|
Conjugatae
The Zygnematales ( el, ζυγός (''zygós'') and νῆμα (''nḗma'') ( nom.), νήματος (''nḗmatos'') (gen.)), also called the Conjugatales, are an order of green algae, comprising several thousand different species in two families. The larger family Zygnemataceae, with well-known genera such as ''Zygnema'' and '' Spirogyra'', includes members that grow as unbranched filaments, which grow longer through normal cell division. This group includes the desmids. Most members of both families live in freshwater, and form an important component of the algal scum that grows on or near plants, rocks, and various debris. Systematically they fall within the division Charophyta/ Streptophyta, in which the land plants ( Embryophyta) emerged. Sexual reproduction in Zygnematales takes place through a process called ''conjugation''. Here filaments of opposite gender line up, and tubes form between corresponding cells. The male cells then become amoeboid and crawl across, or sometime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
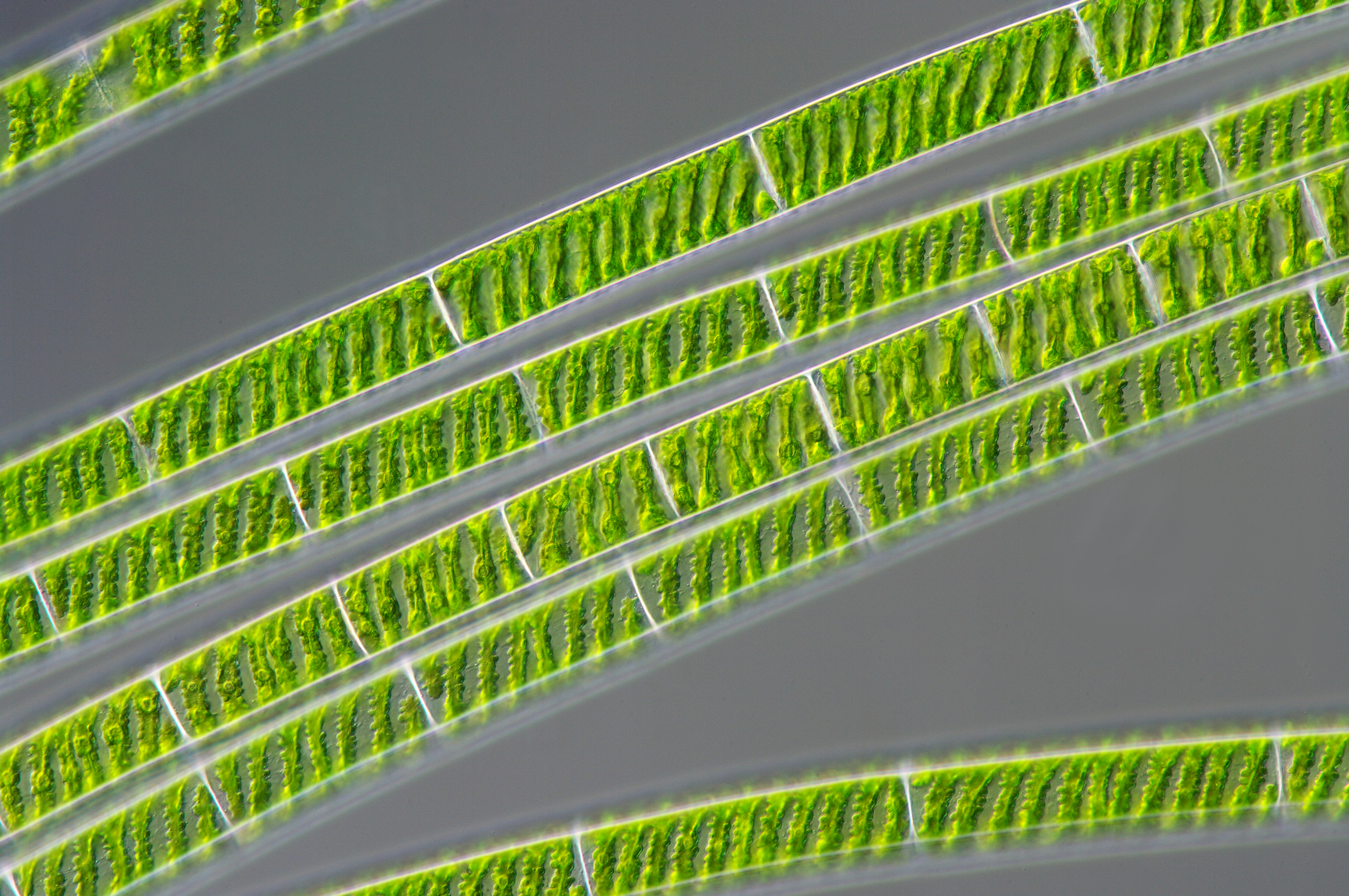
Spirogyra
''Spirogyra'' (common names include water silk, mermaid's tresses, and blanket weed) is a genus of filamentous charophyte green algae of the order Zygnematales, named for the helical or spiral arrangement of the chloroplasts that is characteristic of the genus. ''Spirogyra'' species, of which there are more than 400, are commonly found in freshwater habitats. ''Spirogyra'' measures approximately 10 to 100 μm in width and may grow to several centimetres in length. It is often observed as green slimy patches on the ground near ponds and other water bodies having stagnant water. General characteristics ''Spirogyra'' is very common in relatively clear eutrophic water, developing slimy filamentous green masses. In spring ''Spirogyra'' grows under water, but when there is enough sunlight and warmth they produce large amounts of oxygen, adhering as bubbles between the tangled filaments. The filamentous masses come to the surface and become visible as slimy green mats. ''Spirogyr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embryophyte
The Embryophyta (), or land plants, are the most familiar group of green plants that comprise vegetation on Earth. Embryophytes () have a common ancestor with green algae, having emerged within the Phragmoplastophyta clade of green algae as sister of the Zygnematophyceae. The Embryophyta consist of the bryophytes plus the polysporangiophytes. Living embryophytes therefore include hornworts, liverworts, mosses, lycophytes, ferns, gymnosperms and flowering plants. The land plants have diplobiontic life cycles and it is accepted now that they emerged from freshwater, multi-celled algae. The embryophytes are informally called land plants because they live primarily in terrestrial habitats (with exceptional members who evolved to live once again in aquatic habitats), while the related green algae are primarily aquatic. Embryophytes are complex multicellular eukaryotes with specialized reproductive organs. The name derives from their innovative characteristic of nurturing the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zygnema
''Zygnema'' is a genus of freshwater filamentous thalloid alga Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular mic ... comprising about 100 species. A terrestrial species, ''Z. terrestre'', is known from India. ''Zygnema'' grows as a free-floating mass of filaments, although young plants may be found anchored to streambeds with a holdfast. The filaments form a yellow-green to bright green colored tangled mat, and are composed of elongate barrel-shaped cells, each with two star-shaped (stellate) chloroplasts arrayed along the axis of the cell. Species Some species include: * ''Z. atrocoeruleum'' * ''Z. binuclearioides'' * ''Z. carinthiacum'' * ''Z. carteri'' * ''Z. circumcarinatum'' * ''Z. coeruleum'' * ''Z. conspicuum'' * ''Z. cruciatum'' * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Netrium
''Netrium'' is a genus of algae belonging to the family Mesotaeniaceae The Mesotaeniaceae are a small family of unicellular green algae known as the "saccoderm desmids". The Mesotaeniaceae appear to be sister or ancestral to the Zygnemataceae. The desmids are a deep branching group of Zygnemataceae. ''Spirotaeni .... The species of this genus are found in Europe, America and Australia. Species: *'' Netrium digitus'' *'' Netrium interruptum'' *'' Netrium lamellosum'' *'' Netrium naegelii'' *'' Netrium obesus'' *'' Netrium oblongum'' References {{Taxonbar, from=Q1231838 Zygnematales Charophyta genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desmidiales
Desmidiales, commonly called desmids (''Gr.'' ''desmos'', bond or chain), are an order in the Charophyta, a division of green algae in which the land plants (Embryophyta) emerged. Or in other words, Desmid, (order Desmidiales), order of single-celled (sometimes filamentous or colonial) microscopic green algae. Desmids are sometimes treated as a family (Desmidiaceae) of the order Zygnematales. The desmids belong to the class Zygnematophyceae. Although they are sometimes grouped together as a single family Desmidiaceae, most classifications recognize three to five families, either within the order Zygnematales or as their own order Desmidiales. The Desmidiales comprise around 40 genera and 5,000 to 6,000 species, found mostly but not exclusively in fresh water. Many species may be found in the fissures between patches of sphagnum moss in marshes. With a pH level of approximately 4.0, sphagnum peat provides the ideal environment for this flora. Morphology The structure of these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spirotaenia
''Spirotaenia'' is a genus of basal green algae that may be sister to the Chlorokybophyceae. It was previously considered to be part of the Zygnemataceae. It is sexually conjugating, a mode of reproduction that was previously only known in the Zygnemataceae/Mesotaeniaceae, the sister groups to the land plants The Embryophyta (), or land plants, are the most familiar group of green plants that comprise vegetation on Earth. Embryophytes () have a common ancestor with green algae, having emerged within the Phragmoplastophyta clade of green algae as sist .... This is surprising, as ''Spirotaenia'' is much more basal. The conjugating process is substantially aberrant. ''Spirotaenia'' may actually be more than one distinct lineage which may not be closely related. Phylogeny References Green algae {{Alga-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesotaeniaceae
The Mesotaeniaceae are a small family of unicellular green algae known as the "saccoderm desmids". The Mesotaeniaceae appear to be sister or ancestral to the Zygnemataceae. The desmids are a deep branching group of Zygnemataceae. ''Spirotaenia'' was found to be a basal green alga. Genera The Mesotaeniaceae includes the following genera: * ''Ancylonema'' Berggren, 1872 * ''Cylindrocystis'' Meneghini ex De Bary, 1858 * '' Geniculus'' Prescott, 1967 * ''Mesotaenium'' Nägeli, 1849 * ''Netrium'' (Nägeli) Itzigsohn & Rothe, 1856 * '' Nucleotaenium'' Gontcharov & Melkonian, 2010 * '' Planotaenium'' (Ohtani) Petlovany & Palamar-Mordvintseva, 2009 * '' Roya'' West & G.S.West, 1896 * ''Spirotaenia'' Brébisson, 1848 * '' Tortitaenia'' A.J.Brook, 1998 Synonyms: * ''Endospira'' Brébisson, nom. inval., is a synonym of Spirotaenia * ''Entospira'' Kuntze, 1898 is a synonym of ''Spirotaenia'' * ''Polytaenia'' A.J.Brook, 1997, nom. illeg. ''Nomen illegitimum'' (Latin for illegitimate na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloroplast
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant and algal cells. The photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll captures the energy from sunlight, converts it, and stores it in the energy-storage molecules ATP and NADPH while freeing oxygen from water in the cells. The ATP and NADPH is then used to make organic molecules from carbon dioxide in a process known as the Calvin cycle. Chloroplasts carry out a number of other functions, including fatty acid synthesis, amino acid synthesis, and the immune response in plants. The number of chloroplasts per cell varies from one, in unicellular algae, up to 100 in plants like ''Arabidopsis'' and wheat. A chloroplast is characterized by its two membranes and a high concentration of chlorophyll. Other plastid types, such as the leucoplast and the chromoplast, contain little chlorophyll and do not carry out photosynthesis. Chloroplasts are highly dynamic—they circulat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meiosis
Meiosis (; , since it is a reductional division) is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, such as sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately result in four cells with only one copy of each chromosome ( haploid). Additionally, prior to the division, genetic material from the paternal and maternal copies of each chromosome is crossed over, creating new combinations of code on each chromosome. Later on, during fertilisation, the haploid cells produced by meiosis from a male and female will fuse to create a cell with two copies of each chromosome again, the zygote. Errors in meiosis resulting in aneuploidy (an abnormal number of chromosomes) are the leading known cause of miscarriage and the most frequent genetic cause of developmental disabilities. In meiosis, DNA replication is followed by two rounds of cell division to produce four daughter cells, each with half the number of chr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zygote
A zygote (, ) is a eukaryotic cell formed by a fertilization event between two gametes. The zygote's genome is a combination of the DNA in each gamete, and contains all of the genetic information of a new individual organism. In multicellular organisms, the zygote is the earliest developmental stage. In humans and most other anisogamous organisms, a zygote is formed when an egg cell and sperm cell come together to create a new unique organism. In single-celled organisms, the zygote can divide asexually by mitosis to produce identical offspring. German zoologists Oscar and Richard Hertwig made some of the first discoveries on animal zygote formation in the late 19th century. Humans In human fertilization, a released ovum (a haploid secondary oocyte with replicate chromosome copies) and a haploid sperm cell (male gamete) combine to form a single diploid cell called the zygote. Once the single sperm fuses with the oocyte, the latter completes the division of the second ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isogamy
Isogamy is a form of sexual reproduction that involves gametes of the same morphology (indistinguishable in shape and size), found in most unicellular eukaryotes. Because both gametes look alike, they generally cannot be classified as male or female. Instead, organisms undergoing isogamy are said to have different mating types, most commonly noted as "+" and "−" strains. Etymology The literal meaning of isogamy is "equal marriage" which refers to equal contribution of resources by both gametes to a zygote. The term isogamous was first used in the year 1887. Characteristics of isogamous species Isogamous species often have two mating types. Some isogamous species have more than two mating types, but the number is usually lower than ten. In some extremely rare cases a species can have thousands of mating types. In all cases, fertilization occurs when gametes of two different mating types fuse to form a zygote. Evolution It is generally accepted that isogamy is an an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sexual Reproduction
Sexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that involves a complex life cycle in which a gamete ( haploid reproductive cells, such as a sperm or egg cell) with a single set of chromosomes combines with another gamete to produce a zygote that develops into an organism composed of cells with two sets of chromosomes ( diploid). This is typical in animals, though the number of chromosome sets and how that number changes in sexual reproduction varies, especially among plants, fungi, and other eukaryotes. Sexual reproduction is the most common life cycle in multicellular eukaryotes, such as animals, fungi and plants. Sexual reproduction also occurs in some unicellular eukaryotes. Sexual reproduction does not occur in prokaryotes, unicellular organisms without cell nuclei, such bacteria and archaea. However, some process in bacteria may be considered analogous to sexual reproduction in that they incorporate new genetic information, including bacterial conjugation, transformatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |