|
Cognitive Abilities Test
The Cognitive Abilities Test (CogAT) is a group-administered K–12 assessment published by Riverside Insights and intended to estimate students' learned reasoning and problem solving abilities through a battery of verbal, quantitative, and nonverbal test items. The test purports to assess students' acquired reasoning abilities while also predicting achievement scores when administered with the co-normed Iowa Tests. The test was originally published in 1954 as the Lorge-Thorndike Intelligence Test, after the psychologists who authored the first version of it, Irving Lorge and Robert L. Thorndike. The CogAT is one of several tests used in the United States to help teachers or other school staff make student placement decisions for gifted education programs, and is accepted for admission to Intertel, a high IQ society for those who score at or above the 99th percentile on a test of intelligence. Forms 7 and 8 provide comparable scores and may be administered separately or together. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
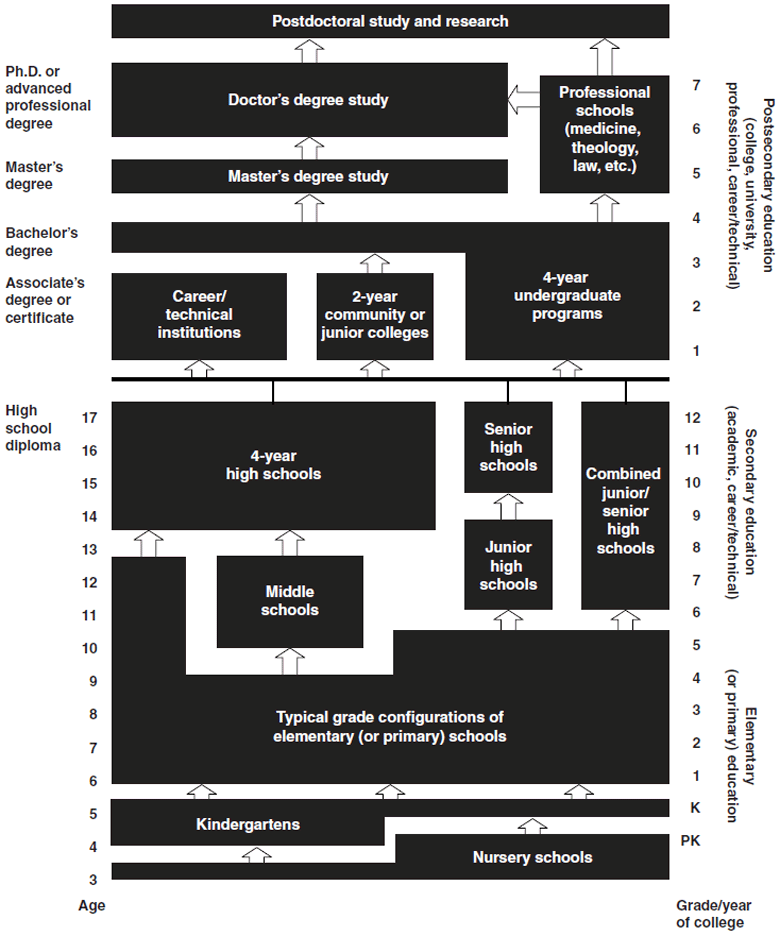
K–12 (education)
K–12, from kindergarten to 12th grade, is an American English expression that indicates the range of years of publicly supported primary and secondary education found in the United States, which is similar to publicly supported school grades before college in several other countries, such as Afghanistan, Australia, Canada, China, Ecuador, Egypt, India, Iran, the Philippines, South Korea, and Turkey. History U.S. public education was conceived of in the late 18th century. In 1790, Pennsylvania became the first state to require some form of free education for everyone regardless of whether they could afford it. New York passed similar legislation in 1805. In 1820, Massachusetts became the first state to create a tuition-free high school, Boston English. The first K–12 public school systems appeared in the early 19th century. In the 1830s and 1840s, Ohioans were taking a significant interest in the idea of public education. At that point in time, schools were commonly opera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Educational Assessment
Educational assessment or educational evaluation is the systematic process of documenting and using empirical data on the knowledge, skill, attitudes, aptitude and beliefs to refine programs and improve student learning. Assessment data can be obtained from directly examining student work to assess the achievement of learning outcomes or can be based on data from which one can make inferences about learning. Assessment is often used interchangeably with test, but not limited to tests. Assessment can focus on the individual learner, the learning community (class, workshop, or other organized group of learners), a course, an academic program, the institution, or the educational system as a whole (also known as granularity). The word 'assessment' came into use in an educational context after the Second World War. As a continuous process, assessment establishes measurable and clear student learning outcomes for learning, providing a sufficient amount of learning opportunities to achi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Riverside Insights
Riverside Insights is a publisher of clinical and educational standardized tests in the United States; it is headquartered in Itasca, Illinois. It is also a charter member of the Association of Test Publishers. Riverside Insights was established as a wholly owned subsidiary of Houghton Mifflin Harcourt, a leading educational publisher in the United States, in 1979. History Early history Riverside originated in 1852 as The Riverside Press, a book printing plant in Boston, Massachusetts. Henry Houghton originally started The Riverside Press in an old Cambridge building along the banks of the Charles River. A visitor described it as "one of the model printing-offices in America". Houghton chose to employ women as well as men as compositors, a radical decision which he said was influenced by the Victoria Press in England. In 1880, George Mifflin entered into a partnership with Henry Houghton and together founded and led Houghton Mifflin Company. They soon established an educa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reasoning
Reason is the capacity of consciously applying logic by drawing conclusions from new or existing information, with the aim of seeking the truth. It is closely associated with such characteristically human activities as philosophy, science, language, mathematics, and art, and is normally considered to be a distinguishing ability possessed by humans. Reason is sometimes referred to as rationality. Reasoning is associated with the acts of thinking and cognition, and involves the use of one's intellect. The field of logic studies the ways in which humans can use formal reasoning to produce logically valid arguments. Reasoning may be subdivided into forms of logical reasoning, such as: deductive reasoning, inductive reasoning, and abductive reasoning. Aristotle drew a distinction between logical discursive reasoning (reason proper), and intuitive reasoning, in which the reasoning process through intuition—however valid—may tend toward the personal and the subjectively opaq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iowa Tests
The Iowa Assessments (previously the Iowa Test of Basic Skills and originally Iowa Every Pupil Test of Basic Skills) also known informally as the Iowa Tests, formerly known as the ITBS tests or the Iowa Basics, are standardized tests provided as a service to schools by the College of Education of the University of Iowa. Developers Everett Franklin Lindquist, Harry Greene, Ernest Horn, Maude McBroom, and Herbert Spitzer first designed and administered the tests in 1935 as a tool for improving student instruction. The tests are administered to students in kindergarten through eighth grade as part of the Iowa Statewide Testing Programs, a division of the Iowa Testing Programs (ITP). Over decades, participation expanded and currently nearly all school districts in Iowa participate annually in the program, as do many other school districts across the United States. In a cooperative relationship, participating schools receive ITBS test materials, scoring and reporting services and con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irving Lorge
Irving Daniel Lorge (April 19, 1905 – January 23, 1961) was an American psychologist known for his work in psychometrics. His research focused on a wide variety of topics, including the measurement of giftedness, human intelligence, and readability. While working at Columbia University's Teachers College with his mentor Edward L. Thorndike, he helped develop what became known as the Lorge-Thorndike Intelligence Tests. Biography Lorge was born on April 19, 1905, in New York City. He joined the faculty at Teachers College, Columbia University in 1927 to work with Edward L. Thorndike. In 1938, he became Associate Professor of Education at Teachers College, and he continued to work there for the rest of his life, save for two years working as a consultant to the United States federal government during World War II. Specifically, from 1942 to 1944, he was a consultant to the special training division of the United States Army, where he significantly changed the way in which the Arm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert L
The name Robert is an ancient Germanic given name, from Proto-Germanic "fame" and "bright" (''Hrōþiberhtaz''). Compare Old Dutch ''Robrecht'' and Old High German ''Hrodebert'' (a compound of '' Hruod'' ( non, Hróðr) "fame, glory, honour, praise, renown" and ''berht'' "bright, light, shining"). It is the second most frequently used given name of ancient Germanic origin. It is also in use as a surname. Another commonly used form of the name is Rupert. After becoming widely used in Continental Europe it entered England in its Old French form ''Robert'', where an Old English cognate form (''Hrēodbēorht'', ''Hrodberht'', ''Hrēodbēorð'', ''Hrœdbœrð'', ''Hrœdberð'', ''Hrōðberχtŕ'') had existed before the Norman Conquest. The feminine version is Roberta. The Italian, Portuguese, and Spanish form is Roberto. Robert is also a common name in many Germanic languages, including English, German, Dutch, Norwegian, Swedish, Scots, Danish, and Icelandic. It can be use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gifted Education
Gifted education (also known as gifted and talented education (GATE), talented and gifted programs (TAG), or G/T education) is a broad group of special practices, procedures, and theories used in the education of children who have been identified as gifted or talented. The main approaches to gifted education are enrichment and acceleration. An enrichment program teaches additional, related material, but keeps the student progressing through the curriculum at the same rate as other students. For example, after the gifted students have completed the normal work in the curriculum, an enrichment program might provide them with additional information about a subject. An acceleration program advances the student through the standard curriculum faster than normal. This is done through many different approaches. There is no standard global definition of what a gifted student is; multiple definitions exist. Most definitions select the students who are the most skilled or talented in a give ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intertel
Intertel (previously the International Legion of Intelligence) is a high-IQ society founded in 1966, that is open to those who have scored at or above the 99th percentile (top 1%) on one of various standardized tests of intelligence. It has been identified as one of the notable high-IQ societies established since the late 1960s with admissions requirements that are stricter and more exclusive than Mensa. History and goals Intertel was founded in 1966 by Ralph Haines, following the example of Roland Berrill and Lancelot Ware (founders of Mensa), who wanted to create an association adapted to the gifted needs without any specific restriction of admission (with the exception of a minimum IQ). Intertel thus became the second oldest organization of this kind, Mensa being the first. The name "Intertel" derives from ''International Legion of Intelligence,'' and its members are still known as "Ilians". The organizations has three purposes, stated in its constitution: * Encouragin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-IQ Society
A high-IQ society is an organization that limits its membership to people who have attained a specified score on an IQ test, usually in the top two percent of the population (98th percentile) or above. These may also be referred to as genius societies. The largest and oldest such society is Mensa International, which was founded by Roland Berrill and Lancelot Ware in 1946. Entry requirements High-IQ societies typically accept a variety of IQ tests for membership eligibility; these include WAIS, Stanford-Binet, and Raven's Advanced Progressive Matrices, amongst many others deemed to sufficiently measure or correlate with intelligence. Tests deemed to insufficiently correlate with intelligence (e.g. post-1994 SAT, in the case of Mensa and Intertel) are not accepted for admission. As IQ significantly above 146 SD15 (approximately three-sigma) cannot be reliably measured with accuracy due to sub-test limitations and insufficient norming, IQ societies with cutoffs significantly h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Educational Psychology
Educational psychology is the branch of psychology concerned with the scientific study of human learning. The study of learning processes, from both cognitive and behavioral perspectives, allows researchers to understand individual differences in intelligence, cognitive development, affect, motivation, self-regulation, and self-concept, as well as their role in learning. The field of educational psychology relies heavily on quantitative methods, including testing and measurement, to enhance educational activities related to instructional design, classroom management, and assessment, which serve to facilitate learning processes in various educational settings across the lifespan.Snowman, Jack (1997). Educational Psychology: What Do We Teach, What Should We Teach?. "Educational Psychology", 9, 151-169 Educational psychology can in part be understood through its relationship with other disciplines. It is informed primarily by psychology, bearing a relationship to that discipline a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
School Psychology
School psychology is a field that applies principles from educational psychology, developmental psychology, clinical psychology, community psychology, and behavior analysis to meet the learning and behavioral health needs of children and adolescents. It is an area of applied psychology practiced by a school psychologist. They often collaborate with educators, families, school leaders, community members, and other professionals to create safe and supportive school environments. They carry out psychological testing, psychoeducational assessment, intervention, prevention, counseling, and consultation in the ethical, legal, and administrative codes of their profession. Historical foundations School psychology dates back to the beginning of American psychology in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The field is tied to both functional and clinical psychology. School psychology actually came out of functional psychology. School psychologists were interested in childhood behav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |