|
Command Module Columbia
Command module ''Columbia'' (CM-107) is the spacecraft that served as the command module during Apollo 11, which was the first mission to land humans on the Moon. ''Columbia'' is the only spacecraft of the 1969 Apollo 11 mission that returned to Earth. The name ''Columbia'' was first suggested to Michael Collins by Julian Scheer, NASA assistant administrator of public affairs during the Apollo program. Scheer mentioned the name, in passing, in a phone conversation, saying "some of us up here have been kicking around ''Columbia''." Collins initially thought it was "a bit pompous" but the name eventually stuck as he could not think of a better alternative and his crewmates Buzz Aldrin and Neil Armstrong had no objections. Collins was also influenced to accept the name because of its similarity to ''Columbiad'', the name of the space gun in Jules Verne's 1865 science fiction novel ''From the Earth to the Moon'', Following the mission and after a tour of U.S. cities, ''Columbi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apollo 11
Apollo 11 (July 16–24, 1969) was the American spaceflight that first landed humans on the Moon. Commander Neil Armstrong and lunar module pilot Buzz Aldrin landed the Apollo Lunar Module ''Eagle'' on July 20, 1969, at 20:17 UTC, and Armstrong became the first person to step onto the Moon's surface six hours and 39 minutes later, on July 21 at 02:56 UTC. Aldrin joined him 19 minutes later, and they spent about two and a quarter hours together exploring the site they had named Tranquility Base upon landing. Armstrong and Aldrin collected of lunar material to bring back to Earth as pilot Michael Collins flew the Command Module ''Columbia'' in lunar orbit, and were on the Moon's surface for 21 hours, 36 minutes before lifting off to rejoin ''Columbia''. Apollo 11 was launched by a Saturn V rocket from Kennedy Space Center on Merritt Island, Florida, on July 16 at 13:32 UTC, and it was the fifth crewed mission of NASA's Apollo program. The Apollo spacecraft had three ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smithsonian Institution
The Smithsonian Institution ( ), or simply the Smithsonian, is a group of museums and education and research centers, the largest such complex in the world, created by the U.S. government "for the increase and diffusion of knowledge". Founded on August 10, 1846, it operates as a trust instrumentality and is not formally a part of any of the three branches of the federal government. The institution is named after its founding donor, British scientist James Smithson. It was originally organized as the United States National Museum, but that name ceased to exist administratively in 1967. Called "the nation's attic" for its eclectic holdings of 154 million items, the institution's 19 museums, 21 libraries, nine research centers, and zoo include historical and architectural landmarks, mostly located in the District of Columbia. Additional facilities are located in Maryland, New York, and Virginia. More than 200 institutions and museums in 45 states,States without Smithsonian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Museum Of Flight
The Museum of Flight is a private non-profit air and space museum in the Seattle metropolitan area. It is located at the southern end of King County International Airport (Boeing Field) in the city of Tukwila, immediately south of Seattle."Museum of Flight." ''Yahoo Travel'' Retrieved: September 2, 2011. It was established in 1965 and is fully accredited by the . As the largest private air and space museum in the world, it also hosts large K–12 educational programs. The museum attracts over 500,000 visitors every year, and also serves more than 140,000 students annually through its onsite p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heinz History Center
The Senator John Heinz History Center, an affiliate of the Smithsonian Institution, is the largest history museum in the Pennsylvania, Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, United States. Named after U.S. Senator H. John Heinz III (1938–1991) from Pennsylvania, it is located in the Strip District, Pittsburgh, Strip District of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, Pittsburgh. The Heinz History Center is a educational institution "that engages and inspires a diverse audience with links to the past, understanding in the present, and guidance for the future by preserving regional history and presenting the American experience with a Western Pennsylvania connection." Senator John Heinz History Center The History Center features the Western Pennsylvania Sports Museum and the Library and Archives, and includes six floors of permanent and changing exhibitions that tell the story of Western Pennsylvania. Though it was originally established in 1879, the Historical Society of Western Pennsylvania opened its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Louis Science Center
The Saint Louis Science Center, founded as a planetarium in 1963, is a collection of buildings including a science museum and planetarium in St. Louis, Missouri, on the southeastern corner of Forest Park. With over 750 exhibits in a complex of over , it is among the largest of its type in the United States. James S. McDonnell Planetarium Funding for the first structure of the current campus began in 1955, with $1 million of a $110 million city bond issue specified for the construction of a planetarium. Two years were spent surveying locations. The first proposed site, on the northern side of Forest Park near the Jefferson Memorial Building at Lindell and DeBaliviere, was scrapped because of restrictions on subdivisions. The location was changed to the southern part of the park, on the site of the old mounted police station, which was demolished in 1960. The plan was to build a planetarium, science museum, and natural history museum. The Planetarium was designed by Gyo Obata o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Center Houston
Space Center Houston is a science museum that serves as the official visitor center of NASA Johnson Space Center in Houston. It was designated a Smithsonian Affiliate museum in 2014. The organization is owned by NASA, and operated under a contract by the nonprofit Manned Spaceflight Education Foundation, a 501(c)(3) organization. The Johnson Space Center is the home of Mission Control and astronaut training. The center opened in 1992 replacing the former Visitor Center in Johnson Space Center Building 2. The museum is and displays over 400 space artifacts, including the Mercury 9, Gemini 5, and Apollo 17 space capsules. Starship gallery This artifact gallery includes three flown spacecraft, several used in training, and a display of Moon rocks: * Mercury 9 capsule (''Faith 7'') flown by Gordon Cooper in 1963 * Gemini 5 capsule flown by Gordon Cooper and Pete Conrad in 1965 * Apollo 17 Command Module ''America'' flown by Gene Cernan, Ronald Evans, and Dr. Harrison " Jack ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
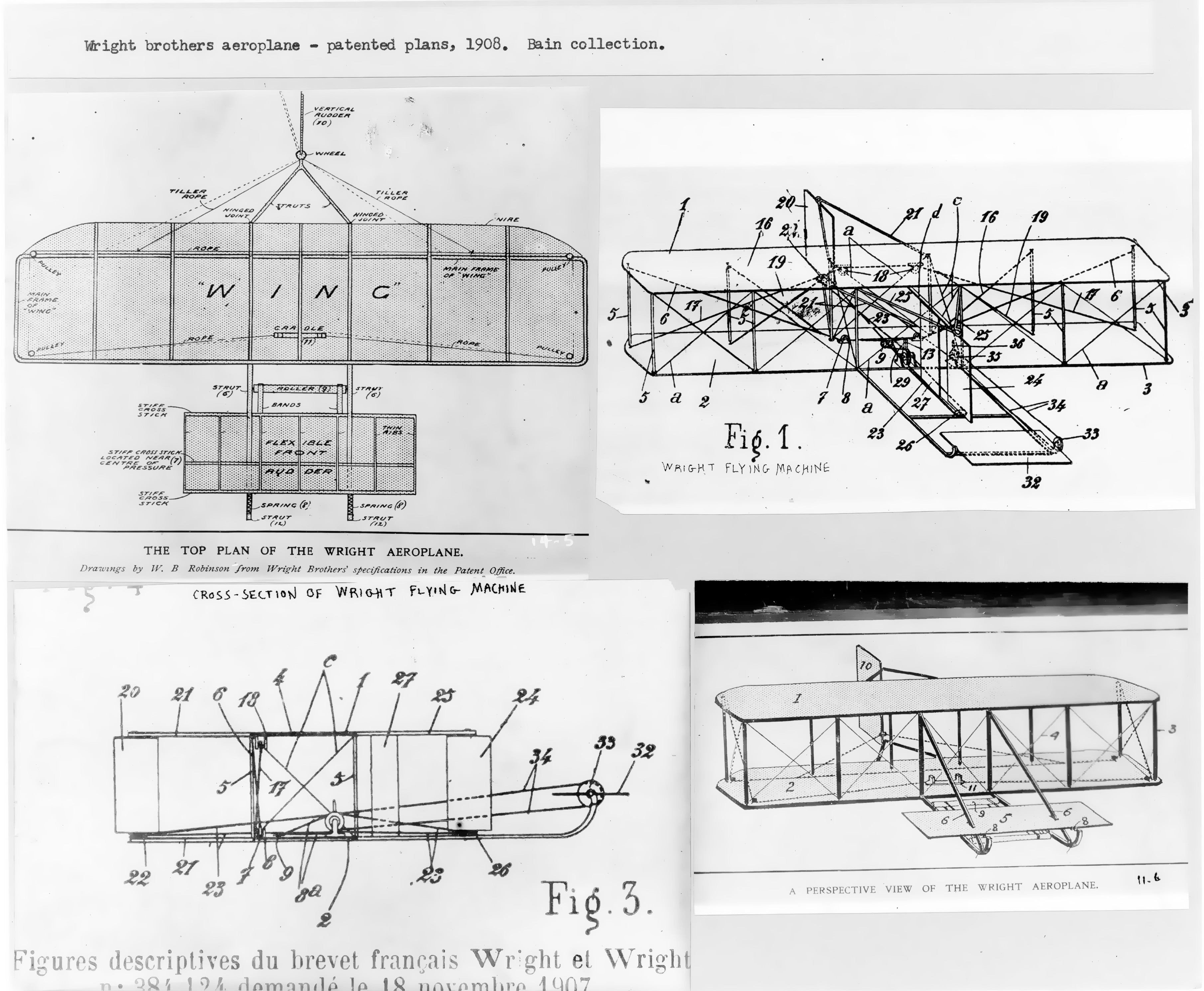
1903 Wright Flyer
The ''Wright Flyer'' (also known as the ''Kitty Hawk'', ''Flyer'' I or the 1903 ''Flyer'') made the first sustained flight by a manned heavier-than-air powered and controlled aircraft—an airplane—on December 17, 1903. Invented and flown by Orville and Wilbur Wright, it marked the beginning of the pioneer era of aviation. The Wright brothers flew the ''Wright Flyer'' four times that day on land now part of the town of Kill Devil Hills, about south of Kitty Hawk, North Carolina. The aircraft was preserved and is now exhibited in the National Air and Space Museum in Washington, D.C. Design and construction The ''Flyer'' was based on the Wrights' experience testing gliders at Kitty Hawk between 1900 and 1902. Their last glider, the 1902 Glider, led directly to the design of the ''Wright Flyer''. The Wrights built the aircraft in 1903 using spruce for straight members of the airframe (such as wing spars) and ash wood for curved components (wing ribs). The wings were desi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
From The Earth To The Moon
''From the Earth to the Moon: A Direct Route in 97 Hours, 20 Minutes'' (french: De la Terre à la Lune, trajet direct en 97 heures 20 minutes) is an 1865 novel by Jules Verne. It tells the story of the Baltimore Gun Club, a post-American Civil War society of weapons enthusiasts, and their attempts to build an enormous Columbiad space gun and launch three people—the Gun Club's president, his Philadelphian armor-making rival, and a French poet—in a projectile with the goal of a Moon landing. Five years later, Verne wrote a sequel called ''Around the Moon''. The story is also notable in that Verne attempted to do some rough calculations as to the requirements for the cannon and in that, considering the comparative lack of empirical data on the subject at the time, some of his figures are remarkably accurate. However, his version of a space gun for a non-rocket spacelaunch turned out to be impractical for safe human space travel since a much longer barrel would have been require ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jules Verne
Jules Gabriel Verne (;''Longman Pronunciation Dictionary''. ; 8 February 1828 – 24 March 1905) was a French novelist, poet, and playwright. His collaboration with the publisher Pierre-Jules Hetzel led to the creation of the ''Voyages extraordinaires'', a series of bestselling adventure novels including ''Journey to the Center of the Earth'' (1864), ''Twenty Thousand Leagues Under the Seas'' (1870), and '' Around the World in Eighty Days'' (1872). His novels, always well documented, are generally set in the second half of the 19th century, taking into account the technological advances of the time. In addition to his novels, he wrote numerous plays, short stories, autobiographical accounts, poetry, songs and scientific, artistic and literary studies. His work has been adapted for film and television since the beginning of cinema, as well as for comic books, theater, opera, music and video games. Verne is considered to be an important author in France and most of Europe, where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Gun
{{disambiguation ...
Space Gun may refer to: *Space gun, a method of launching an object into space * ''Space Gun'' (album), a 2018 album by Guided by Voices * ''Space Gun'' (video game), a 1990 arcade game *Ljutic Space Gun, a 12 gauge single-shot shotgun See also * Hand-Held Maneuvering Unit, or maneuvering gun or zip gun, a device used in spacewalks * Raygun, a science-fiction directed-energy weapon * TP-82 Cosmonaut survival pistol, carried by cosmonauts on space missions * Space warfare and space weapons Space weapons are weapons used in space warfare. They include weapons that can attack space systems in orbit (i.e. anti-satellite weapons), attack targets on the earth from space or disable missiles travelling through space. In the course of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neil Armstrong
Neil Alden Armstrong (August 5, 1930 – August 25, 2012) was an American astronaut and aeronautical engineer who became the first person to walk on the Moon in 1969. He was also a naval aviator, test pilot, and university professor. Armstrong was born and raised in Wapakoneta, Ohio. A graduate of Purdue University, he studied aeronautical engineering; his college tuition was paid for by the U.S. Navy under the Holloway Plan. He became a midshipman in 1949 and a naval aviator the following year. He saw action in the Korean War, flying the Grumman F9F Panther from the aircraft carrier . In September 1951, while making a low bombing run, Armstrong's aircraft was damaged when it collided with an anti-aircraft cable, strung across a valley, which cut off a large portion of one wing. Armstrong was forced to bail out. After the war, he completed his bachelor's degree at Purdue and became a test pilot at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) High-Speed Fligh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buzz Aldrin
Buzz Aldrin (; born Edwin Eugene Aldrin Jr.; January 20, 1930) is an American former astronaut, engineer and fighter pilot. He made three spacewalks as pilot of the 1966 Gemini 12 mission. As the Lunar Module ''Eagle'' pilot on the 1969 Apollo 11 mission, he and mission commander Neil Armstrong were the first two people to land on the Moon. Born in Glen Ridge, New Jersey, Aldrin graduated third in the class of 1951 from the United States Military Academy at West Point, with a degree in mechanical engineering. He was commissioned into the United States Air Force, and served as a jet fighter pilot during the Korean War. He flew 66 combat missions and shot down two MiG-15 aircraft. After earning a Doctor of Science degree in astronautics from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Aldrin was selected as a member of NASA's Astronaut Group 3, making him the first astronaut with a doctoral degree. His doctoral thesis, ''Line-of-Sight Guidance Techniques for Manned Orbita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |