|
Coincidence Circuit
In physics and electrical engineering, a coincidence circuit or coincidence gate is an electronic device with one output and two (or more) inputs. The output activates only when the circuit receives signals within a time window accepted as ''at the same time'' and in parallel at both inputs. Coincidence circuits are widely used in particle detectors and in other areas of science and technology. Walther Bothe shared the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1954 "...for his discovery of the method of coincidence and the discoveries subsequently made by it." Bruno Rossi invented the electronic coincidence circuit for implementing the coincidence method. History Bothe, 1924 In his Nobel Prize lecture,{{cite web , url=http://nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/physics/laureates/1954/bothe-lecture.html , title=Nobel Lecture , author=Bothe, Walther , year=1954 , publisher= Nobel Foundation Bothe described how he had implemented the coincidence method in an experiment on Compton scattering in 1924. The e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physics
Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which relates to the order of nature, or, in other words, to the regular succession of events." Physics is one of the most fundamental scientific disciplines, with its main goal being to understand how the universe behaves. "Physics is one of the most fundamental of the sciences. Scientists of all disciplines use the ideas of physics, including chemists who study the structure of molecules, paleontologists who try to reconstruct how dinosaurs walked, and climatologists who study how human activities affect the atmosphere and oceans. Physics is also the foundation of all engineering and technology. No engineer could design a flat-screen TV, an interplanetary spacecraft, or even a better mousetrap without first understanding the basic laws of physic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmic Ray
Cosmic rays are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the Solar System in our own galaxy, and from distant galaxies. Upon impact with Earth's atmosphere, cosmic rays produce showers of secondary particles, some of which reach the surface, although the bulk is deflected off into space by the magnetosphere or the heliosphere. Cosmic rays were discovered by Victor Hess in 1912 in balloon experiments, for which he was awarded the 1936 Nobel Prize in Physics. Direct measurement of cosmic rays, especially at lower energies, has been possible since the launch of the first satellites in the late 1950s. Particle detectors similar to those used in nuclear and high-energy physics are used on satellites and space probes for research into cosmic rays. Data from the Fermi Space Telescope (2013) have been interpreted as evidenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Experimental Particle Physics
Particle physics or high energy physics is the study of Elementary particle, fundamental particles and fundamental interaction, forces that constitute matter and radiation. The fundamental particles in the universe are classified in the Standard Model as fermions (matter particles) and bosons (force-carrying particles). There are three Generation (particle physics), generations of fermions, but ordinary matter is made only from the first fermion generation. The first generation consists of Up quark, up and down quarks which form protons and neutrons, and electrons and electron neutrinos. The three fundamental interactions known to be mediated by bosons are electromagnetism, the weak interaction, and the strong interaction. Quarks cannot exist on their own but form hadrons. Hadrons that contain an odd number of quarks are called baryons and those that contain an even number are called mesons. Two baryons, the proton and the neutron, make up most of the mass of ordinary matte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Computing Hardware
The history of computing hardware covers the developments from early simple devices to aid calculation to modern day computers. Before the 20th century, most calculations were done by humans. The first aids to computation were purely mechanical devices which required the operator to set up the initial values of an elementary arithmetic operation, then manipulate the device to obtain the result. Later, computers represented numbers in a continuous form (e.g. distance along a scale, rotation of a shaft, or a voltage). Numbers could also be represented in the form of digits, automatically manipulated by a mechanism. Although this approach generally required more complex mechanisms, it greatly increased the precision of results. The development of transistor technology and then the integrated circuit chip led to a series of breakthroughs, starting with transistor computers and then integrated circuit computers, causing digital computers to largely replace analog computers. Met ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coincidence Detection In Neurobiology
Coincidence detection in the context of neurobiology is a process by which a neuron or a neural circuit can encode information by detecting the occurrence of temporally close but spatially distributed input signals. Coincidence detectors influence neuronal information processing by reducing temporal jitter, reducing spontaneous activity, and forming associations between separate neural events. This concept has led to a greater understanding of neural processes and the formation of computational maps in the brain. Principles of coincidence detection Coincidence detection relies on separate inputs converging on a common target. Consider a basic neural circuit with two input neurons, A and B, that have excitatory synaptic terminals converging on a single output neuron, C (Fig. 1). If each input neuron's EPSP is subthreshold for an action potential at C, then C will not fire unless the two inputs from A and B are temporally close together. Synchronous arrival of these two inputs m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
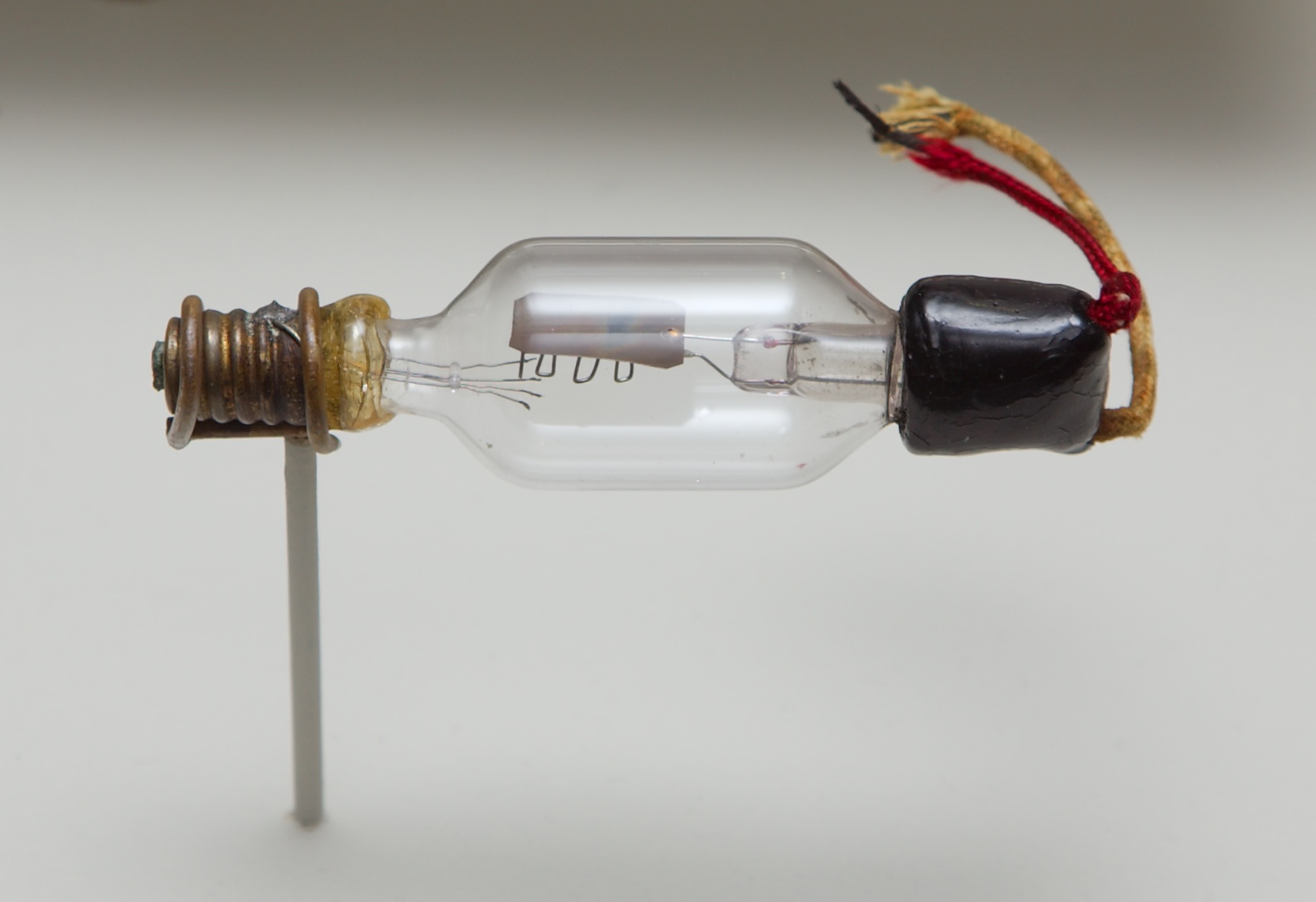
Pentode
A pentode is an electronic device having five electrodes. The term most commonly applies to a three-grid amplifying vacuum tube or thermionic valve that was invented by Gilles Holst and Bernhard D.H. Tellegen in 1926. The pentode (called a ''triple-grid amplifier'' in some literature) was developed from the ''screen-grid tube'' or ''shield-grid tube'' (a type of tetrode tube) by the addition of a grid between the screen grid and the plate. The screen-grid tube was limited in performance as an amplifier due to secondary emission of electrons from the plate. The additional grid is called the ''suppressor grid''. The suppressor grid is usually operated at or near the potential of the cathode and prevents secondary emission electrons from the plate from reaching the screen grid. The addition of the suppressor grid permits much greater output signal amplitude to be obtained from the plate of the pentode in amplifier operation than from the plate of the screen-grid tube at the same plate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Computer
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (computation) automatically. Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as programs. These programs enable computers to perform a wide range of tasks. A computer system is a nominally complete computer that includes the hardware, operating system (main software), and peripheral equipment needed and used for full operation. This term may also refer to a group of computers that are linked and function together, such as a computer network or computer cluster. A broad range of industrial and consumer products use computers as control systems. Simple special-purpose devices like microwave ovens and remote controls are included, as are factory devices like industrial robots and computer-aided design, as well as general-purpose devices like personal computers and mobile devices like smartphones. Computers power the Internet, which links bil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logical Conjunction
In logic, mathematics and linguistics, And (\wedge) is the truth-functional operator of logical conjunction; the ''and'' of a set of operands is true if and only if ''all'' of its operands are true. The logical connective that represents this operator is typically written as \wedge or . A \land B is true if and only if A is true and B is true, otherwise it is false. An operand of a conjunction is a conjunct. Beyond logic, the term "conjunction" also refers to similar concepts in other fields: * In natural language, the denotation of expressions such as English "and". * In programming languages, the short-circuit and control structure. * In set theory, intersection. * In lattice theory, logical conjunction ( greatest lower bound). * In predicate logic, universal quantification. Notation And is usually denoted by an infix operator: in mathematics and logic, it is denoted by \wedge, or ; in electronics, ; and in programming languages, &, &&, or and. In Jan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature (journal)
''Nature'' is a British weekly scientific journal founded and based in London, England. As a multidisciplinary publication, ''Nature'' features peer-reviewed research from a variety of academic disciplines, mainly in science and technology. It has core editorial offices across the United States, continental Europe, and Asia under the international scientific publishing company Springer Nature. ''Nature'' was one of the world's most cited scientific journals by the Science Edition of the 2019 ''Journal Citation Reports'' (with an ascribed impact factor of 42.778), making it one of the world's most-read and most prestigious academic journals. , it claimed an online readership of about three million unique readers per month. Founded in autumn 1869, ''Nature'' was first circulated by Norman Lockyer and Alexander Macmillan as a public forum for scientific innovations. The mid-20th century facilitated an editorial expansion for the journal; ''Nature'' redoubled its efforts in exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuum Tube
A vacuum tube, electron tube, valve (British usage), or tube (North America), is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric voltage, potential difference has been applied. The type known as a thermionic tube or thermionic valve utilizes thermionic emission of electrons from a hot cathode for fundamental electronic functions such as signal amplifier, amplification and current rectifier, rectification. Non-thermionic types such as a vacuum phototube, however, achieve electron emission through the photoelectric effect, and are used for such purposes as the detection of light intensities. In both types, the electrons are accelerated from the cathode to the anode by the electric field in the tube. The simplest vacuum tube, the diode (i.e. Fleming valve), invented in 1904 by John Ambrose Fleming, contains only a heated electron-emitting cathode and an anode. Electrons can only flow in one direction through the device—fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triode
A triode is an electronic amplifying vacuum tube (or ''valve'' in British English) consisting of three electrodes inside an evacuated glass envelope: a heated filament or cathode, a grid, and a plate (anode). Developed from Lee De Forest's 1906 Audion, a partial vacuum tube that added a grid electrode to the thermionic diode (Fleming valve), the triode was the first practical electronic amplifier and the ancestor of other types of vacuum tubes such as the tetrode and pentode. Its invention founded the electronics age, making possible amplified radio technology and long-distance telephony. Triodes were widely used in consumer electronics devices such as radios and televisions until the 1970s, when transistors replaced them. Today, their main remaining use is in high-power RF amplifiers in radio transmitters and industrial RF heating devices. In recent years there has been a resurgence in demand for low power triodes due to renewed interest in tube-type audio systems by audiophi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |