|
Codex Mendoza
The Codex Mendoza is an Aztec codex, believed to have been created around the year 1541. It contains a history of both the Aztec rulers and their conquests as well as a description of the daily life of pre-conquest Aztec society. The codex is written in the Nahuatl language using traditional Aztec pictograms with a translation and explanation of the text provided in Spanish. It is named after Don Antonio de Mendoza (1495-1552), the viceroy of New Spain, who supervised its creation and who was a leading patron of native artists. Mendoza knew that the ravages of the conquest had destroyed multiple native artifacts, and that the craft traditions that generated them had been effaced. When the Spanish crown ordered Mendoza to provide evidence of the Aztec political and tribute system, he invited skilled artists and scribes who were being schooled at the Franciscan college in Tlatelolco to gather in a workshop under the supervision of Spanish priests where they could recreate the docu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selden Roll
Selden may refer to: Places In the United States: *Fort Selden, in New Mexico *Selden, Kansas *Selden, New York In Switzerland: *Selden (Kandersteg) Other uses *Selden (surname) *Selden, character from Conan Doyle's ''The Hound of the Baskervilles'' *Selden Motor Vehicle Company, an early automobile manufacturer See also *Seldon (other) Seldon may refer to: Places *Fort Seldon, a US Cavalry fort in New Mexico People *Robert Seldon Lady (born 1954), noted member of the U.S. intelligence community *Anthony Seldon (born 1953), political commentator *Arthur Seldon (1916–2005), jo ... * Justice Selden (other) {{disambiguation, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
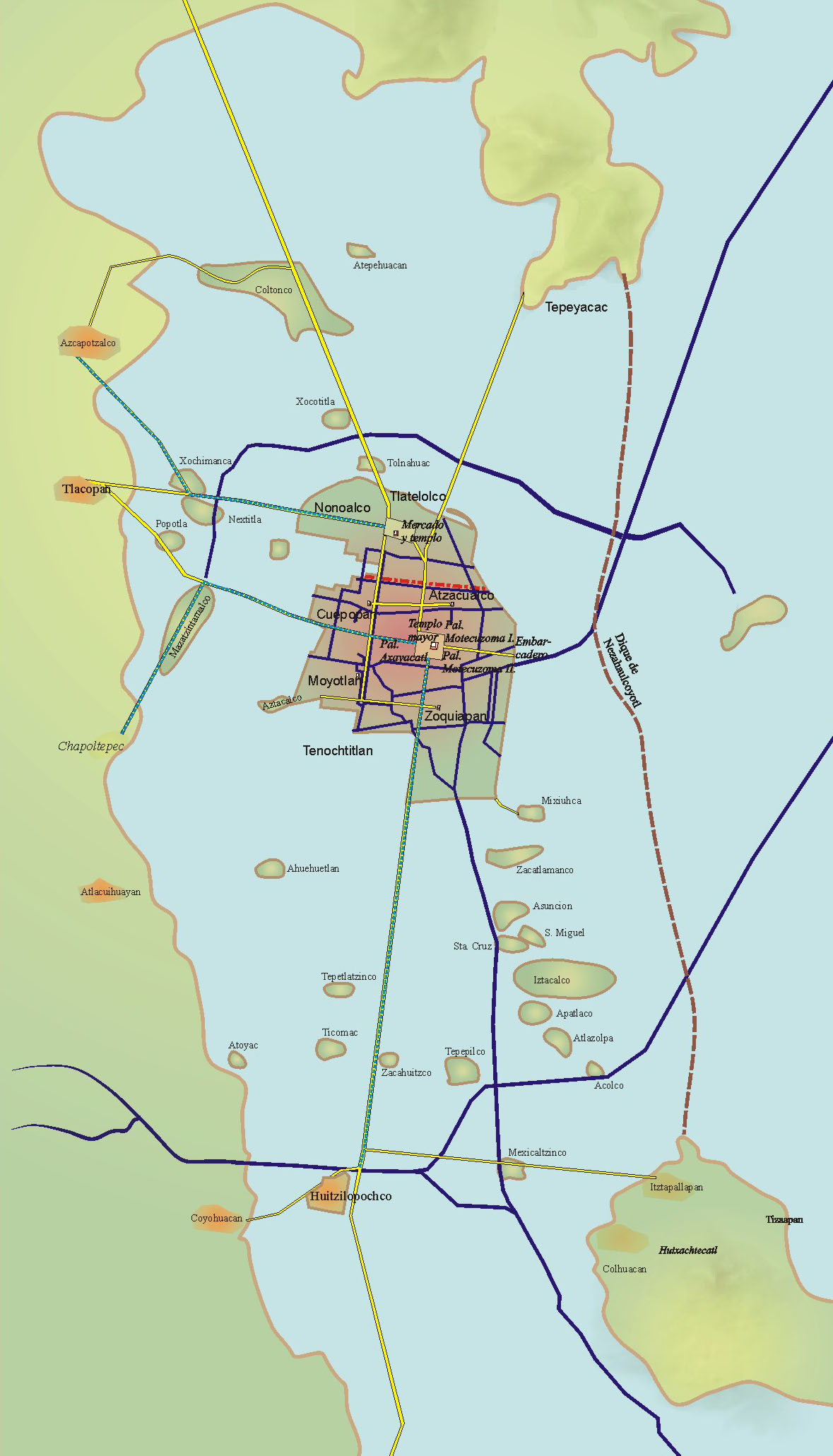
Tenochtitlan
, ; es, Tenochtitlan also known as Mexico-Tenochtitlan, ; es, México-Tenochtitlan was a large Mexican in what is now the historic center of Mexico City. The exact date of the founding of the city is unclear. The date 13 March 1325 was chosen in 1925 to celebrate the 600th anniversary of the city. The city was built on an island in what was then Lake Texcoco in the Valley of Mexico. The city was the capital of the expanding Aztec Empire in the 15th century until it was captured by the Spanish in 1521. At its peak, it was the largest city in the pre-Columbian Americas. It subsequently became a '' cabecera'' of the Viceroyalty of New Spain. Today, the ruins of are in the historic center of the Mexican capital. The World Heritage Site of contains what remains of the geography (water, boats, floating gardens) of the Mexica capital. was one of two Mexica (city-states or polities) on the island, the other being . The city is located in modern-day Mexico City. Etymolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward King, Viscount Kingsborough
Edward King, Viscount Kingsborough (16 November 1795 – 27 February 1837) was an Irish antiquarian who sought to prove that the indigenous peoples of the Americas were a Lost Tribe of Israel. His principal contribution was in making available facsimiles of ancient documents and some of the earliest explorers' reports on pre-Columbian ruins and Maya civilisation. He was the eldest son of George King, 3rd Earl of Kingston, Lord Kingsborough, the latter a Tory, of Mitchelstown Castle, County Cork. He represented Cork County in parliament between 1818 and 1826 as a Whig. In 1831, Lord Kingsborough published the first volume of ''Antiquities of Mexico'', a collection of copies of various Mesoamerican codices, including the first complete publication of the Dresden Codex. The exorbitant cost of the reproductions, which were often hand-painted, landed him in debtors' prison. These lavish publications represented some of the earliest published documentation of the ancient cultures ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Selden
John Selden (16 December 1584 – 30 November 1654) was an English jurist, a scholar of England's ancient laws and constitution and scholar of Jewish law. He was known as a polymath; John Milton hailed Selden in 1644 as "the chief of learned men reputed in this land." Early life He was born at Salvington, in the parish of West Tarring, West Sussex (now part of the town of Worthing), and was baptised at St Andrew's, the parish church. The cottage in which he was born survived until 1959 when it was destroyed by a fire caused by an electrical fault. His father, also named John Selden, had a small farm. It is said that his skill as a violin-player was what attracted his wife, Margaret, who was from a better family, being the only child of Thomas Baker of Rustington and descended from a knightly family of Kent. Selden was educated at the free grammar school at Chichester, The Prebendal School, and in 1600 he went on to Hart Hall, Oxford. In 1603, he was admitted to Cliffor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Livre
The livre (abbreviation: £ or ₶., French for (pound)) was the currency of Kingdom of France and its predecessor state of West Francia from 781 to 1794. Several different livres existed, some concurrently. The livre was the name of coins and of units of account. History Origin and etymology The livre was established by Charlemagne as a unit of account equal to one pound of silver. It was subdivided into 20 ''sous'' (also ''sols''), each of 12 '' deniers''. The word ''livre'' came from the Latin word ''libra'', a Roman unit of weight and still the name of a pound in modern French, and the denier comes from the Roman denarius. This system and the denier itself served as the model for many of Europe's currencies, including the British pound, Italian lira, Spanish dinero and the Portuguese dinheiro. This first livre is known as the . Only deniers were initially minted, but debasement led to larger denominations being issued. Different mints in different regions used diff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Hakluyt
Richard Hakluyt (; 1553 – 23 November 1616) was an English writer. He is known for promoting the English colonization of North America through his works, notably ''Divers Voyages Touching the Discoverie of America'' (1582) and ''The Principal Navigations, Voyages, Traffiques and Discoveries of the English Nation'' (1589–1600). Hakluyt was educated at Westminster School and Christ Church, Oxford. Between 1583 and 1588 he was chaplain and secretary to Sir Edward Stafford, English ambassador at the French court. An ordained priest, Hakluyt held important positions at Bristol Cathedral and Westminster Abbey and was personal chaplain to Robert Cecil, 1st Earl of Salisbury, principal Secretary of State to Elizabeth I and James I. He was the chief promoter of a petition to James I for letters patent to colonize Virginia, which were granted to the London Company and Plymouth Company (referred to collectively as the Virginia Company) in 1606. The Hakluyt Society, which pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry II Of France
Henry II (french: Henri II; 31 March 1519 – 10 July 1559) was King of France from 31 March 1547 until his death in 1559. The second son of Francis I and Duchess Claude of Brittany, he became Dauphin of France upon the death of his elder brother Francis in 1536. As a child, Henry and his elder brother spent over four years in captivity in Spain as hostages in exchange for their father. Henry pursued his father's policies in matters of art, war, and religion. He persevered in the Italian Wars against the Habsburgs and tried to suppress the Reformation, even as the Huguenot numbers were increasing drastically in France during his reign. Under the April 1559 Peace of Cateau-Cambrésis which ended the Italian Wars, France renounced its claims in Italy, but gained certain other territories, including the Pale of Calais and the Three Bishoprics. These acquisitions strengthened French borders while the abdication of Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor in January 1556 and division of h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmographer
The term cosmography has two distinct meanings: traditionally it has been the protoscience of mapping the general features of the cosmos, heaven and Earth; more recently, it has been used to describe the ongoing effort to determine the large-scale features of the observable universe. Traditional usage The 14th-century work '' 'Aja'ib al-makhluqat wa-ghara'ib al-mawjudat'' by Persian physician Zakariya al-Qazwini is considered to be an early work of cosmography. Traditional Hindu, Buddhist and Jain cosmography schematize a universe centered on Mount Meru surrounded by rivers, continents and seas. These cosmographies posit a universe being repeatedly created and destroyed over time cycles of immense lengths. In 1551, Martín Cortés de Albacar, from Zaragoza, Spain, published ''Breve compendio de la esfera y del arte de navegar''. Translated into English and reprinted several times, the work was of great influence in Britain for many years. He proposed spherical charts and ment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
André Thévet
André — sometimes transliterated as Andre — is the French and Portuguese form of the name Andrew, and is now also used in the English-speaking world. It used in France, Quebec, Canada and other French-speaking countries. It is a variation of the Greek name ''Andreas'', a short form of any of various compound names derived from ''andr-'' 'man, warrior'. The name is popular in Norway and Sweden. Cognate names Cognate names are: * Bulgarian language, Bulgarian: Andrei, Andrey * Breton language, Breton : Andrev * Canada, Canadian: André * Catalan language, Catalan: Andreu * Czech language, Czech: Andrej, Ondřej * Dutch language, ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Privateer
A privateer is a private person or ship that engages in maritime warfare under a commission of war. Since robbery under arms was a common aspect of seaborne trade, until the early 19th century all merchant ships carried arms. A sovereign or delegated authority issued commissions, also referred to as a letter of marque, during wartime. The commission empowered the holder to carry on all forms of hostility permissible at sea by the usages of war. This included attacking foreign vessels and taking them as prizes, and taking prize crews as prisoners for exchange. Captured ships were subject to condemnation and sale under prize law, with the proceeds divided by percentage between the privateer's sponsors, shipowners, captains and crew. A percentage share usually went to the issuer of the commission (i.e. the sovereign). Privateering allowed sovereigns to raise revenue for war by mobilizing privately owned armed ships and sailors to supplement state power. For participants, privateerin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Purchas
Samuel Purchas ( – 1626) was an England, English Anglican cleric who published several volumes of reports by travellers to foreign countries. Career Purchas was born at Thaxted, Essex, England, Essex son of an English yeoman. He graduated from St John's College, Cambridge, in 1600. In 1604 James I of England, James I presented him to the vicarage of St. Laurence and All Saints Church, Eastwood, St. Laurence and All Saints, in Eastwood, Essex. Eastwood is two miles from Leigh-on-Sea, which was then a prosperous shipping centre and a congregational place of seafaring men. Purchas himself never travelled "200 miles from Thaxted in Essex where I was borne." Instead, he recorded personal narratives shared with him by the sailors, who returned to England from their voyages. He added these accounts to a vast compilation of unsorted manuscripts, which were left to him by Richard Hakluyt and were later published as Purchas's third – and final – book. In 1614, Purchas became cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)