|
Comet Dust
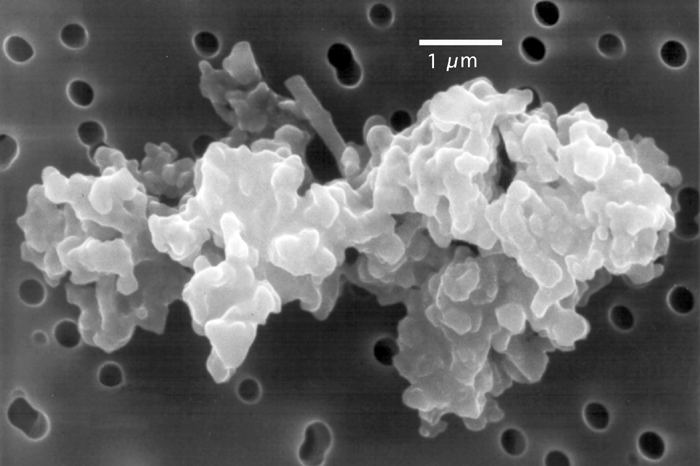
Comet dust refers to cosmic dust that originates from a comet. Comet dust can provide clues to comets' origin. When the Earth passes through a comet dust trail, it can produce a meteor shower. Physical characteristics Size The majority of dust from comet activity is sub-micrometer to roughly micrometer in size. However, this fraction is short-lived, as radiation pressure causes them to blow out of the Solar System or spiral inwards. The next size class is large, "fluffy" or "cluster-type" aggregates of the above grains. These are typically 20-100 micrometers, a size not arbitrary but observed as the porous aggregates tend to fracture or compact. Larger particles are micrometeoroids, not dust. "...in practice the term is most often applied to objects smaller than approximately 100 um. These size ranges need to be modified." "By this definition, IDPs are particles smaller than 10um."" In the absence of a definition from the IAU, groups devised their own definitions of dust: small ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmic Dust
Cosmic dust, also called extraterrestrial dust, star dust or space dust, is dust which exists in outer space, or has fallen on Earth. Most cosmic dust particles measure between a few molecules and 0.1 mm (100 micrometers). Larger particles are called meteoroids. Cosmic dust can be further distinguished by its astronomical location: intergalactic dust, interstellar dust, interplanetary dust (such as in the zodiacal cloud) and circumplanetary dust (such as in a planetary ring). There are several methods to obtain space dust measurement. In the Solar System, interplanetary dust causes the zodiacal light. Solar System dust includes comet dust, asteroidal dust, dust from the Kuiper belt, and interstellar dust passing through the Solar System. Thousands of tons of cosmic dust are estimated to reach the Earth's surface every year, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stardust (spacecraft)
''Stardust'' was a 385-kilogram robotic space probe launched by NASA on 7 February 1999. Its primary mission was to collect dust samples from the coma of comet Wild 2, as well as samples of cosmic dust, and return them to Earth for analysis. It was the first sample return mission of its kind. En route to comet Wild 2, it also flew by and studied the asteroid 5535 Annefrank. The primary mission was successfully completed on 15 January 2006 when the sample return capsule returned to Earth. A mission extension, codenamed ''NExT'', culminated in February 2011 with ''Stardust'' intercepting comet Tempel 1, a small Solar System body previously visited by '' Deep Impact'' in 2005. ''Stardust'' ceased operations in March 2011. On 14 August 2014, scientists announced the identification of possible interstellar dust particles from the ''Stardust'' capsule returned to Earth in 2006. Mission background History Beginning in the 1980s, scientists began seeking a dedicated mis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the List of Solar System objects by size, largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but slightly less than one-thousandth the mass of the Sun. Jupiter is the List of brightest natural objects in the sky, third brightest natural object in the Earth's night sky after the Moon and Venus, and it has been observed since Pre-history, prehistoric times. It was named after the Jupiter (mythology), Roman god Jupiter, the king of the gods. Jupiter is primarily composed of hydrogen, but helium constitutes one-quarter of its mass and one-tenth of its volume. It probably has a rocky core of heavier elements, but, like the other giant planets in the Solar System, it lacks a well-defined solid surface. The ongoing contraction of Jupiter's interior generates more heat than it receives from the Sun. Because of its rapid rotation, the planet' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
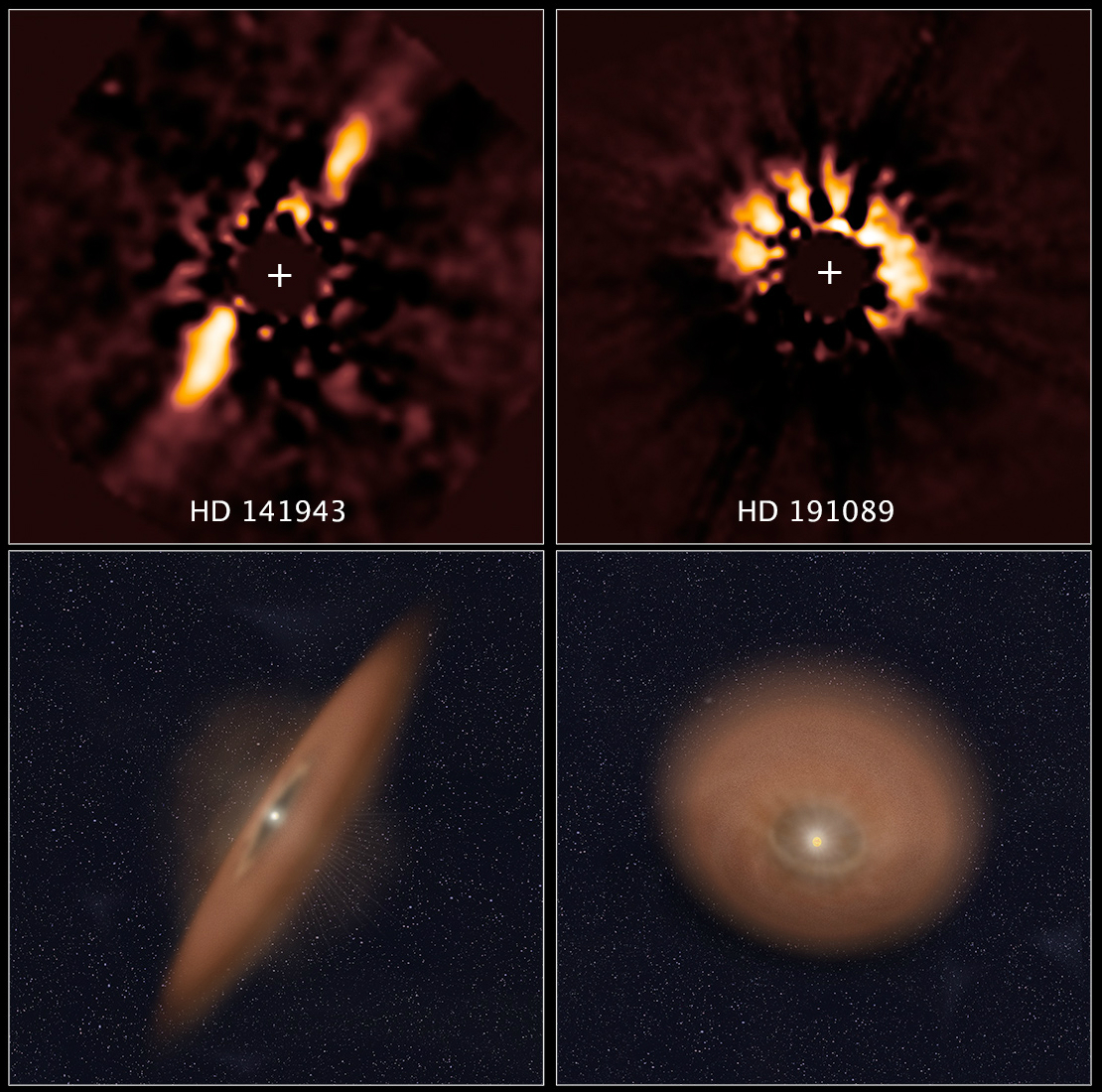
Accretion Disk
An accretion disk is a structure (often a circumstellar disk) formed by diffuse material in orbital motion around a massive central body. The central body is typically a star. Friction, uneven irradiance, magnetohydrodynamic effects, and other forces induce instabilities causing orbiting material in the disk to spiral inward towards the central body. Gravitational and frictional forces compress and raise the temperature of the material, causing the emission of electromagnetic radiation. The frequency range of that radiation depends on the central object's mass. Accretion disks of young stars and protostars radiate in the infrared; those around neutron stars and black holes in the X-ray part of the spectrum. The study of oscillation modes in accretion disks is referred to as diskoseismology. Manifestations Accretion disks are a ubiquitous phenomenon in astrophysics; active galactic nuclei, protoplanetary disks, and gamma ray bursts all involve accretion disks. These disks very ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volatiles
Volatiles are the group of chemical elements and chemical compounds that can be readily vaporized. In contrast with volatiles, elements and compounds that are not readily vaporized are known as refractory substances. On planet Earth, the term 'volatiles' often refers to the volatile components of magma. In astrogeology volatiles are investigated in the crust or atmosphere of a planet or moon. Volatiles include nitrogen, carbon dioxide, ammonia, hydrogen, methane, sulfur dioxide, water and others. Planetary science Planetary scientists often classify volatiles with exceptionally low melting points, such as hydrogen and helium, as gases (as in gas giant), whereas those volatiles with melting points above about 100 K (–173 °C, –280 °F) are referred to as ices. The terms "gas" and "ice" in this context can apply to compounds that may be solids, liquids or gases. Thus, Jupiter and Saturn are gas giants, and Uranus and Neptune are ice giants, even though the vast majori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotopic Ratio
In physics, natural abundance (NA) refers to the abundance of isotopes of a chemical element as naturally found on a planet. The relative atomic mass (a weighted average, weighted by mole-fraction abundance figures) of these isotopes is the atomic weight listed for the element in the periodic table. The abundance of an isotope varies from planet to planet, and even from place to place on the Earth, but remains relatively constant in time (on a short-term scale). As an example, uranium has three naturally occurring isotopes: 238U, 235U and 234U. Their respective natural mole-fraction abundances are 99.2739–99.2752%, 0.7198–0.7202%, and 0.0050–0.0059%. For example, if 100,000 uranium atoms were analyzed, one would expect to find approximately 99,274 238U atoms, approximately 720 235U atoms, and very few (most likely 5 or 6) 234U atoms. This is because 238U is much more stable than 235U or 234U, as the half-life of each isotope reveals: 4.468 × 109 years for 238U com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protostar
A protostar is a very young star that is still gathering mass from its parent molecular cloud. The protostellar phase is the earliest one in the process of stellar evolution. For a low-mass star (i.e. that of the Sun or lower), it lasts about 500,000 years. The phase begins when a molecular cloud fragment first collapses under the force of self-gravity and an opaque, pressure supported core forms inside the collapsing fragment. It ends when the infalling gas is depleted, leaving a pre-main-sequence star, which contracts to later become a main-sequence star at the onset of hydrogen fusion producing helium. History The modern picture of protostars, summarized above, was first suggested by Chushiro Hayashi in 1966. In the first models, the size of protostars was greatly overestimated. Subsequent numerical calculations clarified the issue, and showed that protostars are only modestly larger than main-sequence stars of the same mass. This basic theoretical result has been confirmed b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neptune
Neptune is the eighth planet from the Sun and the farthest known planet in the Solar System. It is the fourth-largest planet in the Solar System by diameter, the third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet. It is 17 times the mass of Earth, and slightly more massive than its near-twin Uranus. Neptune is denser and physically smaller than Uranus because its greater mass causes more gravitational compression of its atmosphere. It is referred to as one of the solar system's two ice giant planets (the other one being Uranus). Being composed primarily of gases and liquids, it has no well-defined "solid surface". The planet orbits the Sun once every 164.8 julian year (astronomy), years at an average distance of . It is named after the Neptune (mythology), Roman god of the sea and has the astronomical symbol , representing Neptune's trident. Neptune is not visible to the unaided eye and is the only planet in the Solar System found by mathematical prediction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uranus
Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun. Its name is a reference to the Greek god of the sky, Uranus (mythology), Uranus (Caelus), who, according to Greek mythology, was the great-grandfather of Ares (Mars (mythology), Mars), grandfather of Zeus (Jupiter (mythology), Jupiter) and father of Cronus (Saturn (mythology), Saturn). It has the third-largest planetary radius and fourth-largest planetary mass in the Solar System. Uranus is similar in composition to Neptune, and both have bulk chemical compositions which differ from that of the larger gas giants Jupiter and Saturn. For this reason, scientists often classify Uranus and Neptune as "ice giants" to distinguish them from the other giant planets. As with gas giants, ice giants also lack a well defined "solid surface." Uranus's Atmosphere#Others, atmosphere is similar to Jupiter's and Saturn's in its primary composition of hydrogen and helium, but it contains more "volatiles, ices" such as water, ammonia, and methane, al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planetesimal
Planetesimals are solid objects thought to exist in protoplanetary disks and debris disks. Per the Chamberlin–Moulton planetesimal hypothesis, they are believed to form out of cosmic dust grains. Believed to have formed in the Solar System about 4.6 billion years ago, they aid study of its formation. Formation A widely accepted theory of planet formation, the so-called planetesimal hypotheses, the Chamberlin–Moulton planetesimal hypothesis and that of Viktor Safronov, states that planets form from cosmic dust grains that collide and stick to form ever-larger bodies. Once a body reaches around a kilometer in size, its constituent grains can attract each other directly through mutual gravity, enormously aiding further growth into moon-sized protoplanets. Smaller bodies must instead rely on Brownian motion or turbulence to cause the collisions leading to sticking. The mechanics of collisions and mechanisms of sticking are intricate. Alternatively, planetesimals may form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
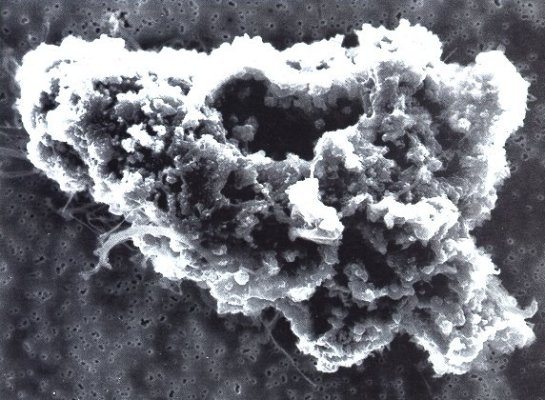
Comet Dust Microscopic Photo
A comet is an icy, small Solar System body that, when passing close to the Sun, warms and begins to release gases, a process that is called outgassing. This produces a visible atmosphere or coma, and sometimes also a tail. These phenomena are due to the effects of solar radiation and the solar wind acting upon the nucleus of the comet. Comet nuclei range from a few hundred meters to tens of kilometers across and are composed of loose collections of ice, dust, and small rocky particles. The coma may be up to 15 times Earth's diameter, while the tail may stretch beyond one astronomical unit. If sufficiently bright, a comet may be seen from Earth without the aid of a telescope and may subtend an arc of 30° (60 Moons) across the sky. Comets have been observed and recorded since ancient times by many cultures and religions. Comets usually have highly eccentric elliptical orbits, and they have a wide range of orbital periods, ranging from several years to potentially several milli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)