|
Compression Arthralgia
Compression arthralgia is pain in the joints caused by exposure to high ambient pressure at a relatively high rate of compression, experienced by underwater divers. Also referred to in the U.S. Navy Diving Manual as compression pains. Compression arthralgia has been recorded as deep aching pain in the knees, shoulders, fingers, back, hips, neck and ribs. Pain may be sudden and intense in onset and may be accompanied by a feeling of roughness in the joints. Onset commonly occurs around 60 msw (meters of sea water), and symptoms are variable depending on depth, compression rate and personal susceptibility. Intensity increases with depth and may be aggravated by exercise. Compression arthralgia is generally a problem of deep diving, particularly deep saturation diving Saturation diving is diving for periods long enough to bring all tissues into equilibrium with the partial pressures of the inert components of the breathing gas used. It is a diving mode that reduces the number of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
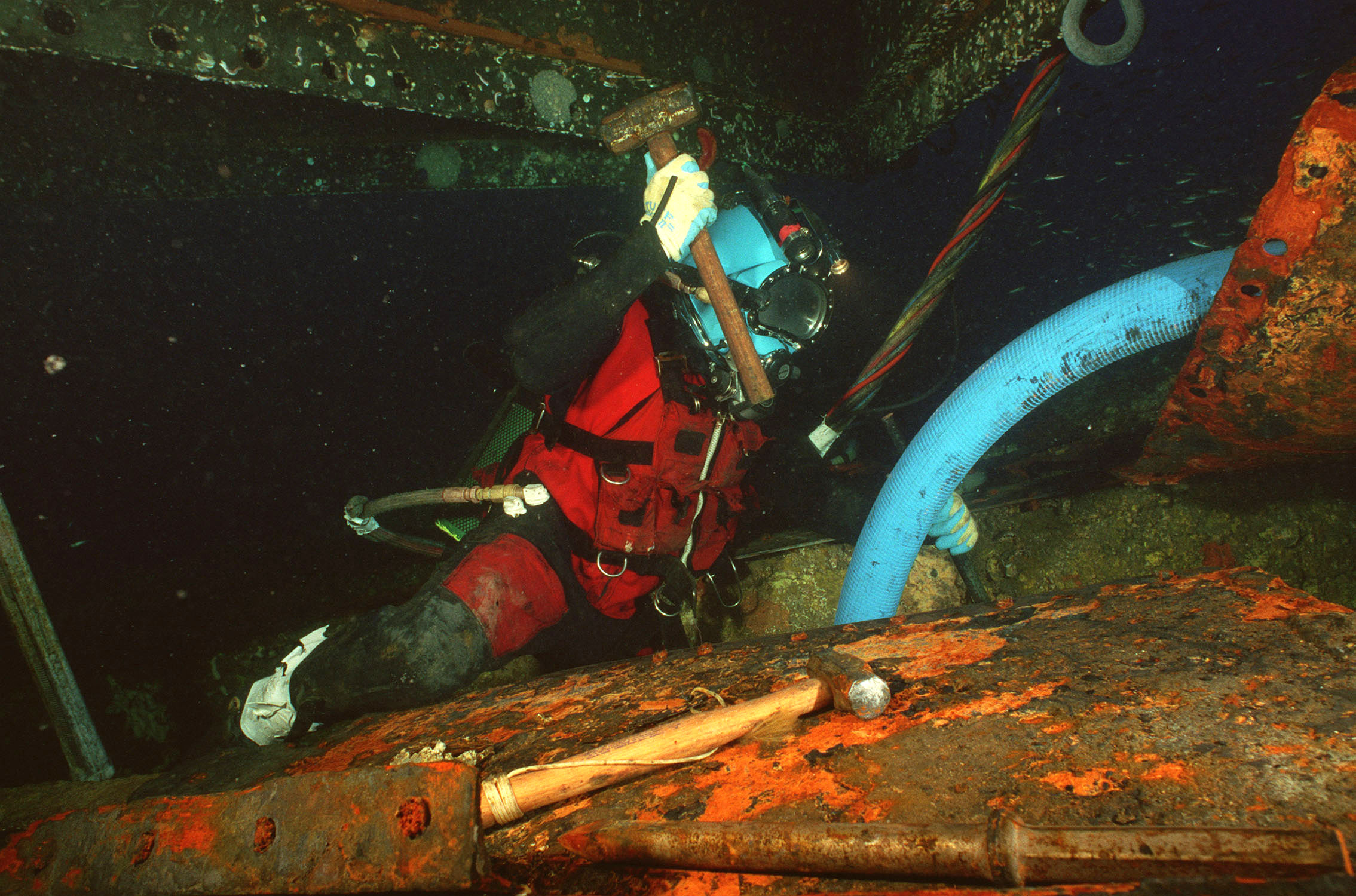
Underwater Diving
Underwater diving, as a human activity, is the practice of descending below the water's surface to interact with the environment. It is also often referred to as diving, an ambiguous term with several possible meanings, depending on context. Immersion in water and exposure to high ambient pressure have physiological effects that limit the depths and duration possible in ambient pressure diving. Humans are not physiologically and anatomically well-adapted to the environmental conditions of diving, and various equipment has been developed to extend the depth and duration of human dives, and allow different types of work to be done. In ambient pressure diving, the diver is directly exposed to the pressure of the surrounding water. The ambient pressure diver may dive on breath-hold (freediving) or use breathing apparatus for scuba diving or surface-supplied diving, and the saturation diving technique reduces the risk of decompression sickness (DCS) after long-duration deep dives ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metres Sea Water
The metre (or meter) sea water (msw) is a metric unit of pressure used in underwater diving. It is defined as one tenth of a bar. The unit used in the US is the foot sea water (fsw), based on standard gravity and a sea-water density of 64 lb/ft3. According to the US Navy Diving Manual, one fsw equals 0.30643 msw, , or , though elsewhere it states that 33 fsw is (one atmosphere), which gives one fsw equal to about 0.445 psi.Page 2-12. The msw and fsw are the conventional units for measurement of diver pressure exposure used in decompression tables and the unit of calibration for pneumofathometers and hyperbaric chamber pressure gauges. Feet of sea water One atmosphere is approximately equal to 33 feet of sea water or 14.7 psi, which gives 4.9/11 or about 0.445 psi per foot. Atmospheric pressure may be considered constant at sea level, and minor fluctuations caused by the weather are usually ignored. Pressures measured in fsw and msw are gauge pressure, rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saturation Diving
Saturation diving is diving for periods long enough to bring all tissues into equilibrium with the partial pressures of the inert components of the breathing gas used. It is a diving mode that reduces the number of decompressions divers working at great depths must undergo by only decompressing divers once at the end of the diving operation, which may last days to weeks, having them remain under pressure for the whole period. A diver breathing pressurized gas accumulates dissolved inert gas used in the breathing mixture to dilute the oxygen to a non-toxic level in his or her tissues, which can cause decompression sickness ("the bends") if permitted to come out of solution within the body tissues; hence, returning to the surface safely requires lengthy decompression so that the inert gases can be eliminated via the lungs. Once the dissolved gases in a diver's tissues reach the saturation point, however, decompression time does not increase with further exposure, as no more inert g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter B
Peter may refer to: People * List of people named Peter, a list of people and fictional characters with the given name * Peter (given name) ** Saint Peter (died 60s), apostle of Jesus, leader of the early Christian Church * Peter (surname), a surname (including a list of people with the name) Culture * Peter (actor) (born 1952), stage name Shinnosuke Ikehata, Japanese dancer and actor * Peter (album), ''Peter'' (album), a 1993 EP by Canadian band Eric's Trip * Peter (1934 film), ''Peter'' (1934 film), a 1934 film directed by Henry Koster *Peter (2021 film), ''Peter'' (2021 film), Marathi language film * Peter (Fringe episode), "Peter" (''Fringe'' episode), an episode of the television series ''Fringe'' * Peter (novel), ''Peter'' (novel), a 1908 book by Francis Hopkinson Smith * Peter (short story), "Peter" (short story), an 1892 short story by Willa Cather Animals * Peter, the Lord's cat, cat at Lord's Cricket Ground in London * Peter (chief mouser), Chief Mouser between 1929 a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trimix (breathing Gas)
Trimix is a breathing gas consisting of oxygen, helium and nitrogen and is used in deep commercial diving, during the deep phase of dives carried out using technical diving techniques, and in advanced recreational diving. The helium is included as a substitute for some of the nitrogen, to reduce the narcotic effect of the breathing gas at depth. With a mixture of three gases it is possible to create mixes suitable for different depths or purposes by adjusting the proportions of each gas. Oxygen content can be optimised for the depth to limit the risk of toxicity, and the inert component balanced between nitrogen (which is cheap but narcotic) and helium (which is not narcotic and reduces work of breathing, but is more expensive and increases heat loss). The mixture of helium and oxygen with a 0% nitrogen content is generally known as heliox. This is frequently used as a breathing gas in deep commercial diving operations, where it is often recycled to save the expensive helium c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Undersea And Hyperbaric Medical Society
The underwater environment is the region below the surface of, and immersed in, liquid water in a natural or artificial feature (called a body of water), such as an ocean, sea, lake, pond, reservoir, river, canal, or aquifer. Some characteristics of the underwater environment are universal, but many depend on the local situation. Liquid water has been present on Earth for most of the history of the planet. The underwater environment is thought to be the place of the origin of life on Earth, and it remains the ecological region most critical to the support of life and the natural habitat of the majority of living organisms. Several branches of science are dedicated to the study of this environment or specific parts or aspects of it. A number of human activities are conducted in the more accessible parts of the underwater environment. These include research, underwater diving for work or recreation, and underwater warfare with submarines. It is hostile to humans in many ways a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diving Medicine
Diving medicine, also called undersea and hyperbaric medicine (UHB), is the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of conditions caused by humans entering the undersea environment. It includes the effects on the body of pressure on gases, the diagnosis and treatment of conditions caused by marine hazards and how relationships of a diver's fitness to dive affect a diver's safety. Diving medical practitioners are also expected to be competent in the examination of divers and potential divers to determine fitness to dive. Hyperbaric medicine is a corollary field associated with diving, since recompression in a hyperbaric chamber is used as a treatment for two of the most significant diving-related illnesses, decompression sickness and arterial gas embolism. Diving medicine deals with medical research on issues of diving, the prevention of diving disorders, treatment of diving accidents and diving fitness. The field includes the effect of breathing gases and their contaminants under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



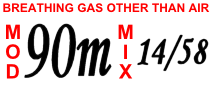
.jpg)
