|
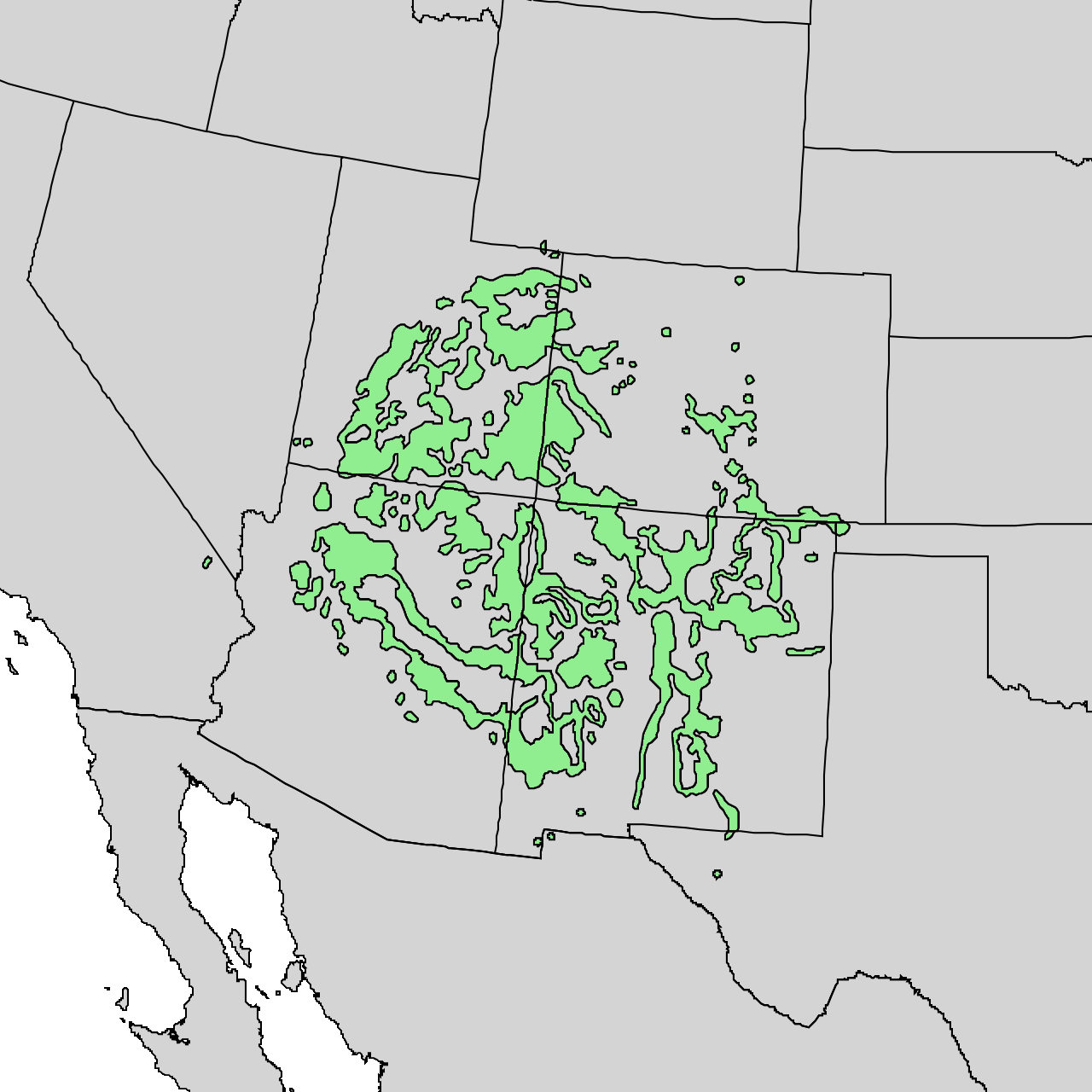
Colorado Plateaus
The Colorado Plateau shrublands is an ecoregion of deserts and xeric shrublands in the Western United States. Geography The Colorado Plateau shrublands occupy the Colorado Plateau. They lie mostly in the basin of the upper Colorado River, and reach into the upper basin of the Rio Grande. Flora The main plant communities, or zones, are woodlands, mountain woodlands, and grassland and shrub. The woodland zone, or pinyon-juniper woodland, covers the largest area. It consists of open woodlands of short trees, mostly pinyon pine ('' Pinus edulis'' throughout the ecoregion, and ''Pinus monophylla'' subsp. ''fallax'' in the southwestern portion of the ecoregion) and species of juniper (''Juniperus'' spp.). The ground is covered by sparse grasses, including grama and other grasses, herbs, and shrubs such as big sagebrush (''Artemisia tridentata'') and alder-leaf mountain mahogany (''Cercocarpus montanus''). Arid grasslands occupy lowland areas. Grasses, sagebrush, and shrubs p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landscape Arch
Landscape Arch is the longest of the many natural rock arches located in Arches National Park, Utah, United States and among the longest natural stone arches in the world. Description The arch is among many in the Devils Garden area in the north of the park. Landscape Arch was named by Frank Beckwith who explored the area in the winter of 1933–1934 as the leader of an Arches National Monument scientific expedition. The arch can be accessed by a graded gravel trail. The Natural Arch and Bridge Society (NABS) considers Landscape Arch the fifth longest natural arch in the world, after four arches in China. The span of Landscape Arch was measured at , ±, in 2004. NABS measured the span of the slightly shorter Kolob Arch in Zion National Park at in 2006. The most recent recorded rockfall events occurred in the 1990s when one large slab fell in 1991 and then two additional large rockfalls occurred in 1995. Since the rockfalls, the trail beneath the arch has been closed. Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cold Semi-arid Climate
A semi-arid climate, semi-desert climate, or steppe climate is a dry climate sub-type. It is located on regions that receive precipitation below potential evapotranspiration, but not as low as a desert climate. There are different kinds of semi-arid climates, depending on variables such as temperature, and they give rise to different biomes. Defining attributes of semi-arid climates A more precise definition is given by the Köppen climate classification, which treats steppe climates (''BSk'' and ''BSh'') as intermediates between desert climates (BW) and humid climates (A, C, D) in ecological characteristics and agricultural potential. Semi-arid climates tend to support short, thorny or scrubby vegetation and are usually dominated by either grasses or shrubs as it usually can't support forests. To determine if a location has a semi-arid climate, the precipitation threshold must first be determined. The method used to find the precipitation threshold (in millimeters): *multiply ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinus Ponderosa
''Pinus ponderosa'', commonly known as the ponderosa pine, bull pine, blackjack pine, western yellow-pine, or filipinus pine is a very large pine tree species of variable habitat native to mountainous regions of western North America. It is the most widely distributed pine species in North America.Safford, H.D. 2013. Natural Range of Variation (NRV) for yellow pine and mixed conifer forests in the bioregional assessment area, including the Sierra Nevada, southern Cascades, and Modoc and Inyo National Forests. Unpublished report. USDA Forest Service, Pacific Southwest Region, Vallejo, CA/ref> ''Pinus ponderosa'' grows in various erect forms from British Columbia southward and eastward through 16 western U.S. states and has been successfully introduced in temperate regions of Europe, and in New Zealand. It was first documented in modern science in 1826 in eastern Washington near present-day Spokane (of which it is the official city tree). On that occasion, David Douglas misidenti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cercocarpus Montanus
''Cercocarpus montanus'' is a North American species of shrub or small tree in the family Rosaceae native to northern Mexico and the western United States. It is known by the common names alder-leaf mountain-mahogany, alder-leaf cercocarpus, and true mountain-mahogany. The variety ''argenteus'' is commonly known as silverleaf mountain-mahogany. Distribution ''Cercocarpus montanus'' is common in chaparral scrub, on mesas, the lower foothills of the Rocky Mountains, and the Great Plains in the United States. Its range extends from Montana, Idaho, and South Dakota south as far as Sonora, Durango, and Nuevo León. Description and ecology ''Cercocarpus montanus'' often remains under in height because of browsing by elk and deer, but can reach . It has thin and smooth bark. The species is considered to be long lived. It is also eaten by yellow-haired porcupine. File:Cercocarpus montanus 1.jpg, Flowers appear red when they first open File:Cercocarpus montanus 2.jpg, Flowers are yel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
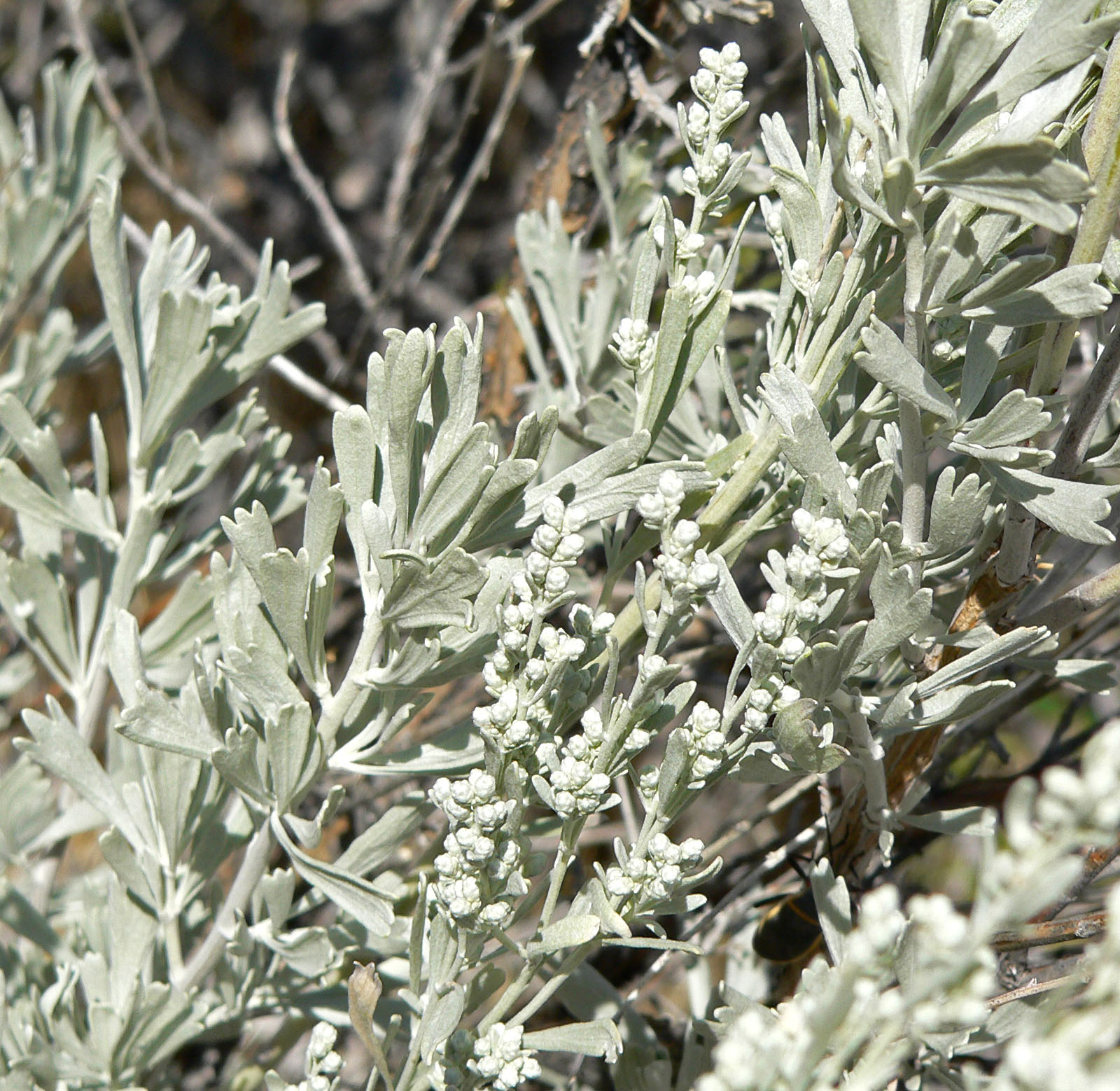
Artemisia Tridentata
''Artemisia tridentata'', commonly called big sagebrush,MacKay, Pam (2013), ''Mojave Desert Wildflowers'', 2nd ed., , p. 264. Great Basin sagebrush or (locally) simply sagebrush, is an aromatic shrub from the family Asteraceae, which grows in arid and semi-arid conditions, throughout a range of cold desert, steppe, and mountain habitats in the Intermountain West of North America. The vernacular name "sagebrush" is also used for several related members of the genus ''Artemisia'', such as California sagebrush (''Artemisia californica''). Big sagebrush and other ''Artemisia'' shrubs are the dominant plant species across large portions of the Great Basin. The range extends northward through British Columbia's southern interior, south into Baja California, and east into the western Great Plains of New Mexico, Colorado, Nebraska, and the Dakotas. Several major threats exist to sagebrush ecosystems, including human settlements, conversion to agricultural land, livestock grazing, inva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bouteloua
''Bouteloua'' is a genus of plants in the grass family. Members of the genus are commonly known as grama grass. Taxonomy and systematics The genus was named for Claudio and Esteban Boutelou, 19th-century Spanish botanists. David Griffiths produced a 1912 monograph on the genus. Description ''Bouteloua'' includes both annual and perennial grasses, which frequently form stolons. Species have an inflorescence of 1 to 80 racemes or spikes positioned alternately on the culm (stem). The rachis (stem) of the spike is flattened. The spikelets are positioned along one side of the spike. Each spikelet contains one fertile floret, and usually one sterile floret. Distribution ''Bouteloua'' is found only the Americas, with most diversity centered in the southwestern United States. Uses Many species are important livestock forage, especially blue grama. Species Species of ''Bouteloua'' include:Gould, F. W. & R. Moran. 1981. The grasses of Baja California, Mexico. Memoir San Die ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juniper
Junipers are coniferous trees and shrubs in the genus ''Juniperus'' () of the cypress family Cupressaceae. Depending on the taxonomy, between 50 and 67 species of junipers are widely distributed throughout the Northern Hemisphere, from the Arctic, south to tropical Africa, throughout parts of West Asia, western, Central Asia, central and South Asia, southern Asia, east to eastern Tibet in the Old World, and in the mountains of Central America. The highest-known juniper forest occurs at an altitude of in southeastern Tibet and the northern Himalayas, creating one of the highest tree lines on earth. Description Junipers vary in size and shape from tall trees, tall, to columnar or low-spreading shrubs with long, trailing branches. They are evergreen with needle-like and/or scale-like leaves. They can be either monoecious or dioecious. The female Conifer cone, seed cones are very distinctive, with fleshy, fruit-like coalescing scales which fuse together to form Juniper berry, a&n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinus Monophylla
''Pinus monophylla'', the single-leaf pinyon, (alternatively spelled piñon) is a pine in the pinyon pine group, native to North America. The range is in southernmost Idaho, western Utah, Arizona, southwest New Mexico, Nevada, eastern and southern California and northern Baja California. It occurs at moderate altitudes from , rarely as low as and as high as . It is widespread and often abundant in this region, forming extensive open woodlands, often mixed with junipers in the Pinyon-juniper woodland plant community. Single-leaf pinyon is the world's only one-needled pine.Gerry Moore et al. 2008 Description Species ''Pinus monophylla'' is a small to medium size tree, reaching tall and with a trunk diameter of up to rarely more. The bark is irregularly furrowed and scaly. The leaves ('needles') are, uniquely for a pine, usually single (not two or more in a fascicle, though trees with needles in pairs are found occasionally), stout, long, and grey-green to strongly glaucous bl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinus Edulis
''Pinus edulis'', the Colorado pinyon, two-needle piñon, pinyon pine, or simply piñon, is a pine in the pinyon pine group whose ancestor was a member of the Madro-Tertiary Geoflora (a group of drought resistant trees) and is native to the United States. Distribution and habitat The range is in Colorado, southern Wyoming, eastern and central Utah, northern Arizona, New Mexico, western Oklahoma, southeastern California, and the Guadalupe Mountains in far western Texas. It occurs at moderate elevations of , rarely as low as and as high as . It is widespread and often abundant in this region, forming extensive open woodlands, usually mixed with junipers in the pinyon-juniper woodland plant community. The Colorado pinyon (piñon) grows as the dominant species on 4.8 million acres () in Colorado, making up 22% of the state's forests. The Colorado pinyon has cultural meaning to agriculture, as strong piñon wood "plow heads" were used to break soil for crop planting at the state's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinyon Pine
The pinyon or piñon pine group grows in southwestern North America, especially in New Mexico, Arizona, and Utah. The trees yield edible nuts, which are a staple food of Native Americans, and widely eaten as a snack and as an ingredient in New Mexican cuisine. The name comes from the Spanish ''pino piñonero'', a name used for both the American varieties and the stone pine common in Spain, which also produces edible nuts typical of Mediterranean cuisine. Harvesting techniques of the prehistoric American Indians are still used today to collect the pinyon seeds for personal use or for commercialization. The pinyon nut or seed is high in fats and calories. Pinyon wood, especially when burned, has a distinctive fragrance, making it a common wood to burn in chimeneas. Pinyon pine trees are also known to influence the soil in which they grow by increasing concentrations of both macronutrients and micronutrients. Some of the species are known to hybridize, the most notable ones being ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rio Grande
The Rio Grande ( and ), known in Mexico as the Río Bravo del Norte or simply the Río Bravo, is one of the principal rivers (along with the Colorado River) in the southwestern United States and in northern Mexico. The length of the Rio Grande is . It originates in south-central Colorado, in the United States, and flows to the Gulf of Mexico. The Rio Grande drainage basin (watershed) has an area of ; however, the endorheic basins that are adjacent to and within the greater drainage basin of the Rio Grande increase the total drainage-basin area to . The Rio Grande with Rio Grande Valley (landform), its fertile valley, along with its tributaries, is a vital watersource for seven US and Mexican states, and flows primarily through arid and semi-arid lands. After traversing the length of New Mexico, the Rio Grande becomes the Mexico–United States border, between the U.S. state of Texas and the northern Mexican states of Chihuahua (state), Chihuahua and Coahuila, Nuevo León a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)