|
Condensation Cloud
A transient condensation cloud, also called a Wilson cloud, is observable surrounding large explosions in humid air. When a nuclear weapon or a large amount of a conventional explosive is detonated in sufficiently humid air, the "negative phase" of the shock wave causes a rarefaction of the air surrounding the explosion, but not contained within it. This rarefaction results in a temporary cooling of that air, which causes a condensation of some of the water vapor contained in it. When the pressure and the temperature return to normal, the Wilson cloud dissipates. Mechanism Since heat does not leave the affected air mass, this change of pressure is adiabatic, with an associated change of temperature. In humid air, the drop in temperature in the most rarefied portion of the shock wave can bring the air temperature below its dew point, at which moisture condenses to form a visible cloud of microscopic water droplets. Since the pressure effect of the wave is reduced by its expans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crossroads Baker Explosion
Crossroads, crossroad, cross road or similar may refer to: * Crossroads (junction), where four roads meet Film and television Films * ''Crossroads'' (1928 film), a 1928 Japanese film by Teinosuke Kinugasa * ''Cross Roads'' (film), a 1930 British film by Reginald Fogwell * ''Crossroads'' (1937 film), a Chinese film starring Zhao Dan * ''Crossroads'' (1942 film), a mystery film starring William Powell and Hedy Lamarr * ''The Crossroads'' (1951 film), an Italian crime film by Fernando Cerchio * ''The Crossroads'' (1952 film), an Argentine film * ''The Crossroads'' (1960 film), a French-Spanish drama film by Alfonso Balcázar * ''Crossroads'' (1976 film), a film by Bruce Conner * ''Crossroad'', a 1976 Hong Kong-Taiwanese film by Chin Han * ''Crossroads'' (1986 film), a film starring Ralph Macchio * '' The Crossroad'', a 1988 documentary film by Ivars Seleckis * ''Crossroads'' (2002 film), a film starring Britney Spears * ''Crossroads: A Story of Forgiveness'', a 2007 film ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Test
Nuclear weapons tests are experiments carried out to determine nuclear weapons' effectiveness, Nuclear weapon yield, yield, and explosive capability. Testing nuclear weapons offers practical information about how the weapons function, how detonations are affected by different conditions, and how personnel, structures, and equipment are affected when subjected to Nuclear explosion, nuclear explosions. However, nuclear testing has often been used as an indicator of scientific and military strength. Many tests have been overtly political in their intention; most List of countries with nuclear weapons, nuclear weapons states publicly declared their nuclear status through a nuclear test. The first nuclear device was detonated as a test by the United States at the Trinity site in New Mexico on July 16, 1945, with a yield approximately TNT equivalent, equivalent to 20 kilotons of TNT. The first thermonuclear weapon technology test of an engineered device, codenamed "Ivy Mike", was teste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerodynamics
Aerodynamics, from grc, ἀήρ ''aero'' (air) + grc, δυναμική (dynamics), is the study of the motion of air, particularly when affected by a solid object, such as an airplane wing. It involves topics covered in the field of fluid dynamics and its subfield of gas dynamics. The term ''aerodynamics'' is often used synonymously with gas dynamics, the difference being that "gas dynamics" applies to the study of the motion of all gases, and is not limited to air. The formal study of aerodynamics began in the modern sense in the eighteenth century, although observations of fundamental concepts such as aerodynamic drag were recorded much earlier. Most of the early efforts in aerodynamics were directed toward achieving heavier-than-air flight, which was first demonstrated by Otto Lilienthal in 1891. Since then, the use of aerodynamics through mathematical analysis, empirical approximations, wind tunnel experimentation, and computer simulations has formed a rational basis fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contrail
Contrails (; short for "condensation trails") or vapor trails are line-shaped clouds produced by aircraft engine exhaust or changes in air pressure, typically at aircraft cruising altitudes several miles above the Earth's surface. Contrails are composed primarily of water, in the form of ice crystals. The combination of water vapor in aircraft engine exhaust and the low ambient temperatures that exist at high altitudes allows the formation of the trails. Impurities in the engine exhaust from the fuel, including sulfur compounds (0.05% by weight in jet fuel) provide some of the particles that can serve as nucleation sites for water droplet growth in the exhaust. If water droplets form, they might freeze to form ice particles that compose a contrail. Their formation can also be triggered by changes in air pressure in wingtip vortices or in the air over the entire wing surface. Contrails, and other clouds directly resulting from human activity, are collectively named homogenitus. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
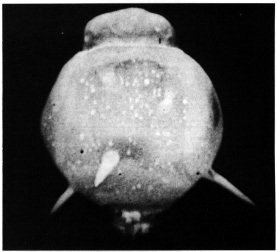
Rope Trick Effect
''Rope trick'' is the term given by physicist John Malik to the curious lines and spikes which emanate from the fireball of certain nuclear explosions just after detonation. Description The adjacent photograph shows two unusual phenomena: bright spikes projecting from the bottom of the fireball, and the peculiar mottling of the expanding fireball surface. The surface of the fireball, with a temperature over 20,000 kelvins, emits huge amounts of visible light radiation, more than 100 times the intensity at the Sun's surface. Anything solid in the area absorbs the light and rapidly heats. The "rope tricks" that protrude from the bottom of the fireball are caused by the heating, rapid vaporization and then expansion of guy wires that extend from the shot cab, the housing at the top of the tower that contains the explosive device, to the ground. Malik observed that when the rope was painted black, spike formation was enhanced, and if it were painted with reflective paint or wra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mushroom Cloud
A mushroom cloud is a distinctive mushroom-shaped flammagenitus cloud of debris, smoke and usually condensed water vapor resulting from a large explosion. The effect is most commonly associated with a nuclear explosion, but any sufficiently energetic detonation or deflagration will produce the same effect. They can be caused by powerful conventional weapons, like thermobaric weapons, including the ATBIP and GBU-43/B Massive Ordnance Air Blast. Some volcanic eruptions and impact events can produce natural mushroom clouds. Mushroom clouds result from the sudden formation of a large volume of lower-density gases at any altitude, causing a Rayleigh–Taylor instability. The buoyant mass of gas rises rapidly, resulting in turbulent vortices curling downward around its edges, forming a temporary vortex ring that draws up a central column, possibly with smoke, debris, condensed water vapor, or a combination of these, to form the "mushroom stem". The mass of gas plus entrained moist a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transonic
Transonic (or transsonic) flow is air flowing around an object at a speed that generates regions of both subsonic and supersonic airflow around that object. The exact range of speeds depends on the object's critical Mach number, but transonic flow is seen at flight speeds close to the speed of sound (343 m/s at sea level), typically between Mach 0.8 and 1.2. The issue of transonic speed (or transonic region) first appeared during World War II. Pilots found as they approached the sound barrier the airflow caused aircraft to become unsteady. Experts found that shock waves can cause large-scale separation downstream, increasing drag and adding asymmetry and unsteadiness to the flow around the vehicle. Research has been done into weakening shock waves in transonic flight through the use of anti-shock bodies and supercritical airfoils. Most modern jet powered aircraft are engineered to operate at transonic air speeds. Transonic airspeeds see a rapid increase in drag fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vapor Cone
A vapor cone (also known as a Mach diamond, shock collar, or shock egg) is a visible cloud of condensed water that can sometimes form around an object moving at high speed through moist air, for example, an aircraft flying at transonic speeds. When the localized air pressure around the object drops, so does the air temperature. If the temperature drops below the saturation temperature, a cloud forms. In the case of aircraft, the cloud is caused by expansion fans decreasing the air pressure, density, and temperature below the dew point. Then pressure, density, and temperature suddenly increase across the stern shock wave associated with a return to subsonic flow behind the aircraft. Since the local Mach number is not uniform over the aircraft, parts of the aircraft may be supersonic while others remain subsonic—a flight regime called transonic flight. In addition to making the shock waves themselves visible, water condensation can also occur in the trough between two crests ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2020 Beirut Explosion
On 4 August 2020, a large amount of ammonium nitrate stored at the Port of Beirut in the capital city of Lebanon exploded, causing at least 218 deaths, 7,000 injuries, and US$15 billion in property damage, as well as leaving an estimated 300,000 people homeless. A cargo of 2,750 tonnes of the substance (equivalent to around 1.1 kilotons of TNT) had been stored in a warehouse without proper safety measures for the previous six years after having been confiscated by the Lebanese authorities from the abandoned ship . The explosion was preceded by a fire in the same warehouse. As of , an investigation by the Lebanese government is ongoing. The blast was so powerful that it physically shook the whole country of Lebanon. It was felt in Turkey, Syria, Palestine, Jordan, and Israel, as well as parts of Europe, and was heard in Cyprus, more than away. It was detected by the United States Geological Survey as a seismic event of magnitude 3.3 and is considered one of the most power ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Sailor Hat
Operation Sailor Hat was a series of explosives effects tests, conducted by the United States Navy Bureau of Ships under the sponsorship of the Defense Atomic Support Agency. The tests consisted of two underwater explosions at San Clemente Island, California in 1964 and three surface explosions at Kahoolawe, Hawaii in 1965. They were non-nuclear tests employing large quantities of conventional explosives (TNT and HBX) to determine the effects of a nuclear weapon blast on naval vessels, and the first major test of this kind since Operation Crossroads in July 1946. Each "Sailor Hat" test at Kahoolawe consisted of a dome-stacked charge of TNT high explosive detonated on the shore close to the ships under test. Since a TNT detonation releases energy more slowly than a nuclear explosion, the blast effect at close range was designed to be equivalent to a nuclear weapon at greater distance. The main ship used for testing was the former Cleveland-class light cruiser . In addition, the g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TNT Detonation On Kaho'olawe Island During Operation Sailor Hat, Shot Bravo, 1965
Trinitrotoluene (), more commonly known as TNT, more specifically 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene, and by its preferred IUPAC name 2-methyl-1,3,5-trinitrobenzene, is a chemical compound with the formula C6H2(NO2)3CH3. TNT is occasionally used as a reagent in chemical synthesis, but it is best known as an explosive material with convenient handling properties. The explosive yield of TNT is considered to be the standard comparative convention of bombs and asteroid impacts. In chemistry, TNT is used to generate charge transfer salts. History TNT was first prepared in 1863 by German chemist Julius Wilbrand and originally used as a yellow dye. Its potential as an explosive was not recognized for three decades, mainly because it was too difficult to detonate because it was less sensitive than alternatives. Its explosive properties were first discovered in 1891 by another German chemist, Carl Häussermann. TNT can be safely poured when liquid into shell cases, and is so insensitive tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)

.jpg)
