|
Coisogenic Strain
Coisogenic strains are one type of inbred strain that differs by a mutation at a single locus and all of the other loci are identical. There are numerous ways to create an inbred strain and each of these strains are unique. Genetically engineered mice can be considered a coisogenic strain if the only difference between the engineered mouse and a wild-type mouse is a specific locus. Coisogenic strains can be used to investigate the function of a certain genetic locus. Coisogenic strains can be induced chemically or through radiation however, other types of alterations within the genome may also occur. Coisogenic strains may also occur through a spontaneous mutation that occurs in an inbred strain. To create a coisogenic strain through breeding, a mouse with the specific mutation on a locus is mated to an inbred strain (e.g., C57BL/6 C57BL/6, often referred to as "C57 black 6", "C57" or "black 6", is a common inbred strain of laboratory mouse. It is the most widely used "genet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inbred Strain
Inbred strains (also called inbred lines, or rarely for animals linear animals) are individuals of a particular species which are nearly identical to each other in genotype due to long inbreeding. A strain is inbred when it has undergone at least 20 generations of brother x sister or offspring x parent mating, at which point at least 98.6% of the loci in an individual of the strain will be homozygous, and each individual can be treated effectively as clones. Some inbred strains have been bred for over 150 generations, leaving individuals in the population to be isogenic in nature. Inbred strains of animals are frequently used in laboratories for experiments where for the reproducibility of conclusions all the test animals should be as similar as possible. However, for some experiments, genetic diversity in the test population may be desired. Thus outbred strains of most laboratory animals are also available, where an outbred strain is a strain of an organism that is effectively ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
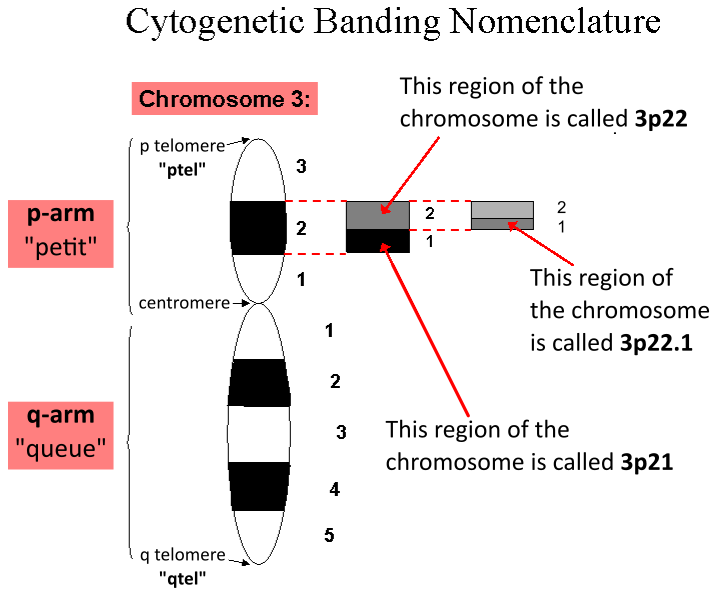
Locus (genetics)
In genetics, a locus (plural loci) is a specific, fixed position on a chromosome where a particular gene or genetic marker is located. Each chromosome carries many genes, with each gene occupying a different position or locus; in humans, the total number of protein-coding genes in a complete haploid set of 23 chromosomes is estimated at 19,000–20,000. Genes may possess multiple variants known as alleles, and an allele may also be said to reside at a particular locus. Diploid and polyploid cells whose chromosomes have the same allele at a given locus are called homozygous with respect to that locus, while those that have different alleles at a given locus are called heterozygous. The ordered list of loci known for a particular genome is called a gene map. Gene mapping is the process of determining the specific locus or loci responsible for producing a particular phenotype or biological trait. Association mapping, also known as "linkage disequilibrium mapping", is a method of ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetically Modified Mouse
A genetically modified mouse or genetically engineered mouse model (GEMM) is a house mouse, mouse (''Mus musculus'') that has had its genome altered through the use of genetic engineering techniques. Genetically modified mice are commonly used for research or as animal models of human diseases, and are also used for research on genes. Together with patient-derived xenografts (PDXs), GEMMs are the most common ''in vivo'' models in cancer research. Both approaches are considered complementary and may be used to recapitulate different aspects of disease. GEMMs are also of great interest for drug development, as they facilitate target validation and the study of response, resistance, toxicity and pharmacodynamics. History In 1974 Beatrice Mintz and Rudolf Jaenisch created the first genetically modified animal by inserting a DNA virus into an early-stage mouse embryo and showing that the inserted genes were present in every cell. However, the mice did not pass the transgene to their offs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C57BL/6
C57BL/6, often referred to as "C57 black 6", "C57" or "black 6", is a common inbred strain of laboratory mouse. It is the most widely used "genetic background" for genetically modified mice for use as models of human disease. They are the most widely used and best-selling mouse strain, due to the availability of congenic strains, easy breeding, and robustness. Origin The inbred strain of C57BL mice was created in 1921 by C. C. Little at the Bussey Institute for Research in Applied Biology. The substrain "6" was the most popular of the surviving substrains. Little's supervisor William E. Castle had obtained the predecessor strain of C57BL/6, "mouse number 57", from Abbie Lathrop who was breeding inbred strains for mammary tumor research in collaboration with Leo Loeb at the time. Appearance and behavior C57BL/6 mice have a dark brown, nearly black coat. They are more sensitive to noise and odours and are more likely to bite than the more docile laboratory strains such as BA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heredity
Heredity, also called inheritance or biological inheritance, is the passing on of traits from parents to their offspring; either through asexual reproduction or sexual reproduction, the offspring cells or organisms acquire the genetic information of their parents. Through heredity, variations between individuals can accumulate and cause species to evolve by natural selection. The study of heredity in biology is genetics. Overview In humans, eye color is an example of an inherited characteristic: an individual might inherit the "brown-eye trait" from one of the parents. Inherited traits are controlled by genes and the complete set of genes within an organism's genome is called its genotype. The complete set of observable traits of the structure and behavior of an organism is called its phenotype. These traits arise from the interaction of its genotype with the environment. As a result, many aspects of an organism's phenotype are not inherited. For example, suntanned skin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Backcrossing
Backcrossing is a crossing of a hybrid with one of its parents or an individual genetically similar to its parent, to achieve offspring with a genetic identity closer to that of the parent. It is used in horticulture, animal breeding, and production of gene knockout organisms. Backcrossed hybrids are sometimes described with acronym "BC"; for example, an F1 hybrid crossed with one of its parents (or a genetically similar individual) can be termed a BC1 hybrid, and a further cross of the BC1 hybrid to the same parent (or a genetically similar individual) produces a BC2 hybrid. Plants Advantages * If the recurrent parent is an elite genotype, at the end of the backcrossing programme, an elite genotype is recovered. * As no "new" recombination results, the elite combination is not lost. Disadvantages * It works poorly for quantitative traits. * It is more restricted for recessive traits. * In practice, sections of genome from the nonrecurrent parents are often still present and c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Model Organisms
A model organism (often shortened to model) is a non-human species that is extensively studied to understand particular biological phenomena, with the expectation that discoveries made in the model organism will provide insight into the workings of other organisms. Model organisms are widely used to research human disease when human experimentation would be unfeasible or unethical. This strategy is made possible by the common descent of all living organisms, and the conservation of metabolic and developmental pathways and genetic material over the course of evolution. Studying model organisms can be informative, but care must be taken when generalizing from one organism to another. In researching human disease, model organisms allow for better understanding the disease process without the added risk of harming an actual human. The species chosen will usually meet a determined taxonomic equivalency to humans, so as to react to disease or its treatment in a way that resembles hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laboratory Mice
The laboratory mouse or lab mouse is a small mammal of the order Rodentia which is bred and used for scientific research or feeders for certain pets. Laboratory mice are usually of the species ''Mus musculus''. They are the most commonly used mammalian research model and are used for research in genetics, physiology, psychology, medicine and other scientific disciplines. Mice belong to the Euarchontoglires clade, which includes humans. This close relationship, the associated high homology with humans, their ease of maintenance and handling, and their high reproduction rate, make mice particularly suitable models for human-oriented research. The laboratory mouse genome has been sequenced and many mouse genes have human homologues. Other mouse species sometimes used in laboratory research include two American species, the white-footed mouse (''Peromyscus leucopus'') and the North American deer mouse (''Peromyscus maniculatus''). History as a biological model Mice have been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laboratory Rats
A laboratory rat or lab rat is a brown rat of the subspecies ''Fancy rat, Rattus norvegicus domestica'' which is bred and kept for scientific research. While Animal testing on rodents, less commonly used for research than mice (see laboratory mouse), rats have served as an important animal model for research in psychology and biomedical science. Origins In 18th century Europe, wild brown rats ran rampant and this infestation fueled the industry of rat-catching. Rat-catchers would not only make money by trapping the rodents, but also by selling them for food or, more commonly, for rat-baiting. Rat-baiting was a popular sport, which involved filling a pit with rats and timing how long it took for a terrier to kill them all. Over time, breeding the rats for these contests may have produced variations in color, notably the albino and hooded varieties. The first time one of these albino mutants was brought into a laboratory for a study was in 1828 for an experiment on fasting. Over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |