|
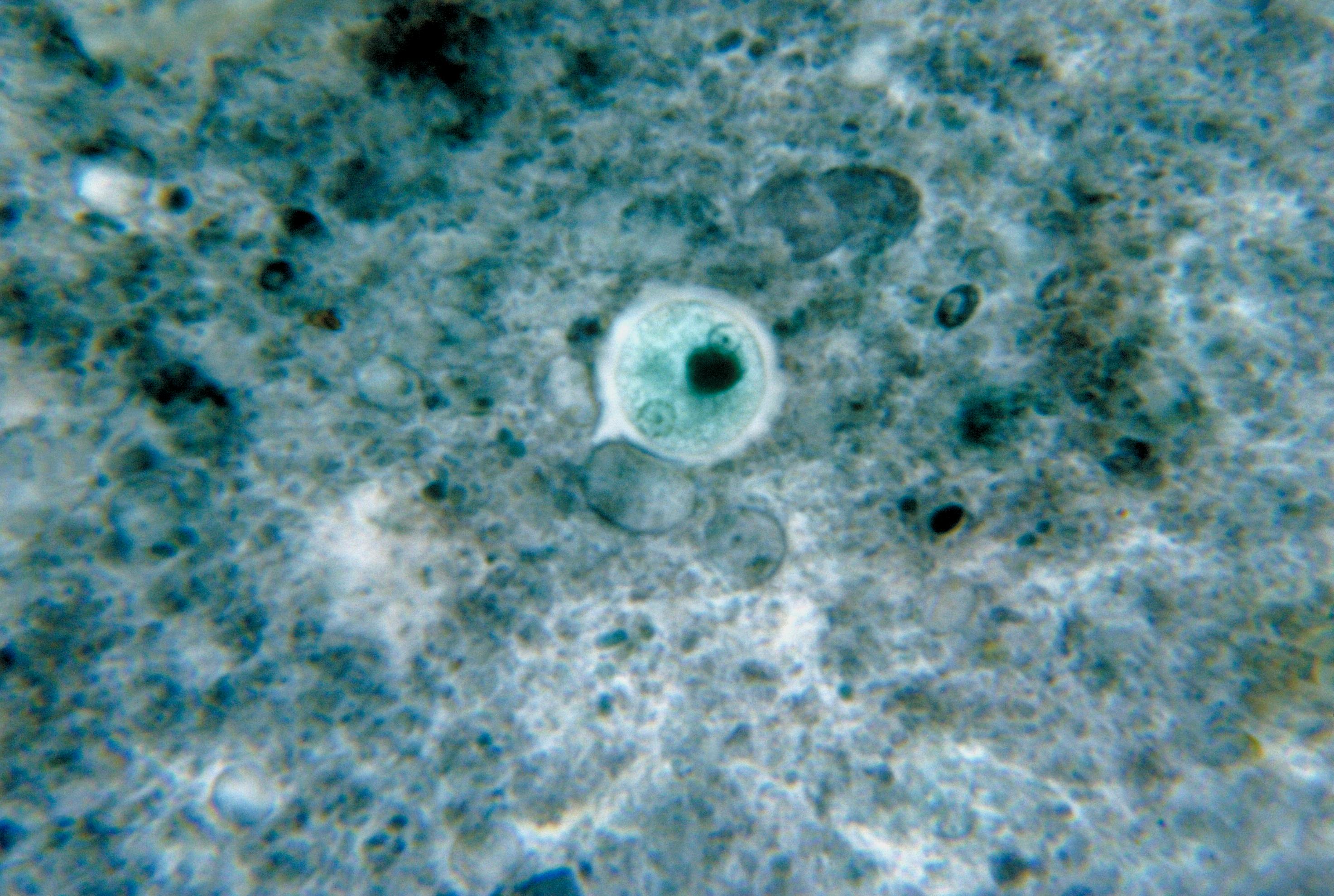
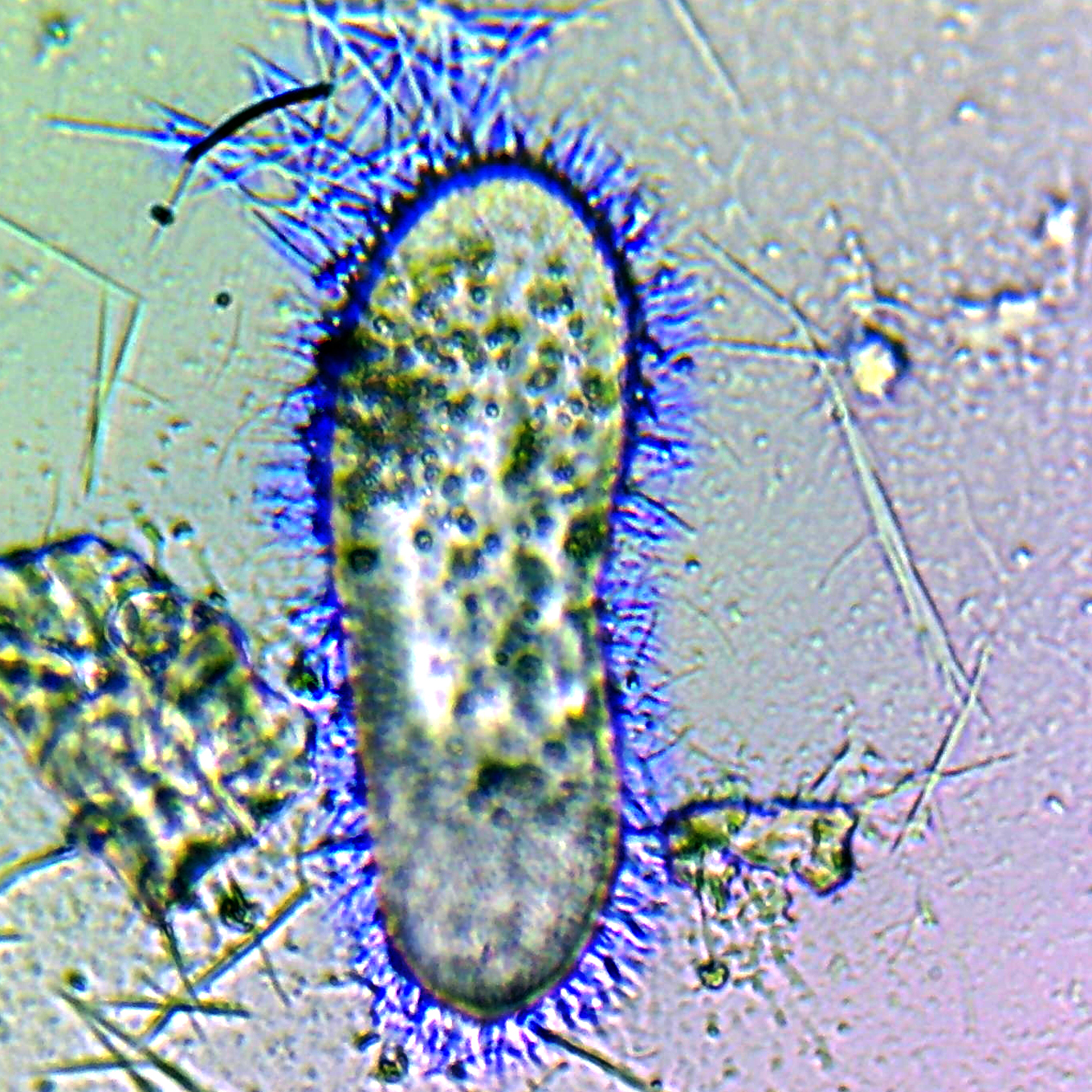
Colpodella
''Colpodella'' is a genus of alveolates comprising 5 species, and two further possible species: They share all the synapomorphies of apicomplexans, but are free-living, rather than parasitic. Many members of this genus were previously assigned to a different genus - '' Spiromonas''. The type species is ''Colpodella pugnax'' Cienkowski 1865. Description These are small ('Dingensia angusta'' (Dujardin 1841) Patterson & Zoelffel 1991 Species transferred to other genera: * ''Colpodella gonderi'' (Foissner & Foissner 1984) Simpson & Patterson 1996 as ''Microvorax gonderi'' (Foissner & Foissner 1984) Cavalier-Smith 2017 * ''Colpodella perforans'' (Hollande 1938) Patterson & Zölffel 1991 as ''Chilovora perforans'' (Hollande 1938) Cavalier-Smith & Chao 2004 * ''Colpodella pontica'' Mylnikov 2000 as ''Voromonas pontica'' (Mylnikov 2000) Cavalier-Smith & Chao 2004 * ''Colpodella pugnax'' Simpson & Patterson 1996 non Cienkowsky 1865 as '' Algovora pugnax'' (Simpson & Patterson 1996) Cava ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colpodella Pugnax
''Colpodella'' is a genus of alveolates comprising 5 species, and two further possible species: They share all the synapomorphies of apicomplexans, but are free-living, rather than parasitic. Many members of this genus were previously assigned to a different genus - '' Spiromonas''. The type species is '' Colpodella pugnax'' Cienkowski 1865. Description These are small ('Dingensia angusta'' (Dujardin 1841) Patterson & Zoelffel 1991 Species transferred to other genera: * ''Colpodella gonderi'' (Foissner & Foissner 1984) Simpson & Patterson 1996 as ''Microvorax gonderi'' (Foissner & Foissner 1984) Cavalier-Smith 2017 * ''Colpodella perforans'' (Hollande 1938) Patterson & Zölffel 1991 as ''Chilovora perforans'' (Hollande 1938) Cavalier-Smith & Chao 2004 * ''Colpodella pontica'' Mylnikov 2000 as ''Voromonas pontica'' (Mylnikov 2000) Cavalier-Smith & Chao 2004 * ''Colpodella pugnax'' Simpson & Patterson 1996 non Cienkowsky 1865 as '' Algovora pugnax'' (Simpson & Patterson 1996) Caval ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apicomplexa
The Apicomplexa (also called Apicomplexia) are a large phylum of parasitic alveolates. Most of them possess a unique form of organelle that comprises a type of non-photosynthetic plastid called an apicoplast, and an apical complex structure. The organelle is an adaptation that the apicomplexan applies in penetration of a host cell. The Apicomplexa are unicellular and spore-forming. All species are obligate endoparasites of animals, except '' Nephromyces'', a symbiont in marine animals, originally classified as a chytrid fungus. Motile structures such as flagella or pseudopods are present only in certain gamete stages. The Apicomplexa are a diverse group that includes organisms such as the coccidia, gregarines, piroplasms, haemogregarines, and plasmodia. Diseases caused by Apicomplexa include: * Babesiosis ('' Babesia'') * Malaria (''Plasmodium'') * Cryptosporidiosis ('' Cryptosporidium parvum'') * Cyclosporiasis ('' Cyclospora cayetanensis'') * Cystoisosporiasis ('' Cys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zoospore
A zoospore is a motile asexual spore that uses a flagellum for locomotion. Also called a swarm spore, these spores are created by some protists, bacteria, and fungi to propagate themselves. Diversity Flagella types Zoospores may possess one or more distinct types of flagella - tinsel or "decorated", and whiplash, in various combinations. *Tinsellated (straminipilous) flagella have lateral filaments known as mastigonemes perpendicular to their main axis, which allow for more surface area, and disturbance of the medium, giving them the property of a rudder, that is, used for steering. *Whiplash flagella are straight, to power the zoospore through its medium. Also, the "default" zoospore only has the propelling, whiplash flagella. Both tinsel and whiplash flagella beat in a sinusoidal wave pattern, but when both are present, the tinsel beats in the opposite direction of the whiplash, to give two axes of control of motility. Morphological types In eukaryotes, the four main type ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perkinsea
Perkinsea is a class of alveolates. Taxonomy ''Perkinsus'' is a genus in the class Perkinsea that is a parasite of bivalve molluscs; it displays a number of features characteristic of the dinoflagellates including laterally inserted heterodynamic flagella. However, it has been settled that ''Perkinsus'' does not belong into the phyla Phyla, the plural of ''phylum'', may refer to: * Phylum, a biological taxon between Kingdom and Class * by analogy, in linguistics, a large division of possibly related languages, or a major language family which is not subordinate to another Phyl ... dinoflagellata, but rather into the phylum Perkinsozoa. Two other genera have been described in this class — '' Cryptophagus'' (now renamed '' Rastrimonas'') and '' Parvilucifera''. References Perkinsozoa Alveolata classes {{Alveolata-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Eukaryotic Microbiology
The ''Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering all aspects of eukaryotic microbiology. The journal publishes research on protists, including lower algae and fungi. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2021 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as ... of 3.880. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracting and indexing by various services for example: * Abstracts in Anthropology (Sage) * Abstracts on Hygiene & Communicable Diseases (CABI) * Academic Search (EBSCO Publishing) * Academic Search Premier (EBSCO Publishing) * AgBiotech News & Information (CABI) * AgBiotechNet (CABI) * AGRICOLA Database (National Agricultural Library) * Animal Breeding Abstracts (CABI) * Biocontrol News & In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microbial Cyst
A microbial cyst is a resting or dormant stage of a microorganism, usually a bacterium or a protist or rarely an invertebrate animal, that helps the organism to survive in unfavorable environmental conditions. It can be thought of as a state of suspended animation in which the metabolic processes of the cell are slowed and the cell ceases all activities like feeding and locomotion. Encystment, the formation of the cyst, also helps the microbe to disperse easily, from one host to another or to a more favorable environment. When the encysted microbe reaches an environment favorable to its growth and survival, the cyst wall breaks down by a process known as excystation. In excystment, the exact stimulus is unknown for most protists. Unfavorable environmental conditions such as lack of nutrients or oxygen, extreme temperatures, lack of moisture and presence of toxic chemicals, which are not conducive for the growth of the microbeEugene W. Nester, Denise G. Anderson, C. Evans Robert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuole
A vacuole () is a membrane-bound organelle which is present in plant and fungal cells and some protist, animal, and bacterial cells. Vacuoles are essentially enclosed compartments which are filled with water containing inorganic and organic molecules including enzymes in solution, though in certain cases they may contain solids which have been engulfed. Vacuoles are formed by the fusion of multiple membrane vesicles and are effectively just larger forms of these. The organelle has no basic shape or size; its structure varies according to the requirements of the cell. Discovery Contractile vacuoles ("stars") were first observed by Spallanzani (1776) in protozoa, although mistaken for respiratory organs. Dujardin (1841) named these "stars" as ''vacuoles''. In 1842, Schleiden applied the term for plant cells, to distinguish the structure with cell sap from the rest of the protoplasm. In 1885, de Vries named the vacuole membrane as tonoplast. Function The function and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myzocytosis
Myzocytosis (from Greek: myzein, (') meaning "to suck" and kytos (') meaning "container", hence referring to "cell") is a method of feeding found in some heterotrophic organisms. It is also called "cellular vampirism" as the predatory cell pierces the cell wall and/or cell membrane of the prey cell with a feeding tube, the conoid, sucks out the cellular content and digests it. Myzocytosis is found in Myzozoa and also in some species of Ciliophora (both comprise the alveolates). A classic example of myzocytosis is the feeding method of the infamous predatory ciliate, '' Didinium'', where it is often depicted devouring a hapless ''Paramecium''. The suctorian ciliates were originally thought to have fed exclusively through myzocytosis, sucking out the cytoplasm of prey via superficially drinking straw A drinking straw is a utensil that is intended to carry the contents of a beverage to one's mouth. Straws are commonly made from plastics but environmental concerns and new regu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protist
A protist () is any eukaryotic organism (that is, an organism whose cells contain a cell nucleus) that is not an animal, plant, or fungus. While it is likely that protists share a common ancestor (the last eukaryotic common ancestor), the exclusion of other eukaryotes means that protists do not form a natural group, or clade. Therefore, some protists may be more closely related to animals, plants, or fungi than they are to other protists. However, like the groups ''algae'', ''invertebrates'', and '' protozoans'', the biological category ''protist'' is used for convenience. Others classify any unicellular eukaryotic microorganism as a protist. The study of protists is termed protistology. History The classification of a third kingdom separate from animals and plants was first proposed by John Hogg in 1860 as the kingdom Protoctista; in 1866 Ernst Haeckel also proposed a third kingdom Protista as "the kingdom of primitive forms". Originally these also included prokaryote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trichocyst
A trichocyst is an organelle found in certain ciliates and dinoflagellates. A trichocyst can be found in tetrahymena ''Tetrahymena'', a Unicellular organism, unicellular eukaryote, is a genus of free-living ciliates. The genus Tetrahymena is the most widely studied member of its phylum. It can produce, store and react with different types of hormones. Tetrah ... and along cila pathways of several metabolic systems. It is also a structure in the cortex of certain ciliate and flagellate protozoans consisting of a cavity and long, thin threads that can be ejected in response to certain stimuli. Trichocysts may be widely distributed over an organism or restricted to certain areas (e.g., tentacles, papillae, around the mouth). There are several types. Mucoid trichocysts are elongated inclusions that may be ejected as visible bodies after artificial stimulation. Filamentous trichocysts in Paramecium and other ciliates are discharged as filaments composed of a cross-striated shaft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microtubule
Microtubules are polymers of tubulin that form part of the cytoskeleton and provide structure and shape to eukaryotic cells. Microtubules can be as long as 50 micrometres, as wide as 23 to 27 nm and have an inner diameter between 11 and 15 nm. They are formed by the polymerization of a dimer of two globular proteins, alpha and beta tubulin into protofilaments that can then associate laterally to form a hollow tube, the microtubule. The most common form of a microtubule consists of 13 protofilaments in the tubular arrangement. Microtubules play an important role in a number of cellular processes. They are involved in maintaining the structure of the cell and, together with microfilaments and intermediate filaments, they form the cytoskeleton. They also make up the internal structure of cilia and flagella. They provide platforms for intracellular transport and are involved in a variety of cellular processes, including the movement of secretory vesicles, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |