|
Comparison Of Software Calculators
This is a list of notable software calculators. Immediate execution calculators (button-oriented) Expression or formula calculators (command-line oriented) See also * Software calculator * Calculator input methods * Formula calculator * Calculator * Graphing calculator * Scientific calculator A scientific calculator is an electronic calculator, either desktop or handheld, designed to perform mathematical operations. They have completely replaced slide rules and are used in both educational and professional settings. In some areas ... {{DEFAULTSORT:Comparison Of Software Calculators Software calculators Comparisons of mathematical software ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Calculator
A software calculator is a calculator that has been implemented as a computer program, rather than as a physical hardware device. They are among the simpler interactive software tools, and, as such, they provide operations for the user to select one at a time. They can be used to perform any process that consists of a sequence of steps each of which applies one of these operations, and have no purpose other than these processes, because the operations are the sole, or at least the primary, features of the calculator, rather than being secondary features that support other functionality that is not normally known simply as calculation. As a ''calculator'', rather than a computer, they usually have a small set of relatively simple operations, perform short processes that are not compute intensive and do not accept large amounts of input data or produce many results. Platforms Software calculators are available for many different platforms, and they can be: * A program for, or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berkeley Software Distribution
The Berkeley Software Distribution or Berkeley Standard Distribution (BSD) is a discontinued operating system based on Research Unix, developed and distributed by the Computer Systems Research Group (CSRG) at the University of California, Berkeley. The term "BSD" commonly refers to its open-source descendants, including FreeBSD, OpenBSD, NetBSD, and DragonFly BSD. BSD was initially called Berkeley Unix because it was based on the source code of the original Unix developed at Bell Labs. In the 1980s, BSD was widely adopted by workstation vendors in the form of proprietary Unix variants such as DEC Ultrix and Sun Microsystems SunOS due to its permissive licensing and familiarity to many technology company founders and engineers. Although these proprietary BSD derivatives were largely superseded in the 1990s by UNIX SVR4 and OSF/1, later releases provided the basis for several open-source operating systems including FreeBSD, OpenBSD, NetBSD, DragonFly BSD, Darwin, and TrueOS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Calculator
A scientific calculator is an electronic calculator, either desktop or handheld, designed to perform mathematical operations. They have completely replaced slide rules and are used in both educational and professional settings. In some areas of study scientific calculators have been replaced by graphing calculators and financial calculators which have the capabilities of a scientific calculator along with the capability to graph input data. Functions When scientific calculators were originally marketed they normally had only four of five capabilities (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division and square root). Modern scientific calculators generally have many more capabilities than the original four or five function calculator, and the capabilities differ between manufacturers and models. The capabilities of a modern scientific calculator include: * scientific notation * floating-point decimal arithmetic * logarithmic functions, using both base 10 and base e * t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphing Calculator
A graphing calculator (also graphics calculator or graphic display calculator) is a handheld computer that is capable of plotting graphs, solving simultaneous equations, and performing other tasks with variables. Most popular graphing calculators are programmable calculators, allowing the user to create customized programs, typically for scientific, engineering or education applications. They have large screens that display several lines of text and calculations. History An early graphing calculator was designed in 1921 by electrical engineer Edith Clarke. The calculator was used to solve problems with electrical power line transmission. Casio produced the first commercially available graphing calculator in 1985. Sharp produced its first graphing calculator in 1986. Hewlett Packard followed in 1988. Texas Instruments in 1990. Features Computer algebra systems Some graphing calculators have a computer algebra system (CAS), which means that they are capable of producing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calculator
An electronic calculator is typically a portable electronic device used to perform calculations, ranging from basic arithmetic to complex mathematics. The first solid-state electronic calculator was created in the early 1960s. Pocket-sized devices became available in the 1970s, especially after the Intel 4004, the first microprocessor, was developed by Intel for the Japanese calculator company Busicom. Modern electronic calculators vary from cheap, give-away, credit-card-sized models to sturdy desktop models with built-in printers. They became popular in the mid-1970s as the incorporation of integrated circuits reduced their size and cost. By the end of that decade, prices had dropped to the point where a basic calculator was affordable to most and they became common in schools. Computer operating systems as far back as early Unix have included interactive calculator programs such as dc and hoc, and interactive BASIC could be used to do calculations on most 1970s a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formula Calculator
A formula calculator is a software calculator that can perform a calculation in two steps: # Enter the calculation by typing it in from the keyboard. # Press a single button or key to see the final result. This is unlike button-operated calculators, such as the Windows calculator or the Mac OS X calculator, which require the user to perform one step for each operation, by pressing buttons to calculate all the intermediate values, before the final result is shown. In this context, a formula is also known as an expression, and so formula calculators may be called ''expression'' calculators. Also in this context, calculation is known as ''evaluation'', and so they may be called formula ''evaluators'', rather than ''calculators''. How they work Formulas as they are commonly written use infix notation for binary operators, such as addition, multiplication, division and subtraction. This notation also uses: * Parentheses to enclose parts of a formula that must be calculated fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calculator Input Methods
There are various ways in which calculators interpret keystrokes. These can be categorized into two main types: * On a single-step or immediate-execution calculator, the user presses a key for each operation, calculating all the intermediate results, before the final value is shown. * On an expression or formula calculator, one types in an expression and then presses a key, such as "=" or "Enter", to evaluate the expression. There are various systems for typing in an expression, as described below. Immediate execution The immediate execution mode of operation (also known as single-step, algebraic entry system (AES) or chain calculation mode) is commonly employed on most general-purpose calculators. In most simple four-function calculators, such as the Windows Calculator, Windows calculator in Standard mode and those included with most early operating systems, each binary operation is executed as soon as the next operator is pressed, and therefore the order of operations in a math ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Calculator
A software calculator is a calculator that has been implemented as a computer program, rather than as a physical hardware device. They are among the simpler interactive software tools, and, as such, they provide operations for the user to select one at a time. They can be used to perform any process that consists of a sequence of steps each of which applies one of these operations, and have no purpose other than these processes, because the operations are the sole, or at least the primary, features of the calculator, rather than being secondary features that support other functionality that is not normally known simply as calculation. As a ''calculator'', rather than a computer, they usually have a small set of relatively simple operations, perform short processes that are not compute intensive and do not accept large amounts of input data or produce many results. Platforms Software calculators are available for many different platforms, and they can be: * A program for, or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bc (programming Language)
bc, for ''basic calculator'' (often referred to as ''bench calculator''), is "''an arbitrary-precision calculator language''" with syntax similar to the C programming language. bc is typically used as either a mathematical scripting language or as an interactive mathematical shell. Overview A typical interactive usage is typing the command bc on a Unix command prompt and entering a mathematical expression, such as , whereupon will be output. While bc can work with arbitrary precision, it actually defaults to zero digits after the decimal point, so the expression yields (results are truncated, not rounded). This can surprise new bc users unaware of this fact. The option to bc sets the default ''scale'' (digits after the decimal point) to 20 and adds several additional mathematical functions to the language. History bc first appeared in Version 6 Unix in 1975. It was written by Lorinda Cherry of Bell Labs as a front end to dc, an arbitrary-precision calculator written by Rob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
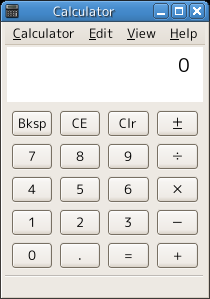
GNOME Calculator
GNOME Calculator, formerly known as gcalctool, is the software calculator integrated with the GNOME desktop environment. It is programmed in C and Vala and part of the GNOME Core Applications. Views * ''Basic'' – interface for basic arithmetic, resembling a desk calculator. * ''Advanced'' – an interface with scientific functions, and support for custom variables. * ''Financial'' – financial calculation and currency conversion. * ''Programming'' – a view with bit manipulation operators and radix conversion. * ''Keyboard'' – most of the space is taken up by the output, with no on-screen buttons. Supports currency and unit conversion. Notation The GNOME calculator uses the common infix notation for binary functions, such as the four basic arithmetic operations. Unlike many other calculators, it uses prefix notation, not postfix notation for unary functions. So to calculate e.g. the sine of one, the user must push the keys "sin", "1", "=" – not "1", "sin" as on many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xcalc
The X.Org Foundation is a non-profit corporation chartered to research, develop, support, organize, administrate, standardize, promote, and defend a free and open accelerated graphics stack. This includes, but is not limited to, the following projects: DRM, Mesa 3D, Wayland and the X Window System and its primary implementation, the X.Org Server. Organization The X.Org Foundation was founded on 22 January 2004. The modern X.Org Foundation came into being when the body that oversaw X standards and published the official reference implementation joined forces with former XFree86 developers. The creation of the Foundation marked a radical change in the governance of X (see the history of the X Window System). Whereas the stewards of X since 1988 (including the previous X.Org, part of The Open Group) had been vendor organizations, the Foundation is led by software developers and using community development on the bazaar model, which relies on outside involvement. Membership is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linux
Linux ( or ) is a family of open-source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically packaged as a Linux distribution, which includes the kernel and supporting system software and libraries, many of which are provided by the GNU Project. Many Linux distributions use the word "Linux" in their name, but the Free Software Foundation uses the name "GNU/Linux" to emphasize the importance of GNU software, causing some controversy. Popular Linux distributions include Debian, Fedora Linux, and Ubuntu, the latter of which itself consists of many different distributions and modifications, including Lubuntu and Xubuntu. Commercial distributions include Red Hat Enterprise Linux and SUSE Linux Enterprise. Desktop Linux distributions include a windowing system such as X11 or Wayland, and a desktop environment such as GNOME or KDE Plasma. Distributions intended for ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)