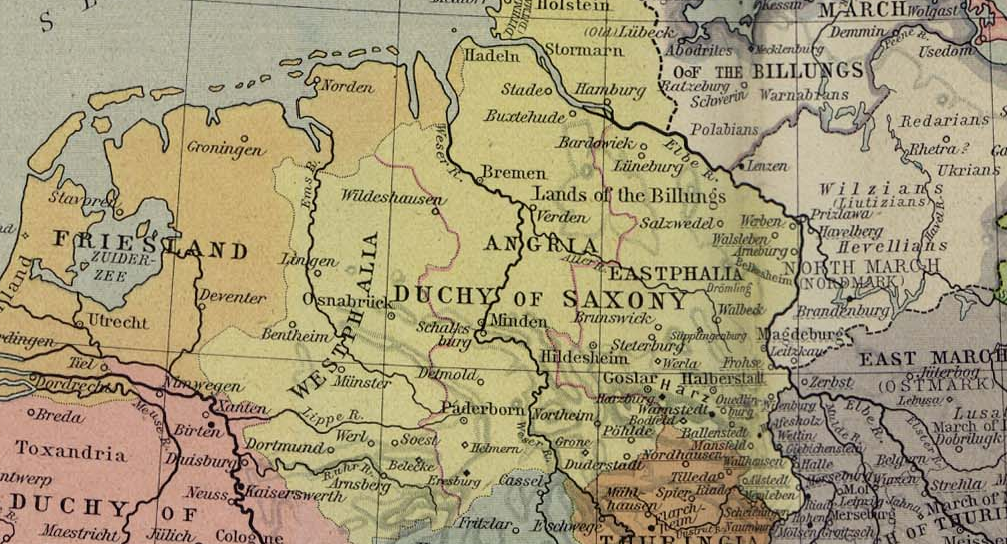
Goslar
Goslar (; Eastphalian: ''Goslär'') is a historic town in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is the administrative centre of the district of Goslar and located on the northwestern slopes of the Harz mountain range. The Old Town of Goslar and the Mines of Rammelsberg are UNESCO World Heritage Sites for their millenium-long testimony to the history of ore mining and their political importance for the Holy Roman Empire and Hanseatic League. Each year Goslar awards the Kaiserring to an international artist, called the "Nobel Prize" of the art world. Geography Goslar is situated in the middle of the upper half of Germany, about south of Brunswick and about southeast of the state capital, Hanover. The Schalke mountain is the highest elevation within the municipal boundaries at . The lowest point of is near the Oker river. Geographically, Goslar forms the boundary between the Hildesheim Börde which is part of the Northern German Plain, and the Harz range, which is the highest, norther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Diet (Holy Roman Empire)
The Imperial Diet ( la, Dieta Imperii Comitium Imperiale; german: Reichstag) was the deliberative body of the Holy Roman Empire. It was not a legislative body in the contemporary sense; its members envisioned it more like a central forum where it was more important to negotiate than to decide. Its members were the Imperial Estates, divided into three colleges. The diet as a permanent, regularized institution evolved from the ''Hoftage'' (court assemblies) of the Middle Ages. From 1663 until the end of the empire in 1806, it was in permanent session at Regensburg. All Imperial Estates enjoyed immediacy and, therefore, they had no authority above them besides the Holy Roman Emperor himself. While all the estates were entitled to a seat and vote, only the higher temporal and spiritual princes of the College of Princes enjoyed an individual vote (''Virilstimme''), while lesser estates such as imperial counts and imperial abbots, were merely entitled to a collective vote (''Kuriats ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saxon Rebellion
The Saxon Rebellion or Rebellion of the Saxons (german: Sachsenkrieg), also commonly called the Saxon Uprising (not to be confused with the Saxon Wars, also called the Saxon Uprising), refers to the struggle between the Salian dynasty ruling the Holy Roman Empire and the rebel Saxons during the reign of Henry IV. The conflict reached its climax in the period from summer 1073 until the end of 1075, in a rebellion that involved several clashes of arms. Origins Undercurrents of discord between the Salian royal family and the Saxons already existed under Henry's father, Emperor Henry III. This may have been primarily due to his Rhenish Franconian origin as well as his numerous stays in the Imperial Palace of Goslar, which were associated with a disproportionately high economic burden on the surrounding population. With the accession of Henry IV in 1065 this conflict intensified, as Henry made demands on numerous Imperial domains (''Reichsgüter'') in the centre of the Saxon heartla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holy Roman Emperor
The Holy Roman Emperor, originally and officially the Emperor of the Romans ( la, Imperator Romanorum, german: Kaiser der Römer) during the Middle Ages, and also known as the Roman-German Emperor since the early modern period ( la, Imperator Germanorum, german: Römisch-deutscher Kaiser, lit, Roman-German emperor), was the ruler and head of state of the Holy Roman Empire. The title was held in conjunction with the title of king of Italy (''Rex Italiae'') from the 8th to the 16th century, and, almost without interruption, with the title of king of Germany (''Rex Teutonicorum'', lit. "King of the Teutons") throughout the 12th to 18th centuries. The Holy Roman Emperor title provided the highest prestige among medieval Roman Catholic monarchs, because the empire was considered by the Roman Catholic Church to be the only successor of the Roman Empire during the Middle Ages and the early modern period. Thus, in theory and diplomacy, the emperors were considered '' primus inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry (VII) Of Germany
Henry (VII) (1211 – 12? February 1242), a member of the Hohenstaufen dynasty, was King of Sicily from 1212 until 1217 and King of Germany (formally '' Rex Romanorum'') from 1220 until 1235, as son and co-ruler of Emperor Frederick II. He was the seventh Henry to rule Germany, but in order to avoid confusion with the Luxembourg emperor Henry VII, he is usually numbered Henry (VII). Under custody Henry was born in Sicily, the only son of King Frederick II and his first wife, Constance of Aragon.Steven Runciman, ''The Sicilian Vespers'', (Cambridge University Press, 2000), 26. He was the elder brother of Conrad IV, who eventually succeeded him as king. While Frederick sought to be elected German king against his Welf rival Otto IV, he had his new-born son crowned King of Sicily (as Henry II) by Pope Innocent III in March 1212, since an agreement between Frederick and the Pope stated that the kingdoms of Germany and Sicily should not be united under one ruler. For this, the regen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Conrad II
Conrad II ( – 4 June 1039), also known as and , was the emperor of the Holy Roman Empire from 1027 until his death in 1039. The first of a succession of four Salian emperors, who reigned for one century until 1125, Conrad ruled the kingdoms of Germany (from 1024), Italy (from 1026) and Burgundy (from 1033). The son of Franconian count Henry of Speyer (also Henry of Worms) and Adelaide of Metz of the ''Matfriding dynasty'', that had ruled the Duchy of Lorraine from 959 until 972, Conrad inherited the titles of count of Speyer and Worms during childhood after his father had died around the year 990. He extended his influence beyond his inherited lands, as he came into favor of the princes of the kingdom. When the imperial dynastic line was left without a successor after Emperor Henry II's death in 1024, on 4 September an assembly of the imperial princes appointed the 34-year-old Conrad king (''Rex romanorum''). Conrad II Ottonian adopted many aspects of his Ottonian predeces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ludovico Antonio Muratori
Lodovico Antonio Muratori (21 October 1672 – 23 January 1750) was an Italian historian, notable as a leading scholar of his age, and for his discovery of the Muratorian fragment, the earliest known list of New Testament books. Biography Born to a poor family in Vignola, near Modena, he was first instructed by the Jesuits, studied law, philosophy, and theology at the University of Modena, and was ordained a priest in 1694. The following year, Count Charles Borromeo called him to the college of "Dottori" at the Ambrosian Library in Milan, where he immediately started collecting unedited ancient writings of various kinds. His first publication was the ''Anecdota Latina ex Ambrosianæ Bibliothecæ codicibus'' (2 vols., Milan, 1697–98), followed by two other volumes (Padua, 1713). Duke Rinaldo I (1700) appointed him archivist and librarian in Modena's Ducal library, which position he held until his death in that city. In 1716 Muratori became, in addition, provost of Santa Mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |