|
Compaq Portable Series
Compaq's first computers' form factors were portable, also called "luggables", and then "lunchbox computers", and together constituted the Compaq Portable series. These computers measured approximately deep, tall, and approximately wide. As the products evolved, laptops and notebooks were created offing a new level of portability that caused the market to explode. Some of the portables, the Portable and Portable II, had CRT monitors, while later the Portable III and the Portable 386) had flat, monochrome, usually amber, plasma displays. The portables came/could come with internal hard disk drives on 0.5" shock mount springs; diskette drives, usually 5-" double- or quadruple-density drives; batteries; and/or a dual- ISA expansion chassis, about one full-drive-height wide. Note this was before the term "ISA" became a standard. The Compaq Portable 486 included mono and color LCD screens and were battery powered. Machines of the series * Compaq Portable – Compaq's fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compaq Portable 286
The Compaq Portable was an early portable computer which was one of the first IBM PC compatible systems. It was Compaq Computer Corporation's first product, to be followed by others in the Compaq Portable series and later Compaq Deskpro series. It was not simply an 8088-CPU computer that ran a Microsoft DOS as a PC "work-alike", but contained a reverse-engineered BIOS, and a version of MS-DOS that was so similar to IBM's PC DOS that it ran nearly all its application software. The computer was also an early variation on the idea of an "all-in-one". It became available two years after the similar, but CP/M-based, Osborne 1 and Kaypro II. Columbia Data Products' MPC 1600 "Multi Personal Computer" had come out in June 1982. Other "work-alikes" included the MS-DOS and 8088-based, but not entirely IBM PC software compatible, Dynalogic Hyperion, Eagle Computer's Eagle 1600 series, including the Eagle Spirit portable, and the Corona personal computer The latter two companies were thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MS-DOS
MS-DOS ( ; acronym for Microsoft Disk Operating System, also known as Microsoft DOS) is an operating system for x86-based personal computers mostly developed by Microsoft. Collectively, MS-DOS, its rebranding as IBM PC DOS, and a few operating systems attempting to be compatible with MS-DOS, are sometimes referred to as "DOS" (which is also the generic acronym for disk operating system). MS-DOS was the main operating system for IBM PC compatibles during the 1980s, from which point it was gradually superseded by operating systems offering a graphical user interface (GUI), in various generations of the graphical Microsoft Windows operating system. IBM licensed and re-released it in 1981 as PC DOS 1.0 for use in its PCs. Although MS-DOS and PC DOS were initially developed in parallel by Microsoft and IBM, the two products diverged after twelve years, in 1993, with recognizable differences in compatibility, syntax, and capabilities. Beginning in 1988 with DR-DO ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
8088
The Intel 8088 ("''eighty-eighty-eight''", also called iAPX 88) microprocessor is a variant of the Intel 8086. Introduced on June 1, 1979, the 8088 has an eight-bit external data bus instead of the 16-bit bus of the 8086. The 16-bit registers and the one megabyte address range are unchanged, however. In fact, according to the Intel documentation, the 8086 and 8088 have the same execution unit (EU)—only the bus interface unit (BIU) is different. The original IBM PC is based on the 8088, as are its clones. History and description The 8088 was designed at Intel's laboratory in Haifa Haifa ( he, חֵיפָה ' ; ar, حَيْفَا ') is the third-largest city in Israel—after Jerusalem and Tel Aviv—with a population of in . The city of Haifa forms part of the Haifa metropolitan area, the third-most populous metropol ..., Israel, as were a large number of Intel's processors. The 8088 was targeted at economical systems by allowing the use of an eight-bit data path ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaypro II
Kaypro Corporation was an American home and personal computer manufacturer based out of San Diego in the 1980s. The company was founded by Non-Linear Systems (NLS) to compete with the popular Osborne 1 portable microcomputer. Kaypro produced a line of rugged, "luggable" CP/M-based computers sold with an extensive software bundle which supplanted its competitors and quickly became one of the top-selling personal computer lines of the early 1980s. Kaypro was exceptionally loyal to its original customer base but slow to adapt to the changing computer market and the advent of IBM PC compatible technology. It faded from the mainstream before the end of the decade and was eventually forced into bankruptcy in 1992. History Kaypro began as Non-Linear Systems, a maker of electronic test equipment, founded in 1952 by Andrew Kay, the inventor of the digital voltmeter. In the 1970s, NLS was an early adopter of microprocessor technology, which enhanced the flexibility of products such as pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osborne 1
The Osborne 1 is the first commercially successful portable computer, released on April 3, 1981 by Osborne Computer Corporation. It weighs , cost US$1,795, and runs the CP/M 2.2 operating system. It is powered from a wall socket, as it has no on-board battery, but it is still classed as a portable device since it can be hand-carried when the keyboard is closed. The computer shipped with a large bundle of software that was almost equivalent in value to the machine itself, a practice adopted by other CP/M computer vendors. Competitors quickly appeared, such as the Kaypro II. History The Osborne 1 was developed by Adam Osborne and designed by Lee Felsenstein, first announced in early 1981. Osborne, an author of computer books decided that he wanted to break the price of computers. The computer's design was based largely on the Xerox NoteTaker, a prototype developed at Xerox PARC in 1976 by Alan Kay. It was designed to be portable, with a rugged ABS plastic case and a handle. The Os ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CP/M
CP/M, originally standing for Control Program/Monitor and later Control Program for Microcomputers, is a mass-market operating system created in 1974 for Intel 8080/ 85-based microcomputers by Gary Kildall of Digital Research, Inc. Initially confined to single-tasking on 8-bit processors and no more than 64 kilobytes of memory, later versions of CP/M added multi-user variations and were migrated to 16-bit processors. The combination of CP/M and S-100 bus computers became an early standard in the microcomputer industry. This computer platform was widely used in business through the late 1970s and into the mid-1980s. CP/M increased the market size for both hardware and software by greatly reducing the amount of programming required to install an application on a new manufacturer's computer. An important driver of software innovation was the advent of (comparatively) low-cost microcomputers running CP/M, as independent programmers and hackers bought them and shared their crea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
All-in-one Computer
An all-in-one computer or all-in-one PC (AIO) is a personal computer that integrates the system's internal components into the same case as the display, thus occupying a smaller footprint (with fewer cables) than desktops that incorporate a tower. Advantages and disadvantages Some advantages of the all-in-one computer compared to other form factors include being easier to set up, a reduced physical footprint, ease of transportation, and the option to interface with the computer via touchscreen (a now-common fixture on all-in-ones). Some disadvantages include generally being more expensive than desktop computers, a lack of customizability—most of the internal hardware such as the RAM and the SSD, especially in post-late-2010s machines, is soldered onto the system board—a lack of upgrade paths for the CPU, RAM, and technology of the display, and the difficulty of repair. History This form factor was popular during the early 1980s for personal computers intended for professi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
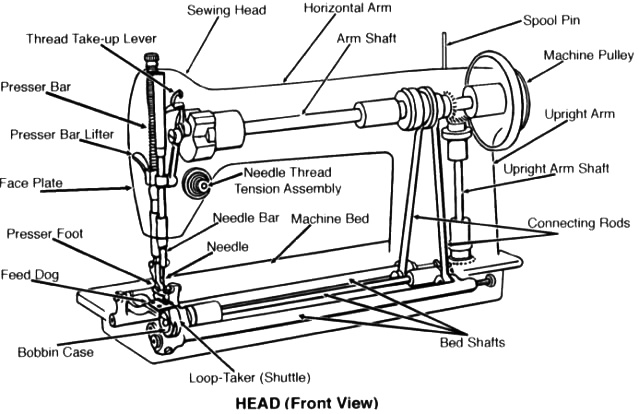
Sewing Machine
A sewing machine is a machine used to sew fabric and materials together with thread. Sewing machines were invented during the first Industrial Revolution to decrease the amount of manual sewing work performed in clothing companies. Since the invention of the first sewing machine, generally considered to have been the work of Englishman Thomas Saint in 1790, the sewing machine has greatly improved the efficiency and productivity of the clothing industry. Home sewing machines are designed for one person to sew individual items while using a single stitch type at a time. In a modern sewing machine, the process of stitching has been automated so that the fabric easily glides in and out of the machine without the inconvenience of needles, thimbles and other tools used in hand sewing. Early sewing machines were powered by either constantly turning a handle or with a foot-operated treadle mechanism. Electrically-powered machines were later introduced. Industrial sewing machines, by co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luggable
A portable computer is a computer designed to be easily moved from one place to another and included a display and keyboard together, with a single plug, much like later desktop computers called '' all-in-ones'' (AIO), that integrate the system's internal components into the same case as the display. The first commercially sold portable might be the MCM/70, released 1974. The next major portables were the IBM 5100 (1975), Osborne's CP/M-based Osborne 1 (1981) and Compaq's , advertised as 100% IBM PC compatible Compaq Portable (1983). These luggable computers still required a continuous connection to an external power source; this limitation was later overcome by the laptop. Laptops were followed by lighter models, so that in the 2000s mobile devices and by 2007 smartphones made the term almost meaningless. The 2010s introduced wearable computers such as smartwatches. Portable computers, by their nature, are generally microcomputers. Larger portable computers were common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
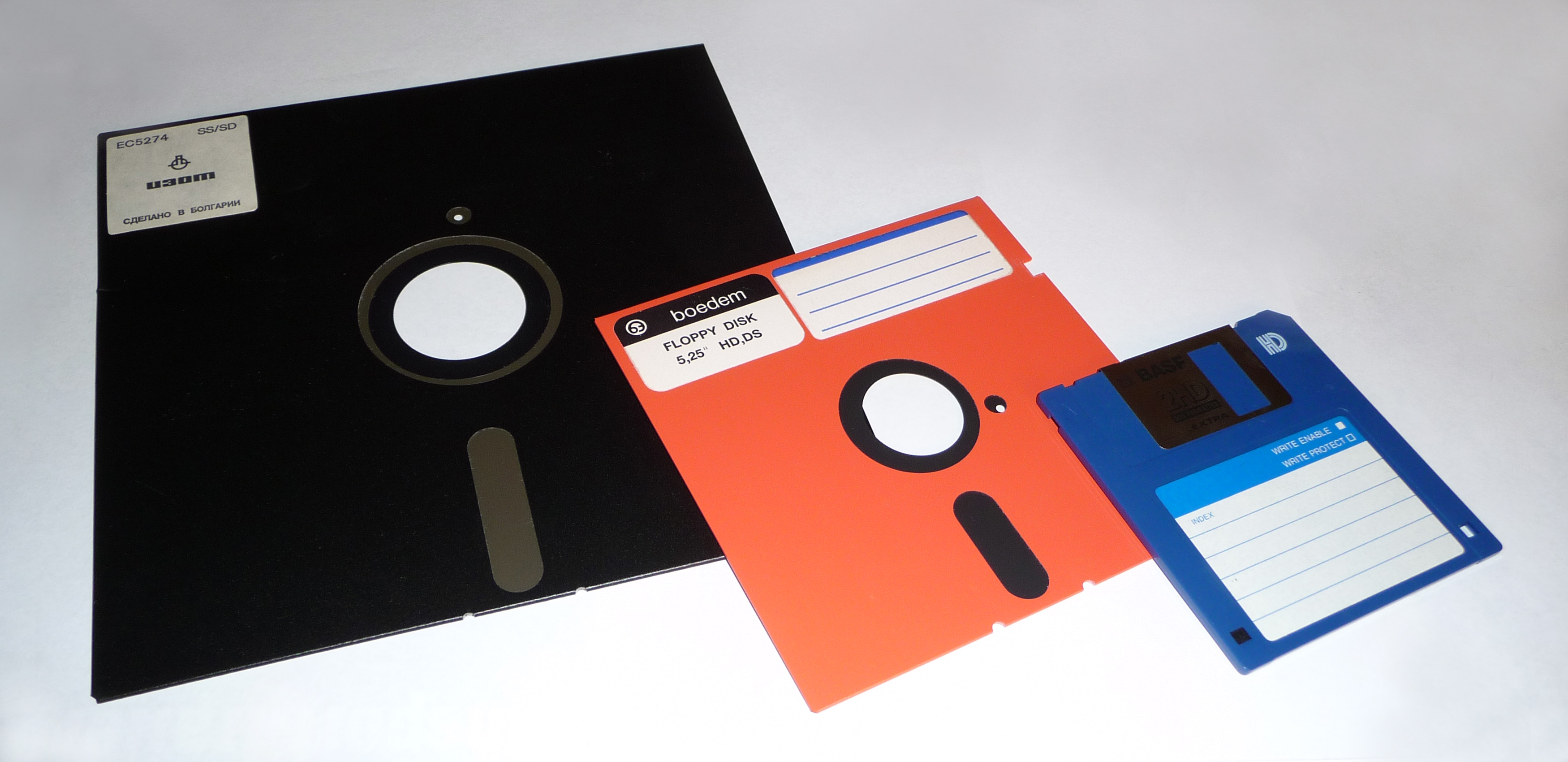
5¼"
A floppy disk or floppy diskette (casually referred to as a floppy, or a diskette) is an obsolescent type of disk storage composed of a thin and flexible disk of a magnetic storage medium in a square or nearly square plastic enclosure lined with a fabric that removes dust particles from the spinning disk. Floppy disks store digital data which can be read and written when the disk is inserted into a floppy disk drive (FDD) connected to or inside a computer or other device. The first floppy disks, invented and made by IBM, had a disk diameter of . Subsequently, the 5¼-inch and then the 3½-inch became a ubiquitous form of data storage and transfer into the first years of the 21st century. 3½-inch floppy disks can still be used with an external USB floppy disk drive. USB drives for 5¼-inch, 8-inch, and other-size floppy disks are rare to non-existent. Some individuals and organizations continue to use older equipment to read or transfer data from floppy disks. Floppy disks w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compaq Deskpro
The Compaq Deskpro is a line of business-oriented personal computers manufactured by Compaq, then discontinued after the merger with Hewlett-Packard. Models were produced containing microprocessors from the 8086 up to the x86-based Intel Pentium 4. History Deskpro (8086) and Deskpro 286 The original Compaq Deskpro (released in 1984), available in several disk configurations, is an XT-class PC equipped with an 8 MHz 8086 CPU and Compaq's unique display hardware that combined Color Graphics Adapter graphics with high resolution Monochrome Display Adapter text. As a result, it was considerably faster than the original IBM PC, the XT and the AT, and had a much better quality text display compared to IBM PCs which were equipped with either the IBM Monochrome Display Adapter or Color Graphics Adapter cards. Its hardware and BIOS were claimed to be 100% compatible with the IBM PC, like the earlier Compaq Portable. This compatibility had given Compaq the lead over companies l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |