|
Conophylline
Conophylline is a autophagy inducing vinca alkaloid found in several species of ''Tabernaemontana'' including '' Ervatamia microphylla'' and ''Tabernaemontana divaricata''. Among its many functional groups is an epoxide: the compound where that ring is replaced with a double bond is called conophyllidine and this co-occurs in the same plants. History Conophylline and conophyllidine were first reported in 1993 after isolation from the ethanol extract of leaves of ''Tabernaemontana divaricata''. Their structures were confirmed by X-ray crystallography. The class of vinca alkaloids to which these compounds belong also contains vincristine and vinblastine, well-known therapeutic agents for human cancers, so they were candidates for a number of biochemical assays to see if they had useful biological activity. By 1996, conophylline it had been reported to inhibit tumours in rats by its action on Ras-expressing cells. This finding did not lead to a useful drug but the molecule continues t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
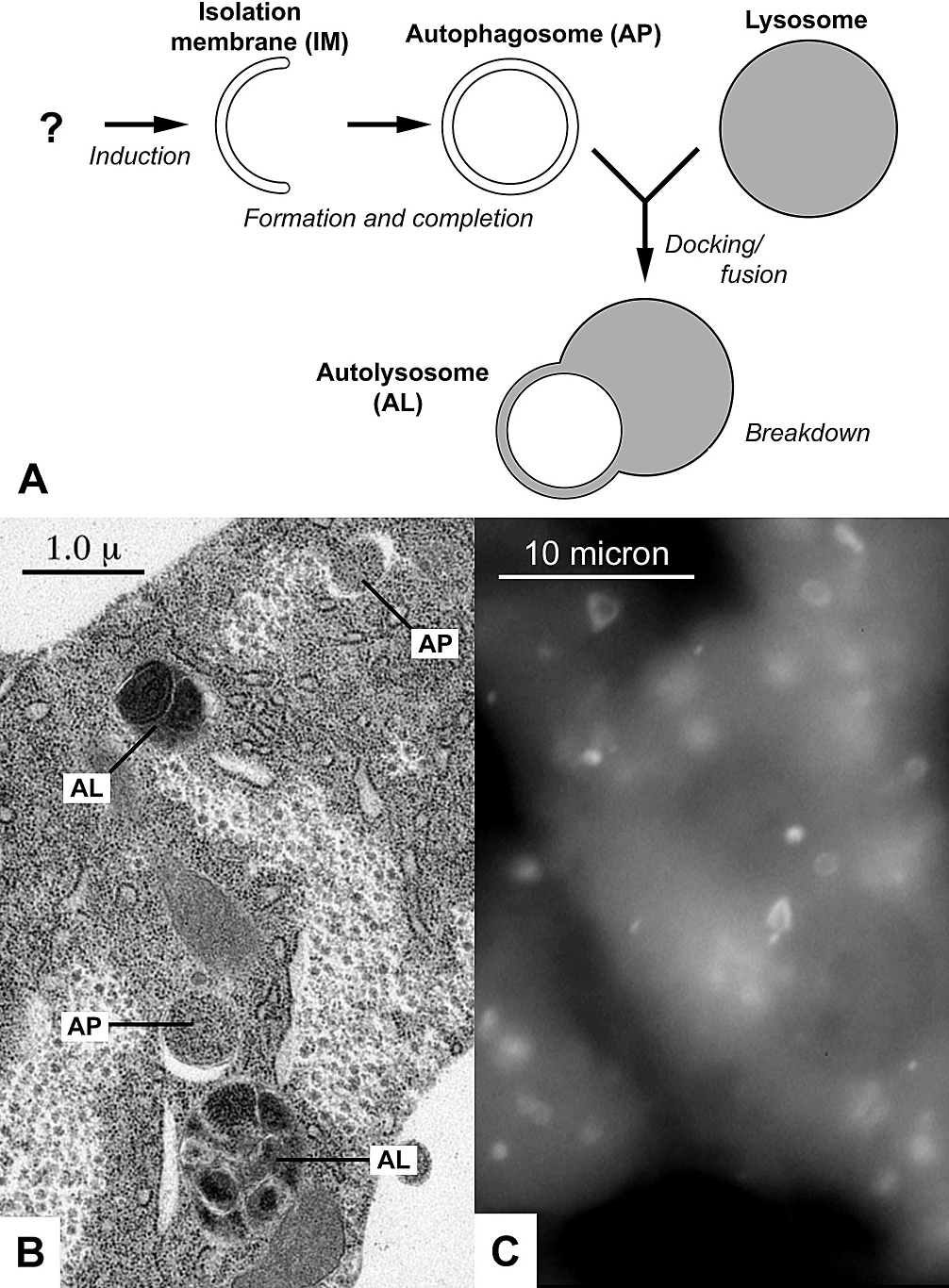
Autophagy
Autophagy (or autophagocytosis; from the Ancient Greek , , meaning "self-devouring" and , , meaning "hollow") is the natural, conserved degradation of the cell that removes unnecessary or dysfunctional components through a lysosome-dependent regulated mechanism. It allows the orderly degradation and recycling of cellular components. Although initially characterized as a primordial degradation pathway induced to protect against starvation, it has become increasingly clear that autophagy also plays a major role in the homeostasis of non-starved cells. Defects in autophagy have been linked to various human diseases, including neurodegeneration and cancer, and interest in modulating autophagy as a potential treatment for these diseases has grown rapidly. Four forms of autophagy have been identified: macroautophagy, microautophagy, chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA), and crinophagy. In macroautophagy (the most thoroughly researched form of autophagy), cytoplasmic components (like mit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tryptophan
Tryptophan (symbol Trp or W) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Tryptophan contains an α-amino group, an α- carboxylic acid group, and a side chain indole, making it a polar molecule with a non-polar aromatic beta carbon substituent. It is essential in humans, meaning that the body cannot synthesize it and it must be obtained from the diet. Tryptophan is also a precursor to the neurotransmitter serotonin, the hormone melatonin, and vitamin B3. It is encoded by the codon UGG. Like other amino acids, tryptophan is a zwitterion at physiological pH where the amino group is protonated (–; pKa = 9.39) and the carboxylic acid is deprotonated ( –COO−; pKa = 2.38). Humans and many animals cannot synthesize tryptophan: they need to obtain it through their diet, making it an essential amino acid. Function Amino acids, including tryptophan, are used as building blocks in protein biosynthesis, and proteins are required to sustain life. Man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conofoline
Conofoline is an alkaloid of the vinca alkaloid class which is closely related to conophylline. It is found in the leaves of some species in the genus ''Tabernaemontana'', including ''Tabernaemontana divaricata'', and in ''Ervatamia peduncularis''. See also * Conolidine * Conopharyngine Conopharyngine is the major alkaloid present in the leaves and stem-bark of ''Tabernaemontana pachysiphon'' and '' Conopharyngia durissima''. It is closely related voacangine and coronaridine. Conopharyngine pseudoindoxyl, a derivative of it, is ... References Indolizidines Indolines Carbazoles Heterocyclic compounds with 6 rings Epoxides Methoxy compounds {{alkaloid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voacristine
Voacristine is a indole alkaloid occurring in ''Voacanga'' and ''Tabernaemontana'' genus. It is also an iboga type alkaloid. Chemistry Its structure is almost similar to voacangine, an alkaloid used in semi-synthesis of ibogaine. Compared to voacangine, it has an extra O-atom. When it is degraded, iboxygaine and ibogaine are formed. Sources Voacristine is found in multiple species of ''Tabernaemontana'' some of which are Tabernaemontana divaricata, Tabernaemontana heyneana, Tabernaemontana ventricosa and in Voacanga africana. See also * Heyneanine * Voacamine * Vobasine Vobasine is a naturally occurring monoterpene indole alkaloid found in several species in the genus ''Tabernaemontana'' including ''Tabernaemontana divaricata''. History Vobasine was first reported by Renner in 1959 after its isolation from ''Voac ... References Tryptamine alkaloids {{Alkaloid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ibogamine
Ibogamine is an anti-convulsant, anti-addictive, CNS stimulant alkaloid found in ''Tabernanthe iboga'' and Crepe Jasmine (''Tabernaemontana divaricata''). Basic research related to how addiction affects the brain has used this chemical. Ibogamine persistently reduced the self-administration of cocaine and morphine in rats. The same study found that ibogamine (40 mg/kg) and coronaridine (40 mg/kg) did not produce "any tremor effects in rats that differ significantly from saline control". While the related alkaloids ibogaine (20–40 mg/kg), harmaline (10–40 mg/kg) and desethylcoronaridine (10–40 mg/kg) were "obviously tremorgenic". Chemistry Synthesis Ibogamine can be prepared from one-step demethoxycarbonylation process through coronaridine. Pharmacology Like ibogaine, it has seems to have similar pharmacology. It has effects on KOR, NMDAR, nAChR and serotonin sites. It also inhibits acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase See also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catharanthine
Catharanthine is a terpene indole alkaloid produced by the medicinal plant ''Catharanthus roseus'' and '' Tabernaemontana divaricata''. Catharanthine is derived from strictosidine, but the exact mechanism by which this happens is currently unknown. Catharanthine is one of the two precursors that form vinblastine, the other being vindoline. Pharmacology (+)-Catharanthine competitively inhibits α9α10 nAChRs with potencies higher than that at α3β4 and α4β2 nAChRs and directly blocks CaV2.2. Catharanthine alkaloids are non competitive antagonist of muscle type nAChRs and this is thought to be the case due to presence of catharanthine moiety in those compounds. In ''in vitro'' study, it increased the levels of cAMP by inhibiting cAMP phosphodiesterase in brain. It is a potent inhibitor of TRPM8, similar to BCTC. Structural analysis of catharanthine shows activity on TRPM8, TRPA1, and butyrylcholinesterase. See also * Akuammicine * Conopharyngine * Stemmadenine St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family (taxonomy), family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laevorotary
Optical rotation, also known as polarization rotation or circular birefringence, is the rotation of the orientation of the plane of polarization about the optical axis of linearly polarized light as it travels through certain materials. Circular birefringence and circular dichroism are the manifestations of optical activity. Optical activity occurs only in chiral materials, those lacking microscopic mirror symmetry. Unlike other sources of birefringence which alter a beam's state of polarization, optical activity can be observed in fluids. This can include gases or solutions of chiral molecules such as sugars, molecules with helical secondary structure such as some proteins, and also chiral liquid crystals. It can also be observed in chiral solids such as certain crystals with a rotation between adjacent crystal planes (such as quartz) or metamaterials. When looking at the source of light, the rotation of the plane of polarization may be either to the right (dextrorotatory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chiral
Chirality is a property of asymmetry important in several branches of science. The word ''chirality'' is derived from the Greek (''kheir''), "hand", a familiar chiral object. An object or a system is ''chiral'' if it is distinguishable from its mirror image; that is, it cannot be superimposed onto it. Conversely, a mirror image of an ''achiral'' object, such as a sphere, cannot be distinguished from the object. A chiral object and its mirror image are called ''enantiomorphs'' (Greek, "opposite forms") or, when referring to molecules, '' enantiomers''. A non-chiral object is called ''achiral'' (sometimes also ''amphichiral'') and can be superposed on its mirror image. The term was first used by Lord Kelvin in 1893 in the second Robert Boyle Lecture at the Oxford University Junior Scientific Club which was published in 1894: Human hands are perhaps the most recognized example of chirality. The left hand is a non-superimposable mirror image of the right hand; no matter ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stereogenic Center
In stereochemistry, a stereocenter of a molecule is an atom (center), axis or plane that is the focus of stereoisomerism; that is, when having at least three different groups bound to the stereocenter, interchanging any two different groups creates a new stereoisomer. Stereocenters are also referred to as stereogenic centers. A stereocenter is geometrically defined as a point (location) in a molecule; a stereocenter is usually but not always a specific atom, often carbon. Stereocenters can exist on chiral or achiral molecules; stereocenters can contain single bonds or double bonds. The number of hypothetical stereoisomers can be predicted by using 2''n'', with ''n'' being the number of tetrahedral stereocenters; however, exceptions such as meso compounds can reduce the prediction to below the expected 2''n''. Chirality centers are a type of stereocenter with four different substituent groups; chirality centers are a specific subset of stereocenters because they can only ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polonovski Reaction
In chemistry, an amine oxide, also known as an amine ''N''-oxide or simply ''N''-oxide, is a chemical compound that contains the functional group , a nitrogen-oxygen coordinate covalent bond with three additional hydrogen and/or substituent-group side chains attached to N. Sometimes it is written as →O or, incorrectly, as . In the strict sense, the term ''amine oxide'' applies only to oxides of tertiary amines. Sometimes it is also used for the analogous derivatives of primary and secondary amines. Examples of amine oxides include pyridine-''N''-oxide, a water-soluble crystalline solid with melting point 62–67 °C, and ''N''-methylmorpholine ''N''-oxide, which is an oxidant. Applications Amine oxides are surfactants commonly used in consumer products such as shampoos, conditioners, detergents, and hard surface cleaners. Alkyl dimethyl amine oxide (chain lengths C10–C16) is the most commercially used amine oxide. They are considered a high production volume class of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indoline
Indoline is an aromatic heterocyclic organic compound with the chemical formula C8H9N. It has a bicyclic structure, consisting of a six-membered benzene ring fused to a five-membered nitrogen-containing ring. The compound is based on the indole structure, but the 2-3 bond is saturated Saturation, saturated, unsaturation or unsaturated may refer to: Chemistry * Saturation, a property of organic compounds referring to carbon-carbon bonds ** Saturated and unsaturated compounds **Degree of unsaturation ** Saturated fat or fatty ac .... By oxidation/dehydrogenation it can be converted to indoles. Indoline was used to make Indocaine. References {{heterocyclic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |