|
Communist Ideologies
Since the time of Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels, a variety of developments have been made in communist theory and attempts to build a communist society, leading to a variety of different communist ideologies. These span philosophical, social, political and economic ideologies and movements, and can be split into three broad categories Marxist-based ideologies, Leninist-based ideologies, and Non-Marxist ideologies, though influence between the different ideologies is found throughout and key theorists may be described as belonging to one or important to multiple ideologies. Background Communist ideologies notable enough in the history of communism include philosophical, social, political and economic ideologies and movements whose ultimate goal is the establishment of a communist society, a socioeconomic order structured upon the ideas of common ownership of the means of production and the absence of social classes, money and the state. Self-identified commun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
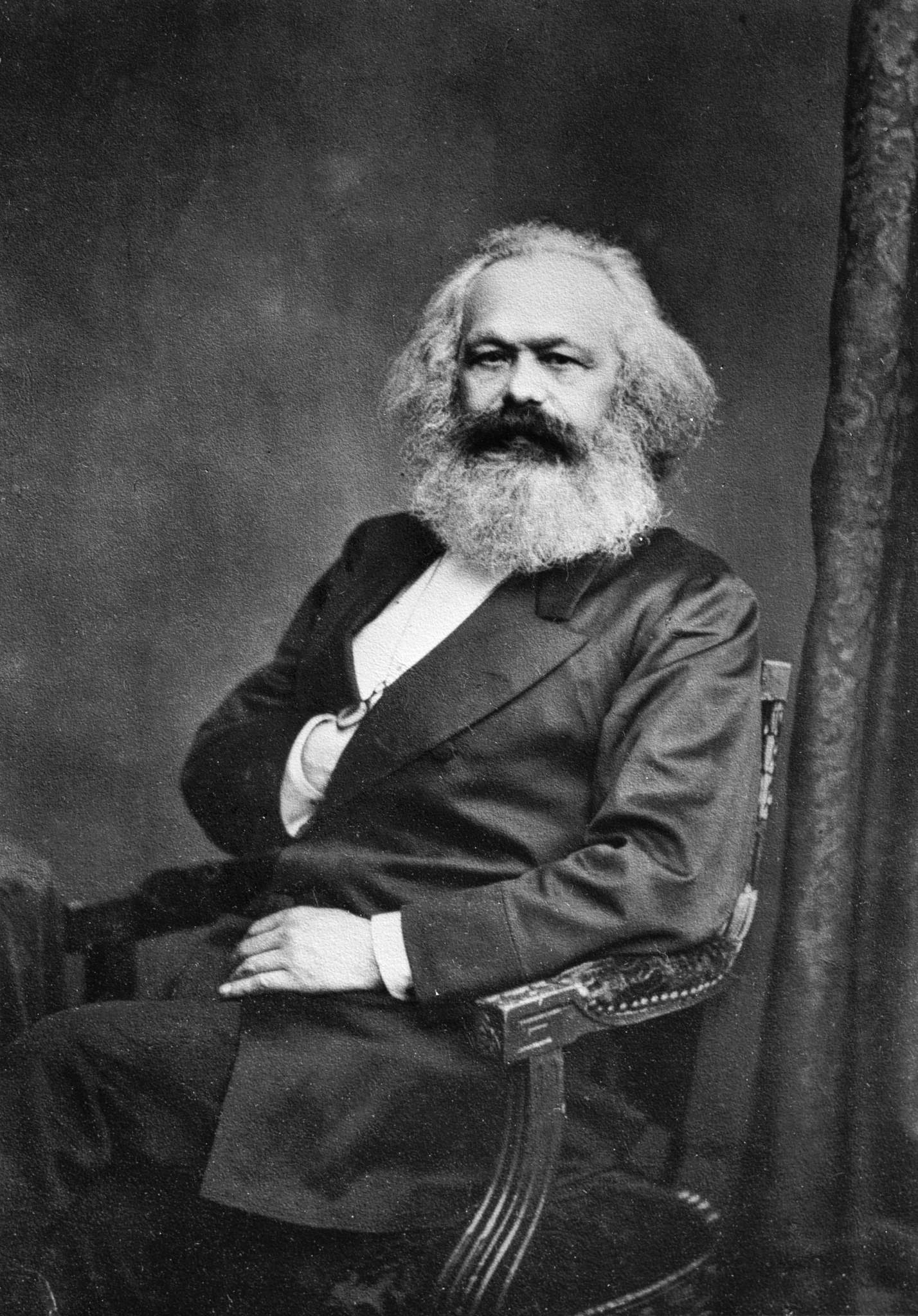
Karl Marx
Karl Heinrich Marx (; 5 May 1818 – 14 March 1883) was a German philosopher, economist, historian, sociologist, political theorist, journalist, critic of political economy, and socialist revolutionary. His best-known titles are the 1848 pamphlet ''The Communist Manifesto'' and the four-volume (1867–1883). Marx's political and philosophical thought had enormous influence on subsequent intellectual, economic, and political history. His name has been used as an adjective, a noun, and a school of social theory. Born in Trier, Germany, Marx studied law and philosophy at the universities of Bonn and Berlin. He married German theatre critic and political activist Jenny von Westphalen in 1843. Due to his political publications, Marx became stateless and lived in exile with his wife and children in London for decades, where he continued to develop his thought in collaboration with German philosopher Friedrich Engels and publish his writings, researching in the British Mus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State (polity)
A state is a centralized political organization that imposes and enforces rules over a population within a territory. There is no undisputed definition of a state. One widely used definition comes from the German sociologist Max Weber: a "state" is a polity that maintains a monopoly on the legitimate use of violence, although other definitions are not uncommon.Cudworth et al., 2007: p. 95Salmon, 2008p. 54 Absence of a state does not preclude the existence of a society, such as stateless societies like the Haudenosaunee Confederacy that "do not have either purely or even primarily political institutions or roles". The level of governance of a state, government being considered to form the fundamental apparatus of contemporary states, is used to determine whether it has failed. In a federal union, the term "state" is sometimes used to refer to the federated polities that make up the federation. (Other terms that are used in such federal systems may include “province”, � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Religious Communism
Religious communism is a form of communism that incorporates religious principles. Scholars have used the term to describe a variety of social or religious movements throughout history that have favored the common ownership of property. Overview The term ''religious communism'' has been used to describe a variety of social or religious movements throughout history. The "commune of early Christians at Jerusalem" has been described as a group that practiced religious communism. The teachings of Mazdak, a religious proto-socialist Persian reformer, have also been referred to as early ''communism''. According to Ben Fowkes and Bulent Gokay, Bolshevik Mikhail Skachko stated at the Congress of the Peoples of the East that "the Muslim religion is rooted in principles of religious communism, by which no man may be a slave to another, and not a single piece of land may be privately owned". Definition T. M. Browning described religious communism as a form of communism that "springs dire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pre-Marxist Communism
While Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels defined communism as a political movement, there were already similar ideas in the past which one could call communist experiments. Marx himself saw primitive communism as the original hunter-gatherer state of humankind. Marx theorized that only after humanity was capable of producing surplus did private property develop. Pre-history Karl Marx and other early communist theorists believed that hunter-gatherer societies as were found in the Paleolithic through to horticultural societies as found in the Chalcolithic were essentially egalitarian and he, therefore, termed their ideology to be primitive communism. Since Marx, sociologists and archaeologists have developed the idea of and research on primitive communism. According to Harry W. Laidler, one of the first writers to espouse a belief in the primitive communism of the past was the Roman Stoic philosopher Seneca who stated, "How happy was the primitive age when the bounties of nature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trotskyism
Trotskyism is the political ideology and branch of Marxism developed by Ukrainian-Russian revolutionary Leon Trotsky and some other members of the Left Opposition and Fourth International. Trotsky self-identified as an orthodox Marxist, a revolutionary Marxist, and Bolshevik–Leninist, a follower of Marx, Engels, and 3L: Vladimir Lenin, Karl Liebknecht, and Rosa Luxemburg. He supported founding a vanguard party of the proletariat, proletarian internationalism, and a dictatorship of the proletariat (as opposed to the " dictatorship of the bourgeoisie", which Marxists argue defines capitalism) based on working-class self-emancipation and mass democracy. Trotskyists are critical of Stalinism as they oppose Joseph Stalin's theory of socialism in one country in favour of Trotsky's theory of permanent revolution. Trotskyists criticize the bureaucracy and anti-democratic current developed in the Soviet Union under Stalin. Vladimir Lenin and Trotsky, despite their ideological disp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marxism–Leninism
Marxism–Leninism is a communist ideology which was the main communist movement throughout the 20th century. Developed by the Bolsheviks, it was the state ideology of the Soviet Union, its satellite states in the Eastern Bloc, and various countries in the Non-Aligned Movement and Third World during the Cold War, as well as the Communist International after Bolshevisation. Today, Marxism–Leninism is the ideology of the ruling parties of China, Cuba, Laos and Vietnam (all one-party 'socialist republics'), as well as many other communist parties, while the state ideology of North Korea is derived from Marxism–Leninism. Marxist–Leninist states are commonly referred to as "communist states" by Western academics. Marxism–Leninism holds that a two-stage communist revolution is needed to replace capitalism. A vanguard party, organized through " democratic centralism", would seize power on behalf of the proletariat and establish a one-party socialist state, called the dict ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leninism
Leninism is a political ideology developed by Russian Marxist revolutionary Vladimir Lenin that proposes the establishment of the Dictatorship of the proletariat#Vladimir Lenin, dictatorship of the proletariat led by a revolutionary Vanguardism, vanguard party as the political prelude to the establishment of communism. The function of the Leninist vanguard party is to provide the working classes with the political consciousness (education and organisation) and revolutionary leadership necessary to depose capitalism in the Russian Empire (1721–1917). Leninist revolutionary leadership is based upon ''The Communist Manifesto'' (1848), identifying the communist party as "the most advanced and resolute section of the working class parties of every country; that section which pushes forward all others." As the vanguard party, the Bolsheviks viewed history through the theoretical framework of dialectical materialism, which sanctioned political commitment to the successful overthrow o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maoism
Maoism, officially called Mao Zedong Thought by the Chinese Communist Party, is a variety of Marxism–Leninism that Mao Zedong developed to realise a socialist revolution in the agricultural, pre-industrial society of the Republic of China and later the People's Republic of China. The philosophical difference between Maoism and traditional Marxism–Leninism is that the peasantry is the revolutionary vanguard in pre-industrial societies rather than the proletariat. This updating and adaptation of Marxism–Leninism to Chinese conditions in which revolutionary praxis is primary and ideological orthodoxy is secondary represents urban Marxism–Leninism adapted to pre-industrial China. Later theoreticians expanded on the idea that Mao had adapted Marxism–Leninism to Chinese conditions, arguing that he had in fact updated it fundamentally, and that Maoism could be applied universally throughout the world. This ideology is often referred to as Marxism–Leninism–Maoism to d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Libertarian Marxism
Libertarian socialism, also known by various other names, is a left-wing,Diemer, Ulli (1997)"What Is Libertarian Socialism?" The Anarchist Library. Retrieved 4 August 2019. anti-authoritarian, anti-statist and libertarianLong, Roderick T. (2012). "Anarchism". In Gaus, Gerald F.; D'Agostino, Fred, eds. ''The Routledge Companion to Social and Political Philosophy''. p. 223. "In the meantime, anarchist theories of a more communist or collectivist character had been developing as well. One important pioneer is French anarcho-communistes Joseph Déjacque (1821–1864), who ..appears to have been the first thinker to adopt the term 'libertarian' for this position; hence 'libertarianism' initially denoted a communist rather than a free-market ideology." political philosophy within the socialist movement which rejects the state's control of the economy under state socialism. Overlapping with anarchism and libertarianism, libertarian socialists criticize wage slavery relationships w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Left Communism
Left communism, or the communist left, is a position held by the left wing of communism, which criticises the political ideas and practices espoused by Marxist–Leninists and social democrats. Left communists assert positions which they regard as more authentically Marxist than the views of Marxism–Leninism espoused by the Communist International after its Bolshevization by Joseph Stalin and during its second congress. In general, there are two currents of left communism, namely the Italian and Dutch–German left. The communist left in Italy was formed during World War I in organizations like the Italian Socialist Party and the Communist Party of Italy. The Italian left considers itself to be Leninist in nature, but denounces Marxism–Leninism as a form of bourgeois opportunism materialized in the Soviet Union under Stalin. The Italian left is currently embodied in organizations such as the Internationalist Communist Party and the International Communist Party. The Dutch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marxist Schools Of Thought
Marxism is a method of socioeconomic analysis that originates in the works of 19th century German philosophers Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels. Marxism analyzes and critiques the development of class society and especially of capitalism as well as the role of class struggles in systemic, economic, social and political change. It frames capitalism through a paradigm of exploitation and analyzes class relations and social conflict using a materialist interpretation of historical development (now known as "historical materialism") – materialist in the sense that the politics and ideas of an epoch are determined by the way in which material production is carried on. From the late 19th century onward, Marxism has developed from Marx's original revolutionary critique of classical political economy and materialist conception of history into a comprehensive world-view. There are now many different branches and schools of thought, with the result that there is now no single definitive M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Council Communism
Council communism is a current of communist thought that emerged in the 1920s. Inspired by the November Revolution, council communism was opposed to state socialism and advocated workers' councils and council democracy. Strong in Germany and the Netherlands during the 1920s, council communism continues to exist as a small minority in the left. History Emergence Council communism emerged in the years after 1918, as some communists in Germany and the Netherlands concluded that the Russian Revolution had led to power being concentrated in the hands of a new political elite. Its most prominent early proponents were the German educator Otto Rühle, the Dutch astronomer Anton Pannekoek, and the Dutch poet Herman Gorter. They were initially enthusiastic supporters of the Bolsheviks and the Russian Revolution. In 1918, Gorter said that the Bolshevik leader Vladimir Lenin "stands out above all other leaders of the Proletariat" and that Karl Marx was Lenin's sole peer. In 1919, Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |








.jpg)