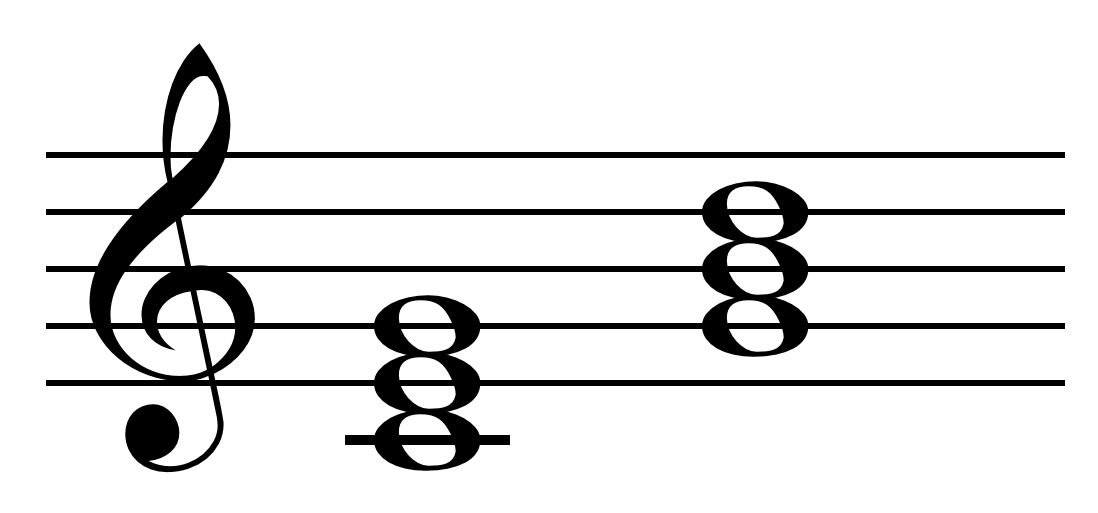|
Concerto (Webern)
Anton Webern's Concerto for Nine Instruments, Op. 24 (German: Konzert für neun Instrumente), written in 1934, is a twelve-tone concerto for nine instruments: flute, oboe, clarinet, horn, trumpet, trombone, violin, viola, and piano. It consists of three movements: The concerto is based on a derived row, "often cited Milton_Babbitt.html"_;"title="uch_as_by_Milton_Babbitt">uch_as_by_Milton_Babbitt_(1972)as_a_paragon_of_symmetry.html" "title="Milton_Babbitt_(1972).html" ;"title="Milton_Babbitt.html" ;"title="uch as by Milton Babbitt">uch as by Milton Babbitt (1972)">Milton_Babbitt.html" ;"title="uch as by Milton Babbitt">uch as by Milton Babbitt (1972)as a paragon of symmetry">symmetrical construction".Bailey (1996), p.246. The tone row is shown below. Whittall, Arnold. 2008. ''The Cambridge Introduction to Serialism. Cambridge Introductions to Music'', p. 97. New York: Cambridge University Press. (pbk). : In the words of Luigi Dallapiccola, the concerto is "a work of incre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anton Webern
Anton Friedrich Wilhelm von Webern (3 December 188315 September 1945), better known as Anton Webern (), was an Austrian composer and conductor whose music was among the most radical of its milieu in its sheer concision, even aphorism, and steadfast embrace of then novel atonal and twelve-tone techniques. With his mentor Arnold Schoenberg and his colleague Alban Berg, Webern was at the core of those within the broader circle of the Second Viennese School. Little known in the earlier part of his life, mostly as a student and follower of Schoenberg, but also as a peripatetic and often unhappy theater music director with a mixed reputation as an exacting conductor, Webern came to some prominence and increasingly high regard as a vocal coach, choirmaster, conductor, and teacher during Red Vienna. With Schoenberg away at the Prussian Academy of Arts (and with the benefit of a publication agreement secured through Universal Edition), Webern began writing music of increasing confidenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symmetry
Symmetry (from grc, συμμετρία "agreement in dimensions, due proportion, arrangement") in everyday language refers to a sense of harmonious and beautiful proportion and balance. In mathematics, "symmetry" has a more precise definition, and is usually used to refer to an object that is invariant under some transformations; including translation, reflection, rotation or scaling. Although these two meanings of "symmetry" can sometimes be told apart, they are intricately related, and hence are discussed together in this article. Mathematical symmetry may be observed with respect to the passage of time; as a spatial relationship; through geometric transformations; through other kinds of functional transformations; and as an aspect of abstract objects, including theoretic models, language, and music. This article describes symmetry from three perspectives: in mathematics, including geometry, the most familiar type of symmetry for many people; in science and nature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Combinatoriality
In music using the twelve tone technique, combinatoriality is a quality shared by twelve-tone tone rows whereby each section of a row and a proportionate number of its transformations combine to form aggregates (all twelve tones). Whittall, Arnold. 2008. ''The Cambridge Introduction to Serialism. Cambridge Introductions to Music'', p. 272. New York: Cambridge University Press. (hardback) (pbk). Much as the pitches of an aggregate created by a tone row do not need to occur simultaneously, the pitches of a combinatorially created aggregate need not occur simultaneously. Arnold Schoenberg, creator of the twelve-tone technique, often combined P-0/I-5 to create "two aggregates, between the first hexachords of each, and the second hexachords of each, respectively." Combinatoriality is a side effect of derived rows, where the initial segment or set may be combined with its transformations (T,R,I,RI) to create an entire row. "Derivation refers to a process whereby, for instance, the ini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complement (music)
In music theory, ''complement'' refers to either traditional interval complementation, or the aggregate complementation of twelve-tone and serialism. In interval complementation a complement is the interval which, when added to the original interval, spans an octave in total. For example, a major 3rd is the complement of a minor 6th. The complement of any interval is also known as its ''inverse'' or ''inversion''. Note that the octave and the unison are each other's complements and that the tritone is its own complement (though the latter is "re-spelt" as either an augmented fourth or a diminished fifth, depending on the context). In the aggregate complementation of twelve-tone music and serialism the complement of one set of notes from the chromatic scale contains all the ''other'' notes of the scale. For example, A-B-C-D-E-F-G is ''complemented'' by B-C-E-F-A. Note that ''musical set theory'' broadens the definition of both senses somewhat. Interval complementation Rule of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trichord
In music theory, a trichord () is a group of three different pitch classes found within a larger group. A trichord is a contiguous three-note set from a musical scale or a twelve-tone row. In musical set theory there are twelve trichords given inversional equivalency, and, without inversional equivalency, nineteen trichords. These are numbered 1–12, with symmetrical trichords being unlettered and with uninverted and inverted nonsymmetrical trichords lettered A or B, respectively. They are often listed in prime form, but may exist in different voicings; different inversions at different transpositions. For example, the major chord, 3-11B (prime form: ,4,7, is an inversion of the minor chord, 3-11A (prime form: ,3,7. 3-5A and B are the Viennese trichord (prime forms: ,1,6and ,5,6. Historical Russian definition In late-19th to early 20th-century Russian musicology, the term trichord (трихорд ()) meant something more specific: a set of three pitches, each at least ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Music Theory Spectrum
''Music Theory Spectrum'' () is a peer-reviewed, academic journal specializing in music theory and analysis. It is the official journal of the Society for Music Theory, and is published by Oxford University Press. The journal was first published in 1979 as the official organ of the Society for Music Theory, which had been founded in 1977 and had its first conference in 1978.. Unlike many other journals (music or otherwise), ''Music Theory Spectrum'' was initially published in an oblong (landscape) page format, to better accommodate such musical graphics as Schenkerian graphs. Published twice annually, ''Music Theory Spectrum'' includes research articles and book reviews. Online access to back issues of the journal up 2017 is provided through JSTOR. In a 1999 study, it was the seventh most frequently cited journal in music theses overall, and the third most frequently cited journal in music theory theses. In Spring 2014, Oxford University Press began publishing ''Music Theory Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musical Gesture
In music, gesture is any movement, either physical (bodily) or mental (imaginary). As such "gesture" includes both categories of movements required to produce sound and categories of perceptual moves associated with those gestures. The concept of musical gestures has received much attention in various musicological disciplines (e.g. music analysis, music therapy, music psychology, NIME) in recent years. For example, the "musical" movement from a close-position tonic C major chord to a close-position dominant G major chord requires on the piano the physical movement from each white key of the first chord to the right (in space, upwards in pitch) four white keys or steps. Thus gesture includes both characteristic physical movements by performers and characteristic melodies, phrases, chord progressions, and arpeggiations produced by (or producing) those movements. Introduction The concept of musical gestures encompasses a large territory stretching from details of sound-pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Texture (music)
In music, texture is how the tempo, melodic, and harmonic materials are combined in a musical composition, determining the overall quality of the sound in a piece. The texture is often described in regard to the density, or thickness, and range, or width, between lowest and highest pitches, in relative terms as well as more specifically distinguished according to the number of voices, or parts, and the relationship between these voices (see Common types below). For example, a thick texture contains many 'layers' of instruments. One of these layers could be a string section or another brass. The thickness also is changed by the amount and the richness of the instruments playing the piece. The thickness varies from light to thick. A piece's texture may be changed by the number and character of parts playing at once, the timbre of the instruments or voices playing these parts and the harmony, tempo, and rhythms used. The types categorized by number and relationship of parts are an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Half Note
''Half Note'' is a live album by saxophonist Clifford Jordan which was recorded in 1974 and first released on the SteepleChase label in 1985. accessed April 9, 2014 Reception In his review on , Scott Yanow notes that this is "An good example of Jordan's music"Track listing ''All compositions by Clifford Jordan except as indicated'' # "Holy Land" (Cedar Walton) - 8:41 # "The Glass Bead Games" - 5:38 # " St. Thomas" ([...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quarter Note
A quarter note (American) or crotchet ( ) (British) is a note (music), musical note played for one quarter of the duration of a whole note (or semibreve). Quarter notes are notated with a filled-in oval note head and a straight, flagless stem (music), stem. The stem usually points upwards if it is below the middle line of the musical staff, staff, and downwards if it is on or above the middle line. An upward stem is placed on the right side of the notehead, a downward stem is placed on the left (see image). The Unicode symbol is U+2669 (♩). A quarter rest (music), rest (or crotchet rest) denotes a silence of the same duration as a quarter note. It typically appears as the symbol , or occasionally, as the older symbol .''Rudiments and Theory of Music'' Associated Board of the Royal Schools of Music, London 1958. I,33 and III,25. The former section shows both forms without distinction, the latter the "old" form only. The book was the Official ABRSM theory manual in the UK ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duration (music)
In music, duration is an amount of time or how long or short a note, phrase, section, or composition lasts. "''Duration'' is the length of time a pitch, or tone, is sounded." A note may last less than a second, while a symphony may last more than an hour. One of the fundamental features of rhythm, or encompassing rhythm, duration is also central to meter and musical form. Release plays an important part in determining the timbre of a musical instrument and is affected by articulation. The concept of duration can be further broken down into those of beat and meter, where beat is seen as (usually, but certainly not always) a 'constant', and rhythm being longer, shorter or the same length as the beat. Pitch may even be considered a part of duration. In serial music the beginning of a note may be considered, or its duration may be (for example, is a 6 the note which begins at the sixth beat, or which lasts six beats?). Durations, and their beginnings and endings, may be describ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Music Theory
The ''Journal of Music Theory'' is a peer-reviewed academic journal specializing in music theory and analysis. It was established by David Kraehenbuehl (Yale University) in 1957. According to its website, " e ''Journal of Music Theory'' fosters conceptual and technical innovations in abstract, systematic musical thought and cultivates the historical study of musical concepts and compositional techniques. The journal publishes research with important and broad applications in the analysis of music and the history of music theory as well as theoretical or metatheoretical work that engages and stimulates ongoing discourse in the field. While remaining true to its original formalist outlook, the journal also addresses the influences of philosophy, mathematics, computer science, cognitive sciences, and anthropology on music theory." The journal is currently edited by Richard Cohn. It has a long and distinguished history of past editors, including Allen Forte Allen, Allen's or Allens ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |