|
Concavification
In mathematics, concavification is the process of converting a non-concave function to a concave function. A related concept is convexification – converting a non-convex function to a convex function. It is especially important in economics and mathematical optimization. Concavification of a quasiconcave function by monotone transformation An important special case of concavification is where the original function is a quasiconcave function. It is known that: * Every concave function is quasiconcave, but the opposite is not true. * Every monotone transformation of a quasiconcave function is also quasiconcave. For example, if f(x) is quasiconcave and g(\cdot) is a monotonically-increasing function, then g(f(x)) is also quasiconcave. Therefore, a natural question is: ''given a quasiconcave function'' f(x), ''does there exist a monotonically increasing'' g(\cdot) ''such that'' g(f(x)) ''is concave?'' Positive and negative examples As a positive example, consider the function f(x ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concave Function
In mathematics, a concave function is the negative of a convex function. A concave function is also synonymously called concave downwards, concave down, convex upwards, convex cap, or upper convex. Definition A real-valued function f on an interval (or, more generally, a convex set in vector space) is said to be ''concave'' if, for any x and y in the interval and for any \alpha \in ,1/math>, :f((1-\alpha )x+\alpha y)\geq (1-\alpha ) f(x)+\alpha f(y) A function is called ''strictly concave'' if :f((1-\alpha )x + \alpha y) > (1-\alpha) f(x) + \alpha f(y)\, for any \alpha \in (0,1) and x \neq y. For a function f: \mathbb \to \mathbb, this second definition merely states that for every z strictly between x and y, the point (z, f(z)) on the graph of f is above the straight line joining the points (x, f(x)) and (y, f(y)). A function f is quasiconcave if the upper contour sets of the function S(a)=\ are convex sets. Properties Functions of a single variable # A differentiab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quasiconcave Function
In mathematics, a quasiconvex function is a real-valued function defined on an interval or on a convex subset of a real vector space such that the inverse image of any set of the form (-\infty,a) is a convex set. For a function of a single variable, along any stretch of the curve the highest point is one of the endpoints. The negative of a quasiconvex function is said to be quasiconcave. All convex functions are also quasiconvex, but not all quasiconvex functions are convex, so quasiconvexity is a generalization of convexity. ''Univariate'' unimodal functions are quasiconvex or quasiconcave, however this is not necessarily the case for functions with multiple arguments. For example, the 2-dimensional Rosenbrock function is unimodal but not quasiconvex and functions with star-convex sublevel sets can be unimodal without being quasiconvex. Definition and properties A function f:S \to \mathbb defined on a convex subset S of a real vector space is quasiconvex if for all x, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
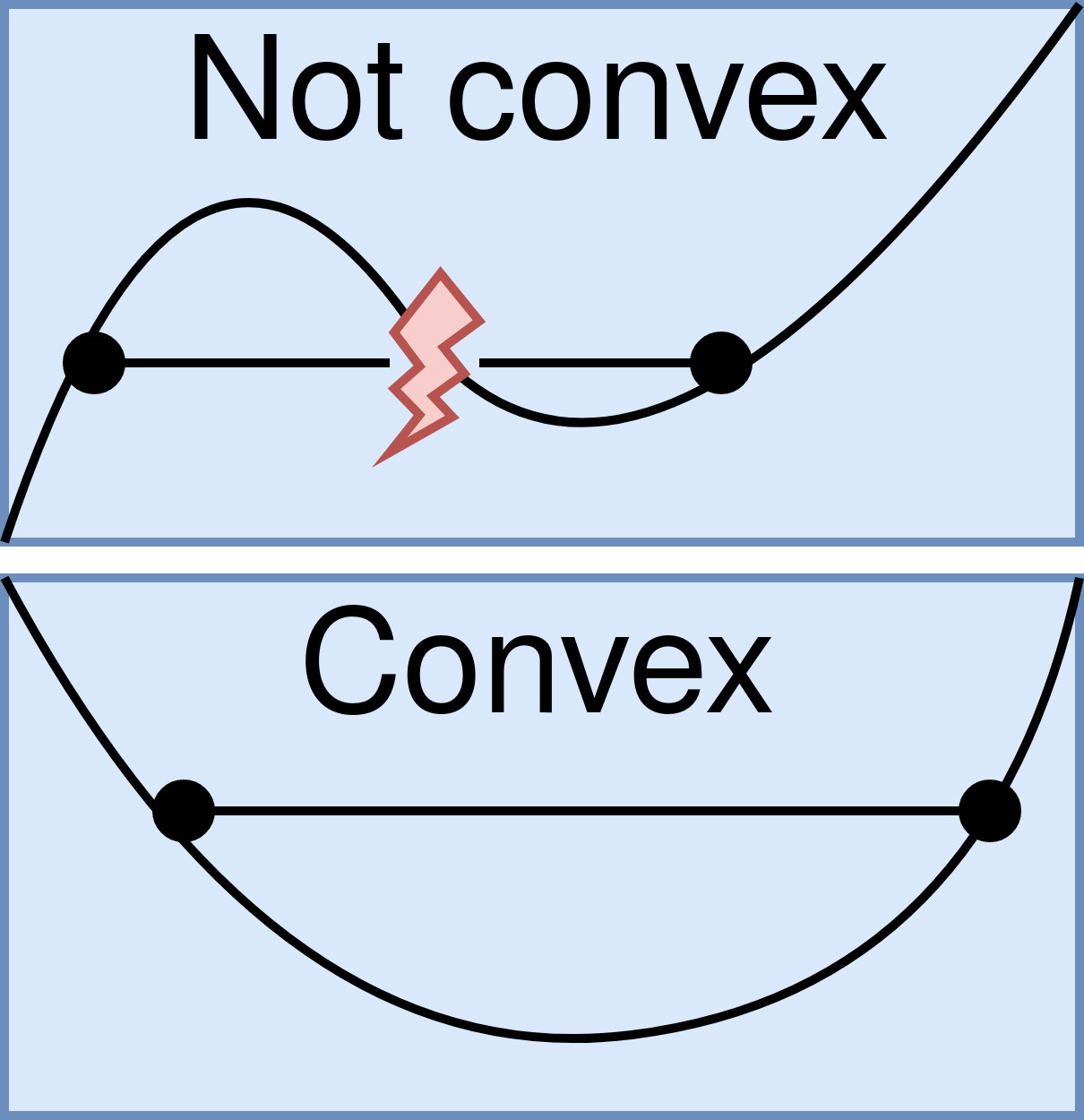
Convex Function
In mathematics, a real-valued function is called convex if the line segment between any two points on the graph of a function, graph of the function lies above the graph between the two points. Equivalently, a function is convex if its epigraph (mathematics), epigraph (the set of points on or above the graph of the function) is a convex set. A twice-differentiable function of a single variable is convex if and only if its second derivative is nonnegative on its entire domain. Well-known examples of convex functions of a single variable include the quadratic function x^2 and the exponential function e^x. In simple terms, a convex function refers to a function whose graph is shaped like a cup \cup, while a concave function's graph is shaped like a cap \cap. Convex functions play an important role in many areas of mathematics. They are especially important in the study of optimization problems where they are distinguished by a number of convenient properties. For instance, a st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economics
Economics () is the social science that studies the Production (economics), production, distribution (economics), distribution, and Consumption (economics), consumption of goods and services. Economics focuses on the behaviour and interactions of Agent (economics), economic agents and how economy, economies work. Microeconomics analyzes what's viewed as basic elements in the economy, including individual agents and market (economics), markets, their interactions, and the outcomes of interactions. Individual agents may include, for example, households, firms, buyers, and sellers. Macroeconomics analyzes the economy as a system where production, consumption, saving, and investment interact, and factors affecting it: employment of the resources of labour, capital, and land, currency inflation, economic growth, and public policies that have impact on glossary of economics, these elements. Other broad distinctions within economics include those between positive economics, desc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematical Optimization
Mathematical optimization (alternatively spelled ''optimisation'') or mathematical programming is the selection of a best element, with regard to some criterion, from some set of available alternatives. It is generally divided into two subfields: discrete optimization and continuous optimization. Optimization problems of sorts arise in all quantitative disciplines from computer science and engineering to operations research and economics, and the development of solution methods has been of interest in mathematics for centuries. In the more general approach, an optimization problem consists of maxima and minima, maximizing or minimizing a Function of a real variable, real function by systematically choosing Argument of a function, input values from within an allowed set and computing the Value (mathematics), value of the function. The generalization of optimization theory and techniques to other formulations constitutes a large area of applied mathematics. More generally, opti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utility Function
As a topic of economics, utility is used to model worth or value. Its usage has evolved significantly over time. The term was introduced initially as a measure of pleasure or happiness as part of the theory of utilitarianism by moral philosophers such as Jeremy Bentham and John Stuart Mill. The term has been adapted and reapplied within neoclassical economics, which dominates modern economic theory, as a utility function that represents a single consumer's preference ordering over a choice set but is not comparable across consumers. This concept of utility is personal and based on choice rather than on pleasure received, and so is specified more rigorously than the original concept but makes it less useful (and controversial) for ethical decisions. Utility function Consider a set of alternatives among which a person can make a preference ordering. The utility obtained from these alternatives is an unknown function of the utilities obtained from each alternative, not the sum of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convex Preferences
In economics, convex preferences are an individual's ordering of various outcomes, typically with regard to the amounts of various goods consumed, with the property that, roughly speaking, "averages are better than the extremes". The concept roughly corresponds to the concept of diminishing marginal utility without requiring utility functions. Notation Comparable to the greater-than-or-equal-to ordering relation \geq for real numbers, the notation \succeq below can be translated as: 'is at least as good as' (in preference satisfaction). Similarly, \succ can be translated as 'is strictly better than' (in preference satisfaction), and Similarly, \sim can be translated as 'is equivalent to' (in preference satisfaction). Definition Use ''x'', ''y'', and ''z'' to denote three consumption bundles (combinations of various quantities of various goods). Formally, a preference relation \succeq on the consumption set ''X'' is called convex if whenever :x, y, z \in X where y \succeq x a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |