|
Comparison Of Multi-paradigm Programming Languages
Programming languages can be grouped by the number and types of paradigms supported. Paradigm summaries A concise reference for the programming paradigms listed in this article. * Concurrent programming – have language constructs for concurrency, these may involve multi-threading, support for distributed computing, message passing, shared resources (including shared memory), or futures ** Actor programming – concurrent computation with ''actors'' that make local decisions in response to the environment (capable of selfish or competitive behaviour) * Constraint programming – relations between variables are expressed as constraints (or constraint networks), directing allowable solutions (uses constraint satisfaction or simplex algorithm) * Dataflow programming – forced recalculation of formulas when data values change (e.g. spreadsheets) * Declarative programming – describes what computation should perform, without specifying detailed state changes cf. imperative pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Programming Language
A programming language is a system of notation for writing computer programs. Programming languages are described in terms of their Syntax (programming languages), syntax (form) and semantics (computer science), semantics (meaning), usually defined by a formal language. Languages usually provide features such as a type system, Variable (computer science), variables, and mechanisms for Exception handling (programming), error handling. An Programming language implementation, implementation of a programming language is required in order to Execution (computing), execute programs, namely an Interpreter (computing), interpreter or a compiler. An interpreter directly executes the source code, while a compiler produces an executable program. Computer architecture has strongly influenced the design of programming languages, with the most common type (imperative languages—which implement operations in a specified order) developed to perform well on the popular von Neumann architecture. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Reflective Programming
In computer science, reflective programming or reflection is the ability of a process to examine, introspect, and modify its own structure and behavior. Historical background The earliest computers were programmed in their native assembly languages, which were inherently reflective, as these original architectures could be programmed by defining instructions as data and using self-modifying code. As the bulk of programming moved to higher-level compiled languages such as ALGOL, COBOL, Fortran, Pascal, and C, this reflective ability largely disappeared until new programming languages with reflection built into their type systems appeared. Brian Cantwell Smith's 1982 doctoral dissertation introduced the notion of computational reflection in procedural programming languages and the notion of the meta-circular interpreter as a component of 3-Lisp. Uses Reflection helps programmers make generic software libraries to display data, process different formats of data, perform ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
BETA (programming Language)
BETA is a pure object-oriented language originating within the "Scandinavian School" in object-orientation where the first object-oriented language Simula was developed.SourceOle Lehrmann Madsen: An overview of BETA Among its notable features, it introduced nested classes, and unified classes with procedures into so called patterns. It has been in development since 1976, with implementations known since 1986, by Kristen Nygaard together with Bent Bruun Kristensen, Ole Lehrmann Madsen, and Birger Møller-Pedersen, at the University of Oslo. The project is inactive as of October 2020. Features Technical overview From a technical perspective, BETA provides several unique features. Classes and Procedures are unified to one concept, a Pattern. Also, classes are defined as properties/attributes of objects. This means that a class cannot be instantiated without an explicit object context. A consequence of this is that BETA supports nested classes. Classes can be virtually defined, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
APL (programming Language)
APL (named after the book ''A Programming Language'') is a programming language developed in the 1960s by Kenneth E. Iverson. Its central datatype is the multidimensional array. It uses a large range of special graphic symbols to represent most functions and operators, leading to very concise code. It has been an important influence on the development of concept modeling, spreadsheets, functional programming, and computer math packages. It has also inspired several other programming languages. History Mathematical notation A mathematical notation for manipulating arrays was developed by Kenneth E. Iverson, starting in 1957 at Harvard University. In 1960, he began work for IBM where he developed this notation with Adin Falkoff and published it in his book ''A Programming Language'' in 1962. The preface states its premise: This notation was used inside IBM for short research reports on computer systems, such as the Burroughs B5000 and its stack mechanism when stack m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
AmigaE
Amiga E is a programming language created by Wouter van Oortmerssen on the Amiga computer. The work on the language started in 1991 and was first released in 1993. The original incarnation of Amiga E was being developed until 1997, when the popularity of the Amiga platform dropped significantly after the bankruptcy of Amiga intellectual property owner Escom AG. According to Wouter van Oortmerssen:"It is a general-purpose programming language, and the Amiga implementation is specifically targeted at programming system applications. ..ref name=":0">"In his own words:"Amiga E was a tremendous success, it became one of the most popular programming languages on the Amiga." Overview Amiga E combines features from several languages but follows the original C programming language most closely in terms of basic concepts. Amiga E's main benefits are fast compilation (allowing it to be used in place of a scripting language), very readable source code, flexible type system, powerful mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Algebraic Logic Functional Programming Language
Algebraic Logic Functional (ALF) programming language combines functional and logic programming techniques. Its foundation is Horn clause logic with equality, which consists of predicates and Horn clauses for logic programming, and functions and equations for functional programming. ALF was designed to be genuine integration of both programming paradigms, and thus any functional expression can be used in a goal literal and arbitrary predicates can occur in conditions of equations. ALF's operational semantics is based on the resolution rule to solve literals and narrowing to evaluate functional expressions. To reduce the number of possible narrowing steps, a leftmost-innermost basic narrowing strategy is used which, it is claimed, can be efficiently implemented. Terms are simplified by rewriting before a narrowing step is applied and equations are rejected if the two sides have different constructors at the top. Rewriting and rejection are supposed to result in a large reduction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ada (programming Language)
Ada is a structured, statically typed, imperative, and object-oriented high-level programming language, inspired by Pascal and other languages. It has built-in language support for '' design by contract'' (DbC), extremely strong typing, explicit concurrency, tasks, synchronous message passing, protected objects, and non-determinism. Ada improves code safety and maintainability by using the compiler to find errors in favor of runtime errors. Ada is an international technical standard, jointly defined by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). , the standard, ISO/IEC 8652:2023, is called Ada 2022 informally. Ada was originally designed by a team led by French computer scientist Jean Ichbiah of Honeywell under contract to the United States Department of Defense (DoD) from 1977 to 1983 to supersede over 450 programming languages then used by the DoD. Ada was named after Ada Lovelace (1815–185 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Institute Of Electrical And Electronics Engineers
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) is an American 501(c)(3) public charity professional organization for electrical engineering, electronics engineering, and other related disciplines. The IEEE has a corporate office in New York City and an operations center in Piscataway, New Jersey. The IEEE was formed in 1963 as an amalgamation of the American Institute of Electrical Engineers and the Institute of Radio Engineers. History The IEEE traces its founding to 1884 and the American Institute of Electrical Engineers. In 1912, the rival Institute of Radio Engineers was formed. Although the AIEE was initially larger, the IRE attracted more students and was larger by the mid-1950s. The AIEE and IRE merged in 1963. The IEEE is headquartered in New York City, but most business is done at the IEEE Operations Center in Piscataway, New Jersey, opened in 1975. The Australian Section of the IEEE existed between 1972 and 1985, after which it split into state- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Simulink
Simulink is a MATLAB-based graphical programming environment for modeling, simulating and analyzing multidomain dynamical systems. Its primary interface is a graphical block diagramming tool and a customizable set of block libraries. It offers tight integration with the rest of the MATLAB environment and can either drive MATLAB or be scripted from it. Simulink is widely used in automatic control and digital signal processing for multidomain simulation and model-based design. Add-on products MathWorks and other third-party hardware and software products can be used with Simulink. For example, Stateflow extends Simulink with a design environment for developing state machines and flow charts. Coupled with another of their products, Simulink can automatically generate C source code for real-time implementation of systems. As the efficiency and flexibility of the code improves, this is becoming more widely adopted for production systems, in addition to being a tool for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
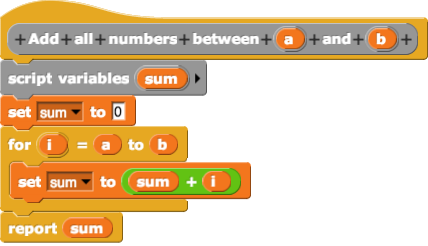
Visual Programming Language
In computing, a visual programming language (visual programming system, VPL, or, VPS), also known as diagrammatic programming, graphical programming or block coding, is a programming language that lets users create computer program, programs by manipulating program elements rather than by specifying them . A VPL allows programming with visual expressions, spatial arrangements of text and graphic symbols, used either as elements of syntax or secondary notation. For example, many VPLs are based on the idea of "boxes and arrows", where boxes or other screen objects are treated as entities, connected by arrows, lines or arcs which represent relations. VPLs are generally the basis of low-code development platforms. Definition VPLs may be further classified, according to the type and extent of visual expression used, into icon-based languages, form-based languages, and diagram languages. Visual programming environments provide graphical or iconic elements which can be manipulated by u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Rule-based Programming
In computer science, a rule-based system is a computer system in which domain-specific knowledge is represented in the form of rules and general-purpose reasoning is used to solve problems in the domain. Two different kinds of rule-based systems emerged within the field of artificial intelligence in the 1970s: * Production systems, which use ''if-then rules'' to derive ''actions'' from ''conditions''. * Logic programming systems, which use ''conclusion if conditions rules'' to derive ''conclusions'' from ''conditions''. The differences and relationships between these two kinds of rule-based system has been a major source of misunderstanding and confusion. Both kinds of rule-based systems use either forward or backward chaining, in contrast with imperative programs, which execute commands listed sequentially. However, logic programming systems have a logical interpretation, whereas production systems do not. Production system rules A classic example of a production rule-b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |