|
Composition Roller
A composition roller is a tool used in letterpress printing to apply ink to a bed of type in a printing press. It consists of a cylinder made of a substance known as "roller composition" or simply "composition", a mixture of glue and sugar (in the form of molasses or treacle), with various additives such as glycerin depending on the particular recipe. Early recipes also included gypsum plaster and tar, though these were eventually found unnecessary. Before its invention, most inking of printing presses was done by manually pounding the type with ink balls, specially treated leather balls stuffed with wool. The difficulty and time involved in making and using ink balls led to various attempts to use cylinders, which could be rolled rather than pounded. Leather rollers (or "skin rollers") were attempted, and were used on the earliest steam-powered cylinder presses, yet these did not work as well as the ink balls, and the stitching seam would appear on the printed type. Eventuall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typograph Composition Kettle - Section
Typography is the art and technique of typesetting, arranging type to make written language legibility, legible, readability, readable and beauty, appealing when displayed. The arrangement of type involves selecting typefaces, Point (typography), point sizes, line lengths, line-spacing (leading), and letter-spacing (tracking), as well as adjusting the space between pairs of letters (kerning). The term ''typography'' is also applied to the style, arrangement, and appearance of the letters, numbers, and symbols created by the process. Type design is a closely related craft, sometimes considered part of typography; most typographers do not design typefaces, and some type designers do not consider themselves typographers. Typography also may be used as an ornamental and decorative device, unrelated to the communication of information. Typography is the work of typesetting, typesetters (also known as Compositor (typesetting), compositors), typographers, graphic designers, art dire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seam (sewing)
In sewing, a seam is the join where two or more layers of fabric, leather, or other materials are held together with stitches. Prior to the invention of the sewing machine, all sewing was done by hand. Seams in modern mass-produced household textiles, sporting goods, and ready-to-wear clothing are sewn by computerized machines, while home shoemaking, dressmaking, quilting, crafts, haute couture and tailoring may use a combination of hand and machine sewing.Schaeffer (2001), p. 35 In clothing construction, seams are classified by their ''type'' (plain, lapped, abutted, or French seams) and ''position'' in the finished garment (center back seam, inseam, side seam). Seams are ''finished'' with a variety of techniques to prevent raveling of raw fabric edges and to neaten the inside of garments. Types All basics seams used in clothing construction are variants on four basic types of seams: * Plain seams * French seams * Flat or abutted seams * Lapped seams A plain seam is the mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ink Ball
An ink ball, inking ball, or dabber was a tool used in printmaking and letterpress printing to apply ink to the plate or type to be printed. Ink balls had been used since the dawn of the printing press in the 15th century. In printmaking, they were used individually, to make the ink smooth and applying it. In letterpress printing, they were used in pairs: ink was placed on one of the two balls, which were then held together and worked around until a proper thickness, consistency, and uniformity was reached. The inker then "beat" the type to apply the ink, making sure to get neither too much nor too little ink on the form. An ink ball consists of a piece of specially-treated sheepskin stuffed with wool, with wooden cupped rod as a handle ("stock"). After the invention of composition (a mixture of glue, molasses, and tar) in the early 19th century, some ink balls began to be made from that until they faded from use. By the mid- to late-19th century, they had been largely supersed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brayer
A brayer is a hand-tool used historically in printing and printmaking to break up and "rub out" (spread) ink, before it was "beaten" using inking balls or composition rollers. The word is derived from the verb to "bray", meaning "to break, pound, or grind small, as in a mortar". A brayer consists of a short wooden cylinder with a handle fitted to one end; the other, flat end is used to rub the ink. In the late nineteenth century the term was applied in the United States to a small hand-roller, "used for spreading ink on the inking table, and for applying it to the distributing plates or rollers connected with presses". Such small rollers were sold as "brayers" from at least 1912 and later in the century the term was applied in the U.S. to hand-rollers of all sorts and sizes. It retains its original meaning in Europe. Materials Brayers in the original sense were generally made of wood (though Southward refers to their being made of "wood or glass").John Southward, ''Practical prin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Candy
Candy, also called sweets (British English) or lollies (Australian English Australian English (AusE, AusEng, AuE, AuEng, en-AU) is the set of varieties of the English language native to Australia. It is the country's common language and ''de facto'' national language; while Australia has no official language, Engli ..., New Zealand English), is a Confectionery, confection that features sugar as a principal ingredient. The category, called ''sugar confectionery'', encompasses any sweet confection, including chocolate, chewing gum, and sugar candy. Vegetable, Vegetables, fruit, or Nut (fruit), nuts which have been glaze (cooking technique), glazed and coated with sugar are said to be ''Candied fruit, candied''. Physically, candy is characterized by the use of a significant amount of sugar or sugar substitutes. Unlike a cake or loaf of bread that would be shared among many people, candies are usually made in smaller pieces. However, the definition of candy also depends ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bryan Donkin
Bryan Donkin FRS FRAS (22 March 1768 – 27 February 1855) developed the first paper making machine and created the world's first commercial canning factory. These were the basis for large industries that continue to flourish today. Bryan Donkin was involved with Thomas Telford's Caledonian Canal, Marc and Isambard Brunel's Thames Tunnel, and Charles Babbage's computer. He was an advisor to the government and held in high esteem by his peers. Early life Raised in Sandhoe, Northumberland, his father was a surveyor and land agent. Donkin initially began work in the same business, and worked from September 1789 to February 1791 as bailiff at Knole House and estate for the Duke of Dorset. Career While working for the Duke of Dorset, Donkin consulted the engineer John Smeaton, an acquaintance of his father, as to how he could become an engineer. At Smeaton's advice in 1792 he apprenticed himself to John Hall in Dartford, Kent, who had founded the Dartford Iron Works (later J & ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Harrild
Robert Harrild (1 January 1780 – 28 July 1853) was an English printing pioneer. Harrild was the founder of the business Harrild & Sons, his history is recorded in 'The House of Harrild' by Edward Liveing written in 1949, which gives the complete history of the Company, and also many names and dates of Harrilds. Early life Robert Harrild, born in Bermondsey, London, England, was the second son of Robert Harrild of Surrey and his wife Sarah Johnson. In 1801, at the age of 21, Harrild set up in partnership with Edward Billing at the Bluecoat-Boy Printing Office, Russell Street, Bermondsey. In the same year, Harrild married Edward Billing's sister, Elizabeth. Joseph Billing, son of Thomas Billing and nephew of Edward, later married Sarah Harrild, daughter of Robert. Seven of Robert and Elizabeth's ten children survived into adulthood, their daughter Mary married the colour-printing innovator George Baxter (printer), Baxter's sister Mary married Robert's eldest son and heir Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elasticity (physics)
In physics and materials science, elasticity is the ability of a body to resist a distorting influence and to return to its original size and shape when that influence or force is removed. Solid objects will deform when adequate loads are applied to them; if the material is elastic, the object will return to its initial shape and size after removal. This is in contrast to ''plasticity'', in which the object fails to do so and instead remains in its deformed state. The physical reasons for elastic behavior can be quite different for different materials. In metals, the atomic lattice changes size and shape when forces are applied (energy is added to the system). When forces are removed, the lattice goes back to the original lower energy state. For rubbers and other polymers, elasticity is caused by the stretching of polymer chains when forces are applied. Hooke's law states that the force required to deform elastic objects should be directly proportional to the distance of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adhesion
Adhesion is the tendency of dissimilar particles or surfaces to cling to one another ( cohesion refers to the tendency of similar or identical particles/surfaces to cling to one another). The forces that cause adhesion and cohesion can be divided into several types. The intermolecular forces responsible for the function of various kinds of stickers and sticky tape fall into the categories of chemical adhesion, dispersive adhesion, and diffusive adhesion. In addition to the cumulative magnitudes of these intermolecular forces, there are also certain emergent mechanical effects. Surface energy Surface energy is conventionally defined as the work that is required to build an area of a particular surface. Another way to view the surface energy is to relate it to the work required to cleave a bulk sample, creating two surfaces. If the new surfaces are identical, the surface energy γ of each surface is equal to half the work of cleavage, W: γ = (1/2)W11. If the surfac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
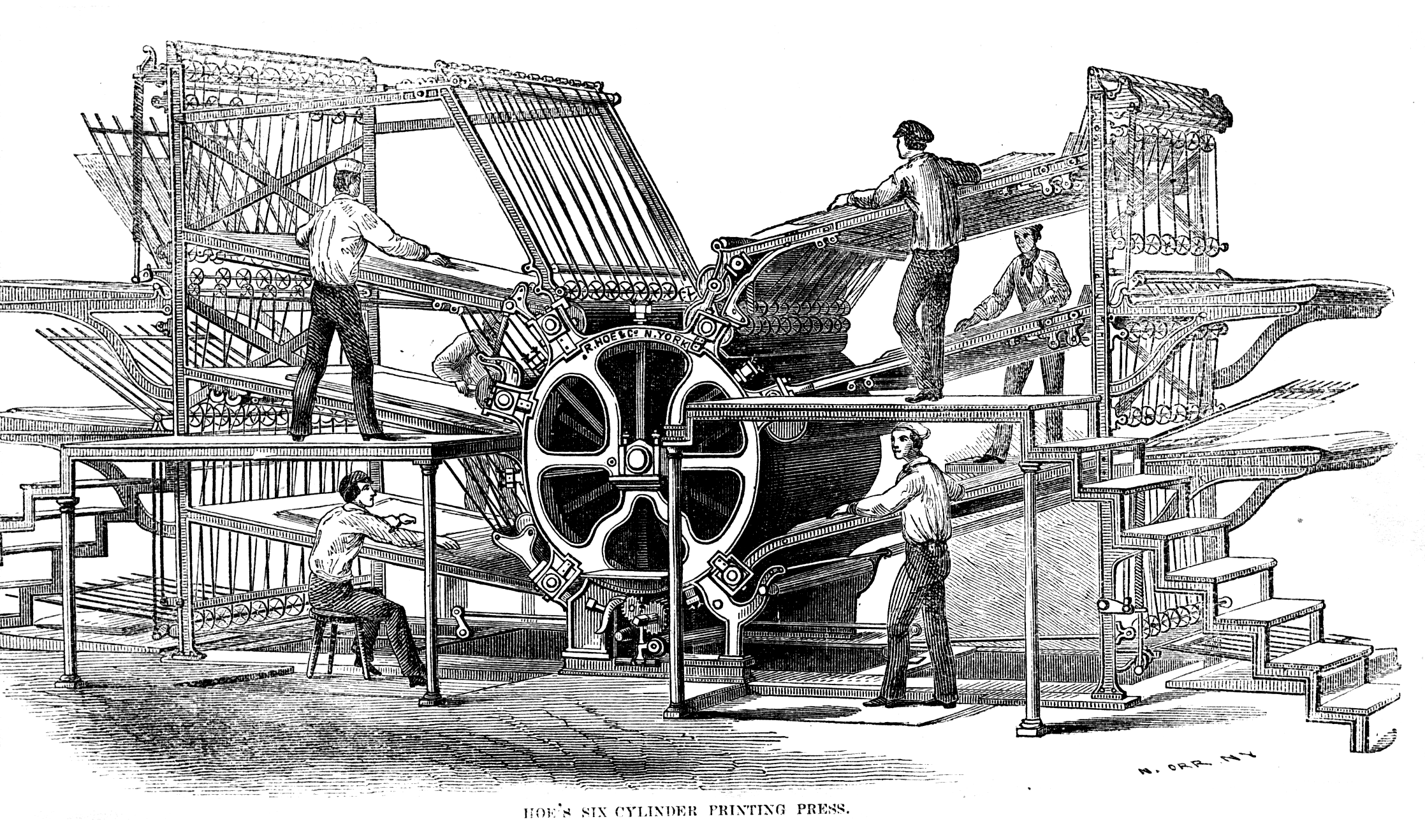
Cylinder Press
A rotary printing press is a printing press in which the images to be printed are curved around a cylinder. Printing can be done on various substrates, including paper, cardboard, and plastic. Substrates can be sheet feed or unwound on a continuous roll through the press to be printed and further modified if required (e.g. die cut, overprint varnished, embossed). Printing presses that use continuous rolls are sometimes referred to as "web presses". Developmental history William Nicholson filed a 1790 patent for a rotary press. The rotary press itself is an evolution of the cylinder press, also patented by William Nicholson, invented by Beaucher of France in the 1780s and by Friedrich Koenig in the early 19th century. Rotary drum printing has been claimed to be invented by Richard March Hoe in 1843, and perhaps slightly earlier by Josiah Warren. A1844 patentreplaced the reciprocating platforms used in earlier designs with a fixed platform served by rotating drums, and through a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Letterpress Printing
Letterpress printing is a technique of relief printing. Using a printing press, the process allows many copies to be produced by repeated direct impression of an inked, raised surface against sheets or a continuous roll of paper. A worker composes and locks movable type into the "bed" or "chase" of a press, inks it, and presses paper against it to transfer the ink from the type, which creates an impression on the paper. In practice, letterpress also includes other forms of relief printing with printing presses, such as wood engravings, photo-etched zinc "cuts" (plates), and linoleum blocks, which can be used alongside metal type, or wood type in a single operation, as well as stereotypes and electrotypes of type and blocks. With certain letterpress units, it is also possible to join movable type with slugs cast using hot metal typesetting. In theory, anything that is "type high" and so forms a layer exactly 0.918 in. thick between the bed and the paper can be printed using l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ink Ball
An ink ball, inking ball, or dabber was a tool used in printmaking and letterpress printing to apply ink to the plate or type to be printed. Ink balls had been used since the dawn of the printing press in the 15th century. In printmaking, they were used individually, to make the ink smooth and applying it. In letterpress printing, they were used in pairs: ink was placed on one of the two balls, which were then held together and worked around until a proper thickness, consistency, and uniformity was reached. The inker then "beat" the type to apply the ink, making sure to get neither too much nor too little ink on the form. An ink ball consists of a piece of specially-treated sheepskin stuffed with wool, with wooden cupped rod as a handle ("stock"). After the invention of composition (a mixture of glue, molasses, and tar) in the early 19th century, some ink balls began to be made from that until they faded from use. By the mid- to late-19th century, they had been largely supersed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)