|
Codman Triangle
The Codman triangle (previously referred to as Codman's triangle) is the triangular area of new subperiosteal bone that is created when a lesion, often a tumour, raises the periosteum away from the bone. A Codman triangle is not actually a full triangle. Instead, it is often a pseudotriangle on radiographic findings, with ossification on the original bone and one additional side of the triangle, which forms a two sided triangle with one open side. This two sided appearance is generated due to a tumor (or growth) that is growing at a rate which is faster than the periosteum can grow or expand, so instead of dimpling, the periosteum tears away and provides ossification on the second edge of the triangle. The advancing tumour displaces the perisosteum away from the bone medulla. The displaced and now lateral periosteum attempts to regenerate underlying bone. This describes a periosteal reaction. The main causes for this sign are osteosarcoma, Ewing's sarcoma, eumycetoma Eumycet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Codman Triangle 2014-01-29 21-07
Codman may refer to: Buildings *Codman Building, historic building at 55 Kilby Street, Boston, Massachusetts *Codman House, historic house set on a estate at 36 Codman Road, Lincoln, Massachusetts *Codman–Davis House, four-story, red brick, 1906, classical revival house in Washington, D.C. **Codman Carriage House and Stable, historic former carriage house and stable in Washington, D.C. * Col. Charles Codman Estate, historic house at 43 Ocean View Avenue in Barnstable, Massachusetts People *Charles Codman Cabot (1900–1976), American jurist *Charles Codman (1800–1842), landscape painter of Portland, Maine *Charles R. Codman (Civil War) (1828–1918), American military commander during the Civil War. * Charles R. Codman (1893–1956), American author, wine expert, and aide to General George S. Patton during World War II *Ernest Amory Codman (1869–1940), Boston surgeon who pioneered outcome-based health care *Henry Codman Potter (1835–1908), bishop of the Episcopal Church ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subperiosteal
The periosteum is a membrane that covers the outer surface of all bones, except at the articular surfaces (i.e. the parts within a joint space) of long bones. Endosteum lines the inner surface of the medullary cavity of all long bones. Structure The periosteum consists of an outer fibrous layer, and an inner cambium layer (or osteogenic layer). The fibrous layer is of dense irregular connective tissue, containing fibroblasts, while the cambium layer is highly cellular containing progenitor cells that develop into osteoblasts. These osteoblasts are responsible for increasing the width of a long bone and the overall size of the other bone types. After a bone fracture, the progenitor cells develop into osteoblasts and chondroblasts, which are essential to the healing process. The outer fibrous layer and the inner cambium layer is differentiated under electron micrography. As opposed to osseous tissue, the periosteum has nociceptors, sensory neurons that make it very sensitive t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Periosteum
The periosteum is a membrane that covers the outer surface of all bones, except at the articular surfaces (i.e. the parts within a joint space) of long bones. Endosteum lines the inner surface of the medullary cavity of all long bones. Structure The periosteum consists of an outer fibrous layer, and an inner cambium layer (or osteogenic layer). The fibrous layer is of dense irregular connective tissue, containing fibroblasts, while the cambium layer is highly cellular containing progenitor cells that develop into osteoblasts. These osteoblasts are responsible for increasing the width of a long bone and the overall size of the other bone types. After a bone fracture, the progenitor cells develop into osteoblasts and chondroblasts, which are essential to the healing process. The outer fibrous layer and the inner cambium layer is differentiated under electron micrography. As opposed to osseous tissue, the periosteum has nociceptors, sensory neurons that make it very sensitive to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tumor
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists in growing abnormally, even if the original trigger is removed. This abnormal growth usually forms a mass, when it may be called a tumor. ICD-10 classifies neoplasms into four main groups: benign neoplasms, in situ neoplasms, malignant neoplasms, and neoplasms of uncertain or unknown behavior. Malignant neoplasms are also simply known as cancers and are the focus of oncology. Prior to the abnormal growth of tissue, as neoplasia, cells often undergo an abnormal pattern of growth, such as metaplasia or dysplasia. However, metaplasia or dysplasia does not always progress to neoplasia and can occur in other conditions as well. The word is from Ancient Greek 'new' and 'formation, creation'. Types A neoplasm can be benign, potentially m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteosarcoma
An osteosarcoma (OS) or osteogenic sarcoma (OGS) (or simply bone cancer) is a cancerous tumor in a bone. Specifically, it is an aggressive malignant neoplasm that arises from primitive transformed cells of mesenchymal origin (and thus a sarcoma) and that exhibits osteoblastic differentiation and produces malignant osteoid. Osteosarcoma is the most common histological form of primary bone sarcoma. It is most prevalent in teenagers and young adults. Signs and symptoms Many patients first complain of pain that may be worse at night, may be intermittent and of varying intensity and may have been occurring for a long time. Teenagers who are active in sports often complain of pain in the lower femur, or immediately below the knee. If the tumor is large, it can present as overt localised swelling. Sometimes a sudden fracture is the first symptom because the affected bone is not as strong as normal bone and may fracture abnormally with minor trauma. In cases of more deep-seated tumors t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ewing's Sarcoma
Ewing sarcoma is a type of cancer that forms in bone or soft tissue. Symptoms may include swelling and pain at the site of the tumor, fever, and a bone fracture. The most common areas where it begins are the legs, pelvis, and chest wall. In about 25% of cases, the cancer has already spread to other parts of the body at the time of diagnosis. Complications may include a pleural effusion or paraplegia. It is a type of small round cell sarcoma. The cause of Ewing sarcoma is unknown. Most cases appear to occur randomly. Sometimes there has been a germline mutation. The underlying mechanism often involves a genetic change known as a reciprocal translocation. Diagnosis is based on biopsy of the tumor. Treatment often includes chemotherapy, radiation therapy, surgery, and stem cell transplant. Targeted therapy and immunotherapy are being studied. Five-year survival is about 70%. A number of factors, however, affect this estimate. James Ewing in 1920 established that the tumor is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
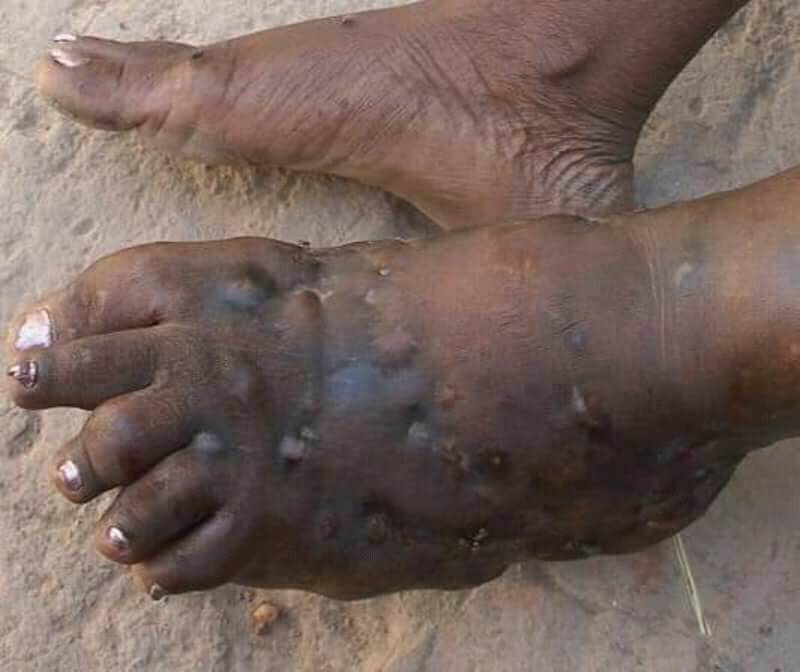
Eumycetoma
Eumycetoma, also known as Madura foot, is a persistent fungal infection of the skin and the tissues just under the skin, affecting most commonly the feet, although it can occur in hands and other body parts. It starts as a painless wet nodule, which may be present for years before ulceration, swelling, grainy discharge and weeping from sinuses and fistulae, followed by bone deformity. Several fungi can cause eumycetoma, including: ''Madurella mycetomatis'', ''Madurella grisea'', '' Leptosphaeria senegalensis'', ''Curvularia lunata'', ''Scedosporium apiospermum'', '' Neotestudina rosatii'', and ''Acremonium'' and ''Fusarium'' species. Diagnosis is by biopsy, visualising the fungi under the microscope and culture. Medical imaging may reveal extent of bone involvement. Other tests include ELISA, immunodiffusion, and DNA Barcoding. Treatment includes surgical removal of affected tissue and antifungal medicines. After treatment, recurrence is common. Sometimes, amputation is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subperiosteal Abscess
The periosteum is a membrane that covers the outer surface of all bones, except at the articular surfaces (i.e. the parts within a joint space) of long bones. Endosteum lines the inner surface of the medullary cavity of all long bones. Structure The periosteum consists of an outer fibrous layer, and an inner cambium layer (or osteogenic layer). The fibrous layer is of dense irregular connective tissue, containing fibroblasts, while the cambium layer is highly cellular containing progenitor cells that develop into osteoblasts. These osteoblasts are responsible for increasing the width of a long bone and the overall size of the other bone types. After a bone fracture, the progenitor cells develop into osteoblasts and chondroblasts, which are essential to the healing process. The outer fibrous layer and the inner cambium layer is differentiated under electron micrography. As opposed to osseous tissue, the periosteum has nociceptors, sensory neurons that make it very sensitive to m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |