|
Collingwood Park, Queensland
Collingwood Park is a Suburbs and localities (Australia), suburb of Ipswich, Queensland, Ipswich in the City of Ipswich, Queensland, Australia. In the , Collingwood Park had a population of 7,104 people. Geography Collingwood Park, a residential suburb, is east of the Ipswich, next to the historic suburb of Redbank. Its eastern boundary is delineated by Goodna Creek and the western boundary by Six Mile Creek. Housing development began circa 1980 with the establishment of two HIA display villages. Redbank Plaza is a large shopping mall, located on the northern boundary of the suburb. The main thoroughfare is Collingwood Drive which runs south from the shopping centre. History The suburb was named and bounded on 28 August 1982. Throughout the 1980s, Collingwood Park was marketed as, "The Dress Circle Suburb of Ipswich". The suburb's name implied a "leafy" residential area which differentiated it from nearby Redbank, the site of several collieries and industries: a map, c1940, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
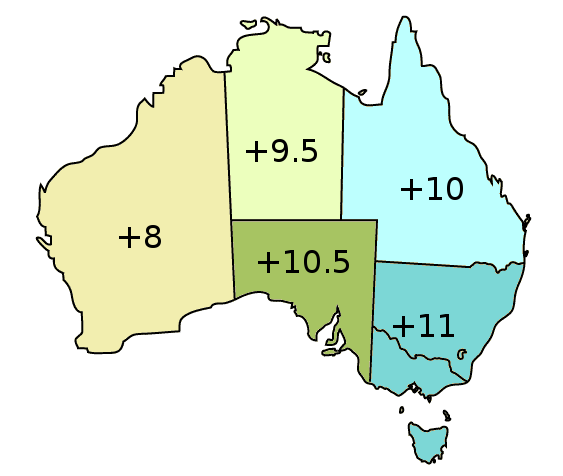
AEST
Australia uses three main time zones: Australian Western Standard Time (AWST; UTC+08:00), Australian Central Standard Time (ACST; UTC+09:30), and Australian Eastern Standard Time (AEST; UTC+10:00). Time is regulated by the individual state governments, some of which observe daylight saving time (DST). Australia's external territories observe different time zones. Standard time was introduced in the 1890s when all of the Australian colonies adopted it. Before the switch to standard time zones, each local city or town was free to determine its local time, called local mean time. Now, Western Australia uses Western Standard Time; South Australia and the Northern Territory use Central Standard Time; while New South Wales, Queensland, Tasmania, Victoria (Australia), Victoria, Jervis Bay Territory, and the Australian Capital Territory use Eastern Standard Time. Daylight saving time (+1 hour) is used in jurisdictions in the south and south-east: South Australia, New South Wales, Vict ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queensland Government
The Queensland Government is the democratic administrative authority of the Australian state of Queensland. The Government of Queensland, a parliamentary constitutional monarchy was formed in 1859 as prescribed in its Constitution, as amended from time to time. Since the Federation of Australia in 1901, Queensland has been a State of Australia, with the Constitution of Australia regulating the relationships between all state and territory governments and the Australian Government. Under the Australian Constitution, all states and territories (including Queensland) ceded powers relating to certain matters to the federal government. The government is influenced by the Westminster system and Australia's federal system of government. The Governor of Queensland, as the representative of Charles III, King of Australia, holds nominal executive power, although in practice only performs ceremonial duties. In practice executive power lies with the Premier and Cabinet. The Cabinet of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glossy Black Cockatoo
The glossy black cockatoo (''Calyptorhynchus lathami''), is the smallest member of the subfamily Calyptorhynchinae found in eastern Australia. Adult glossy black cockatoos may reach in length. They are sexually dimorphic. Males are blackish brown, except for their prominent red tail bands; the females are dark brownish with some yellow spotting. Three subspecies are recognised. Taxonomy The glossy black cockatoo was first described by Dutch naturalist Coenraad Jacob Temminck in 1807. The scientific name honours the English ornithologist John Latham. The glossy black cockatoo's closest relative is the red-tailed black cockatoo; the two species form the genus ''Calyptorhynchus''.Forshaw, p. 89 They are distinguished from the other black cockatoos of the genus '' Zanda'' by different tail colour and head pattern, significant sexual dimorphism, and differences in two juvenile call types, a squeaking begging call and a vocalization when swallowing food. Subspecies The three subsp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black-chinned Honeyeater
The black-chinned honeyeater (''Melithreptus gularis'') is a species of passerine bird in the family Meliphagidae. It is endemic to Australia. Two subspecies are recognised. Its natural habitats are temperate forests and subtropical or tropical dry forests. Taxonomy The black-chinned honeyeater was first described by John Gould in 1837 as ''Haematops gularis''. He also described what he called the golden-backed honeyeater (as ''Melithreptus laetior'') of northern Australia in 1875. Frederick George Waterhouse of the South Australian Museum had sent him four skins, writing of their beauty. Gould noted that it was clearly closely related to ''M. gularis'', but differed in its plumage and smaller size. Richard Schodde united them into a single species in 1975, though Hugh Ford queried this in 1986, as he felt the two forms were as distinct as the yellow-tinted and fuscous honeyeaters that had similar ranges. Schodde countered that the black-chinned and golden-backed honeyeaters shar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Powerful Owl
The powerful owl (''Ninox strenua''), a species of owl native to south-eastern and eastern Australia, is the largest owl on the continent. It is found in coastal areas and in the Great Dividing Range, rarely more than inland. The IUCNRed List of Threatened Species also refers to this species as the powerful boobook. An apex predator in its narrow distribution, powerful owls are often opportunists, like most predators, but generally are dedicated to hunting arboreal mammals, in particular small to medium-sized marsupials. Such prey can comprise about three-quarters of their diet. Generally, this species lives in primary forests with tall, native trees, but can show some habitat flexibility when not nesting. The powerful owl is a typically territorial raptorial bird that maintains a large home range and has long intervals between egg-laying and hatching of clutches. Also, like many types of raptorial birds, they must survive a long stretch to independence in young owls after fle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spotted Dove
The spotted dove (''Spilopelia chinensis'') is a small and somewhat long-tailed pigeon that is a common resident breeding bird across its native range on the Indian subcontinent and in Southeast Asia. The species has been introduced to many parts of the world and feral populations have become established. This species was formerly included in the genus ''Streptopelia'' with other turtle-doves, but studies suggest that they differ from typical members of that genus. This dove is long tailed buff brown with a white-spotted black collar patch on the back and sides of the neck. The tail tips are white and the wing coverts have light buff spots. There are considerable plumage variations across populations within its wide range. The species is found in light forests and gardens as well as in urban areas. They fly from the ground with an explosive flutter and will sometimes glide down to a perch. It is also called the mountain dove, pearl-necked dove, lace-necked dove, and spotted turtl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cane Toad
The cane toad (''Rhinella marina''), also known as the giant neotropical toad or marine toad, is a large, terrestrial true toad native to South and mainland Central America, but which has been introduced to various islands throughout Oceania and the Caribbean, as well as Northern Australia. It is a member of the genus ''Rhinella'', which includes many true toad species found throughout Central and South America, but it was formerly assigned to the genus ''Bufo''. The cane toad is an old species. A fossil toad (specimen UCMP 41159) from the La Venta fauna of the late Miocene in Colombia is indistinguishable from modern cane toads from northern South America. It was discovered in a floodplain deposit, which suggests the ''R. marina'' habitat preferences have long been for open areas. The cane toad is a prolific breeder; females lay single-clump spawns with thousands of eggs. Its reproductive success is partly because of opportunistic feeding: it has a diet, unusual among anuran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cinnamomum Camphora
''Camphora officinarum'' is a species of evergreen tree that is commonly known under the names camphor tree, camphorwood or camphor laurel. Description ''Camphora officinarum'' is native to China south of the Yangtze River, Taiwan, southern Japan, Korea, India and Vietnam, and has been introduced to many other countries. It grows up to tall. In Japan, where the tree is called ''kusunoki'', five camphor trees are known with a trunk circumference above , with the largest individual, , reaching 24.22 m. The leaves have a glossy, waxy appearance and smell of camphor when crushed. In spring, it produces bright green foliage with masses of small white flowers. It produces clusters of black, berry-like fruit around in diameter. Its pale bark is very rough and fissured vertically. Certain trees in Japan are considered sacred. An example of the importance of a sacred tree is the 700-year old camphor growing in the middle of Kayashima Station. Locals protested against moving the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lantana
''Lantana'' () is a genus of about 150 species of perennial flowering plants in the verbena family, Verbenaceae. They are native to tropical regions of the Americas and Africa but exist as an introduced species in numerous areas, especially in the Australian-Pacific region, South and Northeastern part of India. The genus includes both herbaceous plants and shrubs growing to tall. Their common names are shrub verbenas or lantanas. The generic name originated in Late Latin, where it refers to the unrelated ''Viburnum lantana''. Lantana's aromatic flower clusters (called umbels) are a mix of red, orange, yellow, or blue and white florets. Other colors exist as new varieties are being selected. The flowers typically change color as they mature, resulting in inflorescences that are two- or three-colored. "Wild lantanas" are plants of the unrelated genus ''Abronia'', usually called "sand-verbenas". Ecology Some species are invasive, and are considered to be noxious weeds, such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salvinia
''Salvinia'', a genus in the family Salviniaceae, is a floating fern named in honor of Anton Maria Salvini, a 17th-century Italian scientist. Watermoss is a common name for ''Salvinia''. The genus was published in 1754 by Jean-François Séguier, in his description of the plants found round Verona, ''Plantae Veronenses'' Twelve species are recognized, at least three of which (''S. molesta'', ''S. herzogii'', and ''S. minima'') are believed to be hybrids, in part because their sporangia are found to be empty. ''Salvinia'' is related to the other water ferns, including the mosquito fern ''Azolla''. Recent sources include both ''Azolla'' and ''Salvinia'' in Salviniaceae, although each genus was formerly given its own family. ''Salvinia'', like the other ferns in order Salviniales, are heterosporous, producing spores of differing sizes. However, leaf development in ''Salvinia'' is unique. The upper side of the floating leaf, which appears to face the stem axis, is morphologically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulmus Parvifolia
''Ulmus parvifolia'', commonly known as the Chinese elm or lacebark elm, is a species native to eastern Asia, including China, India, Japan, Korea, and Vietnam.Fu, L., Xin, Y. & Whittemore, A. (2002)Ulmaceae in Wu, Z. & Raven, P. (eds) ''Flora of China'', Vol. 5 (Ulmaceae through Basellaceae). Science Press, Beijing, and Missouri Botanical Garden Press, St. Louis, USA; also available as It has been described as "one of the most splendid elms, having the poise of a graceful ''Nothofagus''".''Hilliers' Manual of Trees & Shrubs'', 4th edition, 1977, David & Charles, Newton Abbot, England The tree was introduced to the UK in 1794 by James Main, who collected in China for Gilbert Slater of Low Layton, Essex.Elwes, H. J. & Henry, A. (1913). The Trees of Great Britain & Ireland'. Vol. VII. 1848–1929. Republished 2004 Cambridge University Press, Bean, W. J. (1981). ''Trees and shrubs hardy in Great Britain'', 7th edition. Murray, London. Description A small to medium deciduous or sem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)
