|
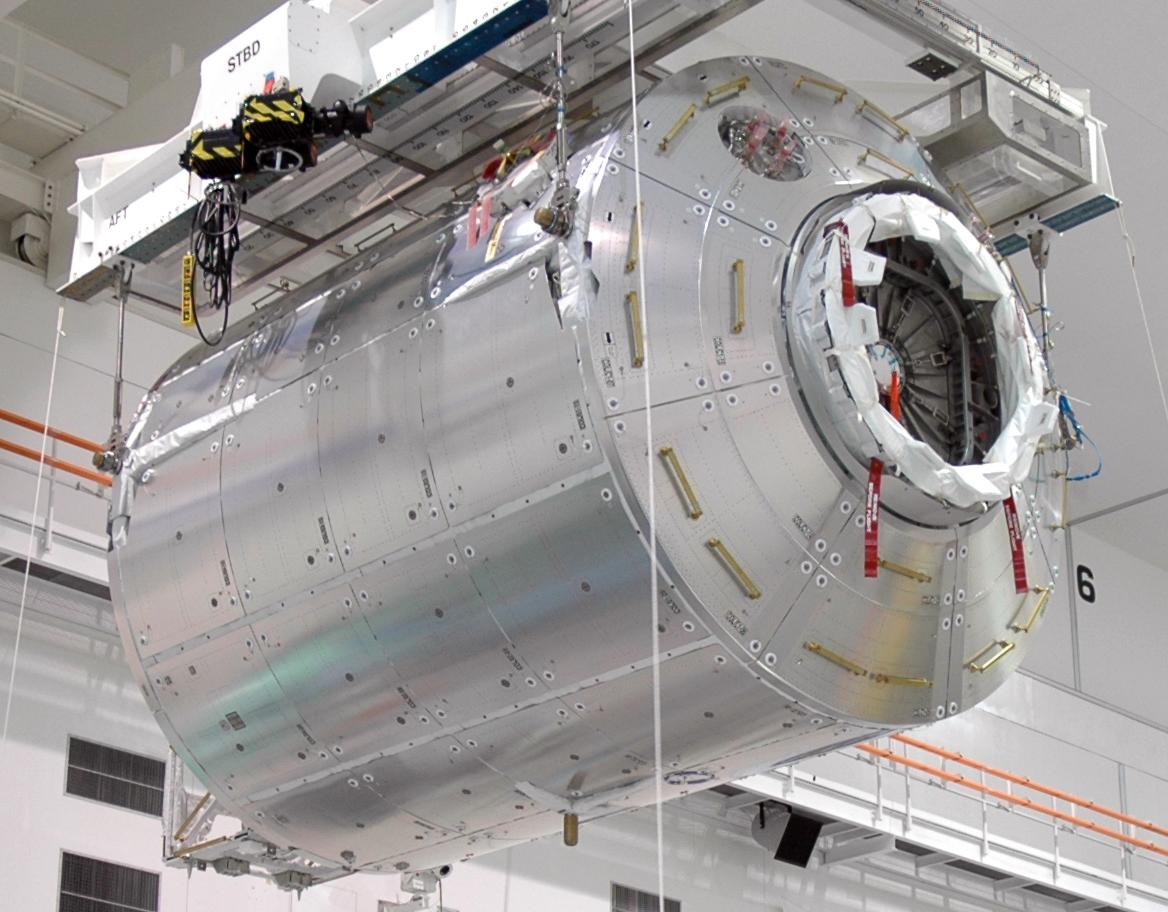
Columbus (spacecraft)
The ''Columbus'' Man-Tended Free Flyer (MTFF) was a European Space Agency (ESA) program to develop a space station that could be used for a variety of microgravity experiments while serving ESA's needs for an autonomous crewed space platform. It consisted of a Columbus module docked to a service module containing solar power collectors, communications and other services. The program ran from 1986 to 1991, was expected to cost $3.56 billion including launch and utilization, and was cancelled while still in the planning stage. Aspects of the program were later realised in the ''Columbus'' science laboratory attached to the International Space Station (ISS). History ESA's Board of Directors approved the Columbus program in 1985. Like the Multi-Purpose Logistics Modules (MPLMs) and the Automated Transfer Vehicle (ATV) resupply craft, Columbus traces its origins to Europe's Spacelab. The Columbus program was intended to supplement NASA's Space Station Freedom. Initially the Columbus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermes (spacecraft)
Hermes was a proposed spaceplane designed by the French Centre National d'Études Spatiales (CNES) in 1975, and later by the European Space Agency (ESA). It was superficially similar to the American Boeing X-20 Dyna-Soar and the larger Space Shuttle. In January 1985, CNES proposed to proceed with Hermes development under the auspices of the ESA. Hermes was to have been part of a crewed spaceflight program. It would have been launched using an Ariane 5 launch vehicle. In November 1987, the project was approved; it was to commence an initial pre-development phase from 1988 to 1990, after which the authorisation to proceed to full-rate development was to depend on the outcome of this phase. However, the project was subject to numerous delays and funding issues around this period. In 1992, Hermes was cancelled. This was in part due to unachievable cost and performance goals, as well as the formation of a partnership with the Russian Aviation and Space Agency (RKA), which reduced the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entwicklungsring Nord
The Entwicklungsring Nord (Northern development circle) - abbreviated ERNO - was a 1961 joint venture of Bremen-based Weserflug and Focke-Wulf with Hamburger Flugzeugbau to develop parts for rockets and get involved in space activities. Jet-powered aircraft VFW 614 In 1961 work began on a small, jet-powered aircraft initially styled Erno-61-4. After Weserflug and Focke Wulf formally merged into Vereinigte Flugtechnische Werke (VFW) in 1964, the machine was redesignated VFW 614. The draft design was amended to a STOL 40-44 passenger jet with overwing engines, for easier operation from unprepared runways. German government subsidies enabled development to start in earnest in 1966. The first prototype started in August 1968, but then VFW and Fokker of the Netherlands formed a joint transnational holding company. The prototype flew on 14 July 1971 but crashed next February. Two more prototypes flew in 1972. German, FAA, and French DGA certifications completed in 1974, 1975, & 1976 resp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STS-122
STS-122 was a NASA Space Shuttle mission to the International Space Station (ISS), flown by the . STS-122 marked the 24th shuttle mission to the ISS, and the 121st Space Shuttle flight overall. The mission was also referred to as ISS-1E by the ISS program. The primary objective of STS-122 was to deliver the European ''Columbus'' science laboratory, built by the European Space Agency (ESA), to the station. It also returned Expedition 16 Flight Engineer Daniel M. Tani to Earth. Tani was replaced on Expedition 16 by Léopold Eyharts, a French Flight Engineer representing ESA. After ''Atlantis'' landing, the orbiter was prepared for STS-125, the final servicing mission for the Hubble Space Telescope. The original target launch date for STS-122 was 6 December 2007, but due to engine cutoff sensor (ECO) reading errors, the launch was postponed to 9 December 2007. During the second launch attempt, the sensors failed again, and the launch was halted. A tanking test on 18 December 2007 r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
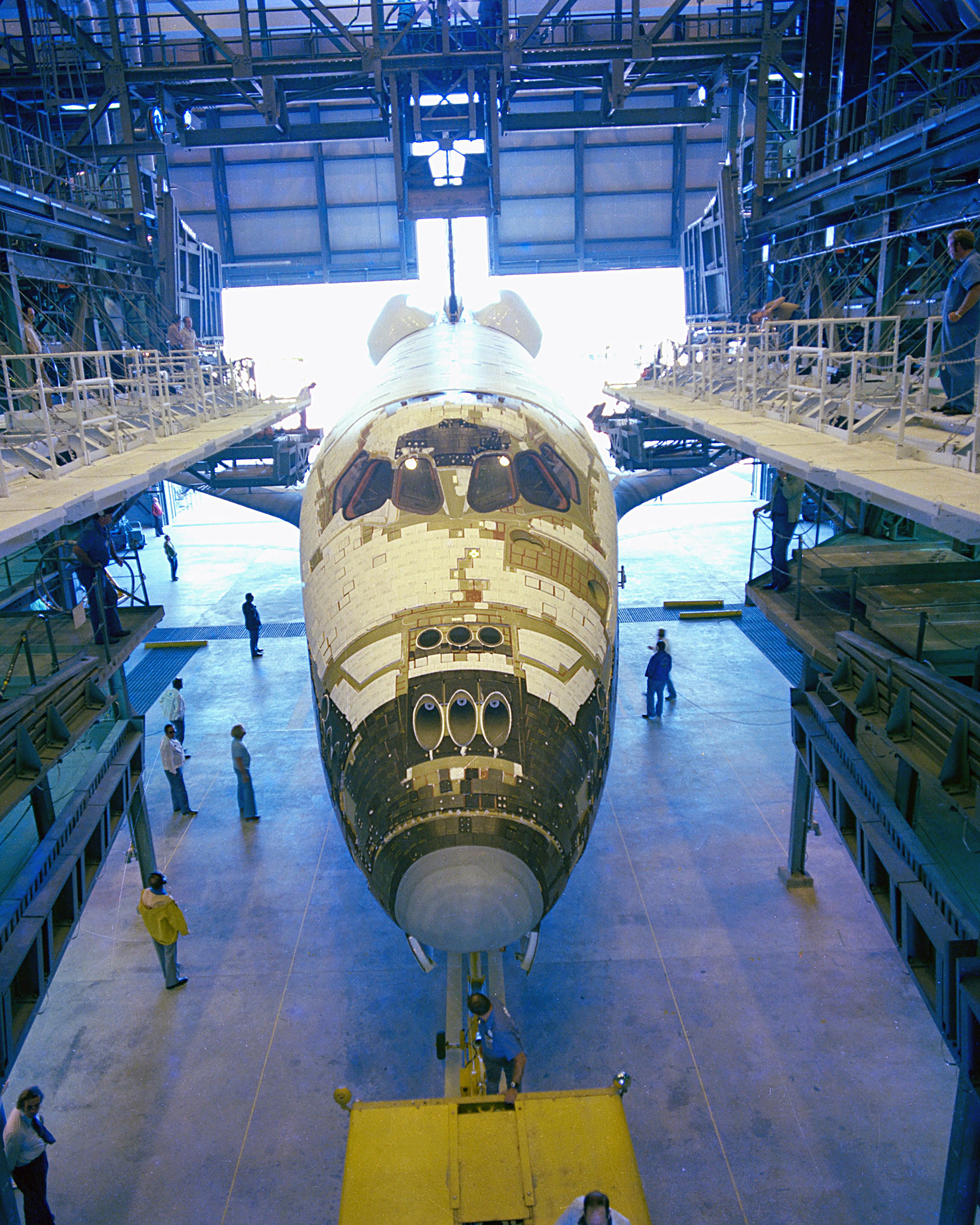
Space Shuttle Atlantis
Space Shuttle ''Atlantis'' (Orbiter Vehicle designation: OV‑104) is a Space Shuttle orbiter vehicle which belongs to NASA, the spaceflight and space exploration agency of the United States. ''Atlantis'' was manufactured by the Rockwell International company in Southern California and was delivered to the Kennedy Space Center in Eastern Florida in April 1985. ''Atlantis'' is also the fourth operational and the second-to-last Space Shuttle built. Its maiden flight was STS-51-J made from October 3 to 7, 1985. ''Atlantis'' embarked on its 33rd and final mission, also the final mission of a space shuttle, STS-135, on July 8, 2011. STS-134 by ''Endeavour'' was expected to be the final flight before STS-135 was authorized in October 2010. STS-135 took advantage of the processing for the STS-335 Launch on Need mission that would have been necessary if STS-134's crew became stranded in orbit. ''Atlantis'' landed for the final time at the Kennedy Space Center on July 21, 2011. By th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle is a retired, partially reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. Its official program name was Space Transportation System (STS), taken from a 1969 plan for a system of reusable spacecraft where it was the only item funded for development. The first ( STS-1) of four orbital test flights occurred in 1981, leading to operational flights (STS-5) beginning in 1982. Five complete Space Shuttle orbiter vehicles were built and flown on a total of 135 missions from 1981 to 2011. They launched from the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in Florida. Operational missions launched numerous satellites, interplanetary probes, and the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), conducted science experiments in orbit, participated in the Shuttle-''Mir'' program with Russia, and participated in construction and servicing of the International Space Station (ISS). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EADS Astrium Space Transportation
Astrium was an aerospace manufacturer subsidiary of the European Aeronautic Defence and Space Company (EADS) that provided civil and military space systems and services from 2006 to 2013. In 2012, Astrium had a turnover of €5.8 billion and 18,000 employees in France, Germany, the United Kingdom, Spain and the Netherlands. Astrium was a member of Institute of Space, its Applications and Technologies. In late 2013 Astrium was merged with Cassidian, the defence division of EADS and Airbus Military to form Airbus Defence and Space. EADS itself was reorganized as the Airbus Group, with three divisions that include Airbus, Airbus Defence and Space, and Airbus Helicopters. Business structure During 2006–2013, the three main areas of activity within Astrium were: * Astrium Satellites for spacecraft and ground segment * EADS Astrium Space Transportation for launchers and orbital infrastructure * Astrium Services for the development and delivery of satellite services. Satellites As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thales Alenia Space
Thales Alenia Space () is a Franco-Italian aerospace manufacturer. A joint venture between the French technology corporation Thales Group (67%) and Italian defense conglomerate Leonardo (33%), the company is the largest satellite manufacturer in Europe. It is headquartered in Cannes, France. Thales Alenia Space designs and builds various space-related products, notably manufacturing numerous ranges of satellites for telecommunications, navigation, earth observation and space exploration purposes. The company is the second largest industrial participant in the International Space Station (ISS), having produced the European Space Agency's (ESA) modules for the ISS. It is also building satellites for Galileo, a European global satellite navigation system (GSNS). History Thales Alenia Space arose as a result of the French defense electronics specialist Thales Group deciding to buy out the participation of Alcatel in two joint-ventures between France's Alcatel and Italy's Finm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helios 2 (satellite)
The Helios 2 system, which consists of the Helios 2A and Helios 2B, is a French-developed military Earth observation satellite program. Financed at 90% by France, the development also involved minor participation from Belgium, Spain, Italy and Greece. Helios 2A was launched on December 18, 2004, by an Ariane 5 rocket from French Guiana. Helios 2B was launched five years later on December 18, 2009, carried also by an Ariane 5. The two satellites are identical. They carry a Thales-built high-resolution visible and thermal infrared instrument with 35 cm resolution, and an Airbus-built medium-resolution instrument. The Helios 2 satellite bus is nearly identical to the platform built by EADS Astrium for the Spot 5 civil-commercial optical observation satellite. The Helios 2 will be replaced by the Composante Spatiale Optique Composante Spatiale Optique (CSO; English: Optical Space Component) is a French military Earth observation satellite program of third generation. It repl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CNES
The (CNES; French: ''Centre national d'études spatiales'') is the French government space agency (administratively, a "public administration with industrial and commercial purpose"). Its headquarters are located in central Paris and it is under the supervision of the French Ministries of Defence and Research. It operates from the Toulouse Space Centre and the Guiana Space Centre, but also has payloads launched from space centres operated by other countries. The president of CNES is Philippe Baptiste. CNES is a member of Institute of Space, its Applications and Technologies. It is Europe's largest and most important national organization of its type. History CNES was established under President Charles de Gaulle in 1961. It is the world's third oldest space agency, after the Soviet space program (Russia), and NASA (United States). CNES was responsible for the training of French astronauts, until the last active CNES astronauts transferred to the European Space Agency in 200 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Unification
The unification of Germany (, ) was the process of building the modern German nation state with federal features based on the concept of Lesser Germany (one without multinational Austria), which commenced on 18 August 1866 with adoption of the North German Confederation Treaty establishing the North German Confederation, initially a Prussian-dominated military alliance which was subsequently deepened through adoption of the North German Constitution. The process symbolically concluded with the ceremonial proclamation of the German Empire on 18 January 1871 celebrated later as the customary date of the German Empire's foundation, although the legally meaningful events relevant to the accomplishment of unification occured on 1 January 1871 ( accession of South German states and constitutional adoption of the name German Empire) and 4 May 1871 (entry into force of the permanent Constitution of the German Empire). Despite the legal, administrative, and political disruption caus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Messerschmitt-Bölkow-Blohm
Messerschmitt-Bölkow-Blohm (MBB) was a West German aerospace manufacturer. It was formed during the late 1960s as the result of efforts to consolidate the West German aerospace industry; aircraft manufacturer Messerschmitt AG merged with the civil engineering and aviation firm Bölkow during 1968, while rival aircraft manufacturer Hamburger Flugzeugbau was acquired by the company in the following year. The company was responsible for the development and manufacture of various aircraft during its existence. Among its best-known products was the MBB Bo 105 light twin-engine helicopter and its enlarged derivative, the MBB/Kawasaki BK 117. MBB was also a key early partner on the Airbus A300, a wide-body twin-jet airliner; the company's involvement in the A300's development and production led to it forming a key component of the multinational Airbus consortium. It was also involved in numerous experimental aircraft programmes, such as the MBB Lampyridae, an aborted stealth aircraft. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |