|
Concepts And Techniques In Modern Geography
''Concepts and Techniques in Modern Geography'', abbreviated CATMOG, is a series of 59 short publications, each focused on an individual method or theory in geography. Background and impact ''Concepts and Techniques in Modern Geography'' were produced by the Study Group in Quantitative Methods of the Institute of British Geographers. Each CATMOG publication was written on an individual topic in geography rather than a series of broad topics like traditional textbooks. This à la carte approach allowed only purchasing publications on topics of interest, keeping each CATMOG relatively cheap and accessible, lowering student costs. The first of these publications was published in 1975, and the last in 1996. Each was written by someone working professionally with its topic. As they focus on core concepts of the discipline and were written by experts in the field, they are still often cited today when discussing specific topics. The Quantitative Methods Research Group (QMRG) at the Roy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geography
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth description") is a field of science devoted to the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. The first recorded use of the word γεωγραφία was as a title of a book by Greek scholar Eratosthenes (276–194 BC). Geography is an all-encompassing discipline that seeks an understanding of Earth and its human and natural complexities—not merely where objects are, but also how they have changed and come to be. While geography is specific to Earth, many concepts can be applied more broadly to other celestial bodies in the field of planetary science. One such concept, the first law of geography, proposed by Waldo Tobler, is "everything is related to everything else, but near things are more related than distant things." Geography has been called "the world discipline" and "the bridge between the human and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cartography
Cartography (; from grc, χάρτης , "papyrus, sheet of paper, map"; and , "write") is the study and practice of making and using maps. Combining science, aesthetics and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality (or an imagined reality) can be modeled in ways that communicate spatial information effectively. The fundamental objectives of traditional cartography are to: * Set the map's agenda and select traits of the object to be mapped. This is the concern of map editing. Traits may be physical, such as roads or land masses, or may be abstract, such as toponyms or political boundaries. * Represent the terrain of the mapped object on flat media. This is the concern of map projections. * Eliminate characteristics of the mapped object that are not relevant to the map's purpose. This is the concern of generalization. * Reduce the complexity of the characteristics that will be mapped. This is also the concern of generalization. * Orchestrate the elements of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spatial Heterogeneity
Spatial heterogeneity is a property generally ascribed to a landscape or to a population. It refers to the uneven distribution of various concentrations of each species within an area. A landscape with spatial heterogeneity has a mix of concentrations of multiple species of plants or animals (biological), or of terrain formations (geological), or environmental characteristics (e.g. rainfall, temperature, wind) filling its area. A population showing spatial heterogeneity is one where various concentrations of individuals of this species are unevenly distributed across an area; nearly synonymous with "patchily distributed." Examples Environments with a wide variety of habitats such as different topographies, soil types, and climates are able to accommodate a greater amount of species. The leading scientific explanation for this is that when organisms can finely subdivide a landscape into unique suitable habitats, more species can coexist in a landscape without competition, a phenome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spatial Autocorrelation
Spatial analysis or spatial statistics includes any of the formal techniques which studies entities using their topological, geometric, or geographic properties. Spatial analysis includes a variety of techniques, many still in their early development, using different analytic approaches and applied in fields as diverse as astronomy, with its studies of the placement of galaxies in the cosmos, to chip fabrication engineering, with its use of "place and route" algorithms to build complex wiring structures. In a more restricted sense, spatial analysis is the technique applied to structures at the human scale, most notably in the analysis of geographic data or transcriptomics data. Complex issues arise in spatial analysis, many of which are neither clearly defined nor completely resolved, but form the basis for current research. The most fundamental of these is the problem of defining the spatial location of the entities being studied. Classification of the techniques of spatia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Council For Geographic Education
The National Council for Geographic Education (NCGE), chartered in 1915, is a non-profit scientific and educational society in the United States that promotes and supports geography education. Annual conference NCGE holds an annual conference every summer, called the National Conference on Geography Education. This annual event offers hands-on workshops in new teaching methods, technologies, resources, as well as research papers, networking opportunities, field trips and more. Conference field trips include local and regional places of geographic and historical significance. An exhibit hall is staffed by government, industry, nonprofit, and academic organizations and offers the latest in books, journals, projects, curriculum, software, hardware, and more to support geography teaching. Each conference is highlighted by an annual keynote address. Past keynote speakers have included: From 1915 to the late 1970s the NCGE conference was held in a few select US cities. In 1979 the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
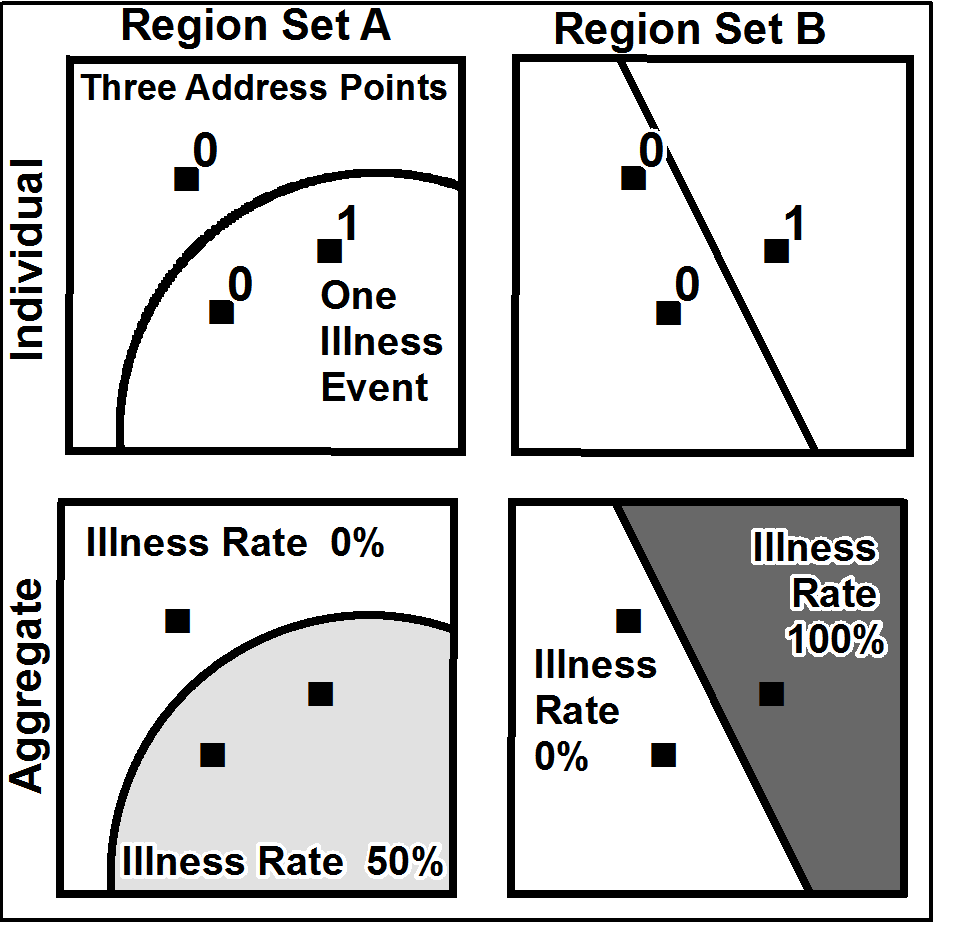
Modifiable Areal Unit Problem
__NOTOC__ The modifiable areal unit problem (MAUP) is a source of statistical bias that can significantly impact the results of statistical hypothesis tests. MAUP affects results when point-based measures of spatial phenomena are aggregated into districts, for example, population density or illness rates. The resulting summary values (e.g., totals, rates, proportions, densities) are influenced by both the shape and scale of the aggregation unit. For example, census data may be aggregated into county districts, census tracts, postcode areas, police precincts, or any other arbitrary spatial partition. Thus the results of data aggregation are dependent on the mapmaker's choice of which "modifiable areal unit" to use in their analysis. A census choropleth map calculating population density using state boundaries will yield radically different results than a map that calculates density based on county boundaries. Furthermore, census district boundaries are also subject to change over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Level Of Analysis
The term "level of analysis" is used in the social sciences to point to the location, size, or scale of a research target. "Level of analysis" is distinct from the term "unit of observation" in that the former refers to a more or less integrated set of relationships while the latter refers to the distinct unit from which data have been or will be gathered. Together, the unit of observation and the level of analysis help define the population of a research enterprise. Level of analysis vs unit of analysis Level of analysis is closely related to the term unit of analysis, and some scholars have used them interchangingly, while others argue for a need for distinction. Ahmet Nuri Yurdusev wrote that "the level of analysis is more of an issue related to the framework/context of analysis and the level at which one conducts one's analysis, whereas the question of the unit of analysis is a matter of the 'actor' or the 'entity' to be studied". Manasseh Wepundi noted the difference between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indicators Of Spatial Association
Indicators of spatial association are statistics that evaluate the existence of clusters in the spatial arrangement of a given variable. For instance, if we are studying cancer rates among census tracts in a given city local clusters in the rates mean that there are areas that have higher or lower rates than is to be expected by chance alone; that is, the values occurring are above or below those of a random distribution in space. Global indicators Notable global indicators of spatial association include: * Global Moran's ''I'': The most commonly used measure of global spatial autocorrelation or the overall clustering of the spatial data developed by Patrick Alfred Pierce Moran. * Geary's ''C'' (Geary's Contiguity Ratio): A measure of global spatial autocorrelation developed by Geary in 1954. It is inversely related to Moran's ''I'', but more sensitive to local autocorrelation than Moran's ''I''. * Getis–Ord ''G'' (Getis–Ord global G, Geleral G-Statistic): Introduced by Geti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geographic Information Science
Geographic information science or geographical information science (GIScience or GISc) is the scientific discipline that studies geographic information, including how it represents phenomena in the real world, how it represents the way humans understand the world, and how it can be captured, organized, and analyzed. It can be contrasted with geographic information systems (GIS), which are the actual repositories of such data, the software tools for carrying out relevant tasks, and the profession of GIS users. That said, one of the major goals of GIScience is to find practical ways to improve GIS data, software, and professional practice. it is more focused on how gis is applied in real life British geographer Michael Goodchild defined this area in the 1990s and summarized its core interests, including spatial analysis, visualization, and the representation of uncertainty. GIScience is conceptually related to geomatics, information science, computer science, but it claims the sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geographic Information Systems
A geographic information system (GIS) is a type of database containing geographic data (that is, descriptions of phenomena for which location is relevant), combined with software tools for managing, analyzing, and visualizing those data. In a broader sense, one may consider such a system to also include human users and support staff, procedures and workflows, body of knowledge of relevant concepts and methods, and institutional organizations. The uncounted plural, ''geographic information systems'', also abbreviated GIS, is the most common term for the industry and profession concerned with these systems. It is roughly synonymous with geoinformatics and part of the broader geospatial field, which also includes GPS, remote sensing, etc. Geographic information science, the academic discipline that studies these systems and their underlying geographic principles, may also be abbreviated as GIS, but the unambiguous GIScience is more common. GIScience is often considered a subdiscip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geodesy
Geodesy ( ) is the Earth science of accurately measuring and understanding Earth's figure (geometric shape and size), orientation in space, and gravity. The field also incorporates studies of how these properties change over time and equivalent measurements for other planets (known as '' planetary geodesy''). Geodynamical phenomena, including crustal motion, tides and polar motion, can be studied by designing global and national control networks, applying space geodesy and terrestrial geodetic techniques and relying on datums and coordinate systems. The job title is geodesist or geodetic surveyor. History Definition The word geodesy comes from the Ancient Greek word ''geodaisia'' (literally, "division of Earth"). It is primarily concerned with positioning within the temporally varying gravitational field. Geodesy in the German-speaking world is divided into "higher geodesy" ( or ), which is concerned with measuring Earth on the global scale, and "practical geodes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geographic Information Science And Technology Body Of Knowledge
__NOTOC__ The Geographic Information Science and Technology Body of Knowledge (GISTBoK) is a reference document produced by the University Consortium for Geographic Information Science (UCGIS) as the first product of its Model Curricula project, started in 1997 by Duane Marble and a select task force, and completed in 2006 by David DiBiase and a team of editors. The ''GISTBoK'' is the most successful effort to date to create a comprehensive outline of the concepts and skills unique to the geospatial realm, including geographic information systems, geographic information science, remote sensing, satellite navigation systems, and cartography. However, it is missing some topics, such as geocoding, and has significant granularity issues: large, mature subfields such as surveying, GPS, and remote sensing are covered in small sections, while the relatively immature field of geocomputation is granted an entire knowledge area. There is also opposition to the document as a whole, especial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |