|
Condensate Pump
A condensate pump is a specific type of pump used to pump the condensate (water) produced in an HVAC (heating or cooling), refrigeration, condensing boiler furnace, or steam system. Applications Condensate pumps may be used to pump the condensate produced from latent water vapor in any of the following gas mixtures: * Conditioned (cooled or heated) building air * Refrigerated air in cooling and freezing systems * Steam in heat exchangers and radiators * The exhaust stream of very-high-efficiency furnaces Condensate recovery systems help reduce three tangible costs of producing steam: * Fuel/energy costs * Boiler water make-up and sewage treatment * Boiler water chemical treatment Construction and operation Condensate pumps are used in hydronic systems that cannot discharge excess condensate water via a gravity feed. Condensate pumps are usually electrically powered centrifugal pumps. They are used to remove condensate water from HVAC systems that cannot be accomplished via ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AIR CONDENSATE PUMP
The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases, known collectively as air, retained by Earth's gravity that surrounds the planet and forms its planetary atmosphere. The atmosphere of Earth protects life on Earth by creating pressure allowing for liquid water to exist on the Earth's surface, absorbing ultraviolet solar radiation, warming the surface through heat retention (greenhouse effect), and reducing temperature extremes between day and night (the diurnal temperature variation). By mole fraction (i.e., by number of molecules), dry air contains 78.08% nitrogen, 20.95% oxygen, 0.93% argon, 0.04% carbon dioxide, and small amounts of other gases. Air also contains a variable amount of water vapor, on average around 1% at sea level, and 0.4% over the entire atmosphere. Air composition, temperature, and atmospheric pressure vary with altitude. Within the atmosphere, air suitable for use in photosynthesis by terrestrial plants and breathing of terrestrial animals is found only in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Condensate Return Pump
Condensate may refer to: * The liquid phase produced by the condensation of steam or any other gas * The product of a chemical condensation reaction, other than water * Natural-gas condensate, in the natural gas industry * ''Condensate'' (album), a 2011 album by The Original 7ven, the band formerly known as The Time Quantum physics * Canonical quantization or vacuum expectation value, in quantum field theory * Bose–Einstein condensate, a substance which occurs at very low temperatures in a system of bosons * Fermionic condensate, a substance which occurs at very low temperatures in a system of fermions * Gluon condensate, a non-perturbative property of the QCD vacuum Theoretical states * Color-glass condensate, an extreme type of matter theorized to exist in atomic nuclei traveling near the speed of light * Top quark condensate, an alternative theory to the Standard Model See also * Biomolecular condensate In biochemistry, biomolecular condensates are a class of membra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microbe
A microorganism, or microbe,, ''mikros'', "small") and ''organism'' from the el, ὀργανισμός, ''organismós'', "organism"). It is usually written as a single word but is sometimes hyphenated (''micro-organism''), especially in older texts. The informal synonym ''microbe'' () comes from μικρός, mikrós, "small" and βίος, bíos, "life". is an organism of microscopic size, which may exist in its single-celled form or as a colony of cells. The possible existence of unseen microbial life was suspected from ancient times, such as in Jain scriptures from sixth century BC India. The scientific study of microorganisms began with their observation under the microscope in the 1670s by Anton van Leeuwenhoek. In the 1850s, Louis Pasteur found that microorganisms caused food spoilage, debunking the theory of spontaneous generation. In the 1880s, Robert Koch discovered that microorganisms caused the diseases tuberculosis, cholera, diphtheria, and anthrax. Because mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dust
Dust is made of fine particles of solid matter. On Earth, it generally consists of particles in the atmosphere that come from various sources such as soil lifted by wind (an aeolian process), volcanic eruptions, and pollution. Dust in homes is composed of about 20–50% dead skin cells. The rest, and in offices, and other human environments is composed of small amounts of plant pollen, human hairs, animal fur, textile fibers, paper fibers, minerals from outdoor soil, burnt meteorite particles, and many other materials which may be found in the local environment. Atmospheric Atmospheric or wind-borne fugitive dust, also known as ''aeolian dust'', comes from arid and dry regions where high velocity winds are able to remove mostly silt-sized material, deflating susceptible surfaces. This includes areas where grazing, ploughing, vehicle use, and other human behaviors have further destabilized the land, though not all source areas have been largely affected by anthropogenic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freezing
Freezing is a phase transition where a liquid turns into a solid when its temperature is lowered below its freezing point. In accordance with the internationally established definition, freezing means the solidification phase change of a liquid or the liquid content of a substance, usually due to cooling. For most substances, the melting and freezing points are the same temperature; however, certain substances possess differing solid-liquid transition temperatures. For example, agar displays a hysteresis in its melting point and freezing point. It melts at 85 °C (185 °F) and solidifies from 32 °C to 40 °C (89.6 °F to 104 °F). Crystallization Most liquids freeze by crystallization, formation of crystalline solid from the uniform liquid. This is a first-order thermodynamic phase transition, which means that as long as solid and liquid coexist, the temperature of the whole system remains very nearly equal to the melting point due to the slow re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siphon
A siphon (from grc, σίφων, síphōn, "pipe, tube", also spelled nonetymologically syphon) is any of a wide variety of devices that involve the flow of liquids through tubes. In a narrower sense, the word refers particularly to a tube in an inverted "U" shape, which causes a liquid to flow upward, above the surface of a reservoir, with no pump, but powered by the fall of the liquid as it flows down the tube under the pull of gravity, then discharging at a level lower than the surface of the reservoir from which it came. There are two leading theories about how siphons cause liquid to flow uphill, against gravity, without being pumped, and powered only by gravity. The traditional theory for centuries was that gravity pulling the liquid down on the exit side of the siphon resulted in reduced pressure at the top of the siphon. Then atmospheric pressure was able to push the liquid from the upper reservoir, up into the reduced pressure at the top of the siphon, like in a baromet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
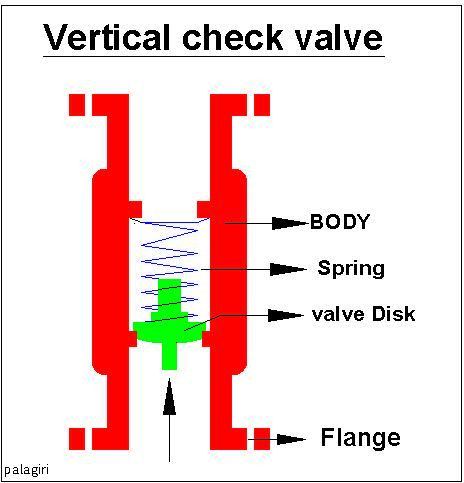
Check Valve
A check valve, non-return valve, reflux valve, retention valve, foot valve, or one-way valve is a valve that normally allows fluid (liquid or gas) to flow through it in only one direction. Check valves are two-port valves, meaning they have two openings in the body, one for fluid to enter and the other for fluid to leave. There are various types of check valves used in a wide variety of applications. Check valves are often part of common household items. Although they are available in a wide range of sizes and costs, check valves generally are very small, simple, and inexpensive. Check valves work automatically and most are not controlled by a person or any external control; accordingly, most do not have any valve handle or stem. The bodies (external shells) of most check valves are made of plastic or metal. An important concept in check valves is the cracking pressure which is the minimum differential upstream pressure between inlet and outlet at which the valve will operate. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plastic
Plastics are a wide range of synthetic or semi-synthetic materials that use polymers as a main ingredient. Their plasticity makes it possible for plastics to be moulded, extruded or pressed into solid objects of various shapes. This adaptability, plus a wide range of other properties, such as being lightweight, durable, flexible, and inexpensive to produce, has led to its widespread use. Plastics typically are made through human industrial systems. Most modern plastics are derived from fossil fuel-based chemicals like natural gas or petroleum; however, recent industrial methods use variants made from renewable materials, such as corn or cotton derivatives. 9.2 billion tonnes of plastic are estimated to have been made between 1950 and 2017. More than half this plastic has been produced since 2004. In 2020, 400 million tonnes of plastic were produced. If global trends on plastic demand continue, it is estimated that by 2050 annual global plastic production will reach over 1, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanitary Sewer
A sanitary sewer is an underground pipe or tunnel system for transporting sewage from houses and commercial buildings (but not stormwater) to a sewage treatment plant or disposal. Sanitary sewers are a type of gravity sewer and are part of an overall system called a "sewage system" or sewerage. Sanitary sewers serving industrial areas may also carry industrial wastewater. In municipalities served by sanitary sewers, separate storm drains may convey surface runoff directly to surface waters. An advantage of sanitary sewer systems is that they avoid combined sewer overflows. Sanitary sewers are typically much smaller in diameter than combined sewers which also transport urban runoff. Backups of raw sewage can occur if excessive stormwater inflow or groundwater infiltration occurs due to leaking joints, defective pipes etc. in aging infrastructure. Purpose Sewage treatment is less effective when sanitary waste is diluted with stormwater, and combined sewer overflows occur when r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cavitation
Cavitation is a phenomenon in which the static pressure of a liquid reduces to below the liquid's vapour pressure, leading to the formation of small vapor-filled cavities in the liquid. When subjected to higher pressure, these cavities, called "bubbles" or "voids", collapse and can generate shock waves that may damage machinery. These shock waves are strong when they are very close to the imploded bubble, but rapidly weaken as they propagate away from the implosion. Cavitation is a significant cause of wear in some engineering contexts. Collapsing voids that implode near to a metal surface cause cyclic stress through repeated implosion. This results in surface fatigue of the metal causing a type of wear also called "cavitation". The most common examples of this kind of wear are to pump impellers, and bends where a sudden change in the direction of liquid occurs. Cavitation is usually divided into two classes of behavior: inertial (or transient) cavitation and non-inertial c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suction Head
In fluid dynamics, total dynamic head (TDH) is the total equivalent height that a fluid is to be pumped, taking into account friction losses in the pipe. : {\rm h_{total} = \frac{P_2-P_1}{\rho g} + \frac{{v_2}^2-{v_1}^2}{2g : TDH = Static Height + Static Lift + Friction Loss + Velocity Head where: : ''Static height'' is the maximum height reached by the pipe after the pump (also known as the ''discharge head''). : ''Static lift'' is the height the water will rise before arriving at the pump (also known as the ''suction head''). : ''Friction loss'' (or ''head loss''). : ''Velocity head'' represents the energy of the fluid due to its bulk motion. This equation can be derived from Bernoulli's Equation. For a relatively incompressible fluid such as water, TDH is simply the pressure head difference between the inlet and outlet of the pump, if measured at the same elevation and with inlet and outlet of equal diameter. TDH is also the work done by the pump per unit weight, per unit v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |