|
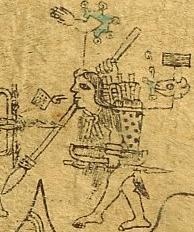
Coanacoch
Coanacochtzin (died 1525) was the last tlatoani (ruler) of Texcoco before the city came under Spanish control. One of Nezahualpilli's sons, he succeeded to throne after the death of his half-brother Cacama in 1520.Diaz, B., 1963, The Conquest of New Spain, London: Penguin Books, When the forces under Hernán Cortés approached Texcoco during their conquest of the Aztec Empire, Coanacoch fled to Tenochtitlan. In his place, Cortés appointed his Spain-aligned brother Tecocoltzin as ''tlatoani'' of Texcoco. Coanacoch assisted Cuauhtémoc Cuauhtémoc (, ), also known as Cuauhtemotzín, Guatimozín, or Guatémoc, was the Aztec ruler (''tlatoani'') of Tenochtitlan from 1520 to 1521, making him the last Aztec Emperor. The name Cuauhtemōc means "one who has descended like an eagle" ... at the Fall of Tenochtitlan in defending the city and was captured after its fall. He was executed by Cortés in 1524. References Year of birth missing 1525 deaths Tlatoque Texcoco (al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuauhtémoc
Cuauhtémoc (, ), also known as Cuauhtemotzín, Guatimozín, or Guatémoc, was the Aztec ruler (''tlatoani'') of Tenochtitlan from 1520 to 1521, making him the last Aztec Emperor. The name Cuauhtemōc means "one who has descended like an eagle", and is commonly rendered in English as "Descending Eagle", as in the moment when an eagle folds its wings and plummets down to strike its prey. This is a name that implies aggressiveness and determination. Cuauhtémoc took power in 1520 as successor of Cuitláhuac and was a cousin of the late emperor Moctezuma II. His young wife, who was later known as Isabel Moctezuma, was one of Moctezuma's daughters. He ascended to the throne when he was around 25 years old, while Tenochtitlan was being besieged by the Spanish and devastated by an epidemic of smallpox brought to the Americas by Spanish conquerors. After the killings in the Great Temple, there were probably few Aztec captains available to take the position. Early life Cuauhtemoc's d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Texcoco Rulers
This is a list of Mesoamerican rulers of the ''altepetl'' of Tetzcoco from the time the city began being ruled by ''tlatoque'' in 1298 to the end of the line of indigenous rulers. From the early 15th century to 1521, Tetzcoco was one of the three leading members of the Triple Alliance, commonly known as the Aztec Empire, but was often subservient to the rulers of Tenochtitlan. The Aztec Empire was conquered by Spain in 1521, but the Spanish colonial authorities continued to appoint ''tlatoque'' of Tetzcoco until the office was abolished in 1564. Pre-colonial rulers (1298–1521) Early Tetzcoco (1298–1431) The ''tlatoque'' of Tetzcoco were descendants and successors of earlier ''tlatoque'' of the Chichimeca, succeeding Xolotl (1172–1232), Nopaltzin (1232–1263) and Tlotzin (1263–1298). In the Triple Alliance (1431–1521) Colonial period (1521–1564) The line of ''tlatoque'' continued in Tetzococo after the Spanish conquest. Adept at navigating the new Span ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tlatoani Of Texcoco
This is a list of Mesoamerican rulers of the ''altepetl'' of Tetzcoco from the time the city began being ruled by ''tlatoque'' in 1298 to the end of the line of indigenous rulers. From the early 15th century to 1521, Tetzcoco was one of the three leading members of the Triple Alliance, commonly known as the Aztec Empire, but was often subservient to the rulers of Tenochtitlan. The Aztec Empire was conquered by Spain in 1521, but the Spanish colonial authorities continued to appoint ''tlatoque'' of Tetzcoco until the office was abolished in 1564. Pre-colonial rulers (1298–1521) Early Tetzcoco (1298–1431) The ''tlatoque'' of Tetzcoco were descendants and successors of earlier ''tlatoque'' of the Chichimeca, succeeding Xolotl (1172–1232), Nopaltzin (1232–1263) and Tlotzin (1263–1298). In the Triple Alliance (1431–1521) Colonial period (1521–1564) The line of ''tlatoque'' continued in Tetzococo after the Spanish conquest. Adept at navigating the new Span ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cacamatzin
Cacamatzin (or Cacama) (1483–1520) was the tlatoani (ruler) of Texcoco,Diaz, B., 1963, The Conquest of New Spain, London: Penguin Books, the second most important city of the Aztec Empire. Cacamatzin was a son of the previous king Nezahualpilli by one of his mistresses. Traditionally, the Texcocan kings were elected by the nobility from the most able of the royal family. Cacamatzin's election to the throne in 1515 was said to have been made under considerable pressure from Moctezuma II, lord of Tenochtitlán. Moctezuma II wished to lessen Texcoco's power in favor of greater centralization in Tenochtitlán. Cacamatzin wrote ''Cacamatzin Icuic'' ("Song of Cacamatzin"), invoking his father and grandfather; he seems to protest against Pedro de Alvarado's attack during the festival of Tóxcatl. Moctezuma II, under orders from Cortés, had Cacamatzin arrested "in his own palace while discussing war-preparations". The ''Caciques'' of Coyoacan, Iztapalapa, and Tacuba were also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fall Of Tenochtitlan
The Fall of Tenochtitlan, the capital of the Aztec Empire, was a decisive event in the Spanish conquest of the empire. It occurred in 1521 following extensive manipulation of local factions and exploitation of pre-existing political divisions by Spanish conquistador Hernán Cortés. He was aided by indigenous allies, and his interpreter and companion La Malinche. Although numerous battles were fought between the Aztec Empire and the Spanish-led coalition, which was composed mainly of Tlaxcaltec men, it was the siege of Tenochtitlan that directly led to the downfall of the Aztec civilization and marked the end of the first phase of the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire. The Aztec population was devastated at the time by high mortality due to a smallpox epidemic, which killed much of its leadership. Because smallpox had been endemic in Asia and Europe for centuries, the Spanish had developed an acquired immunity and were affected relatively little in the epidemic. The conqu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Texcoco (altepetl)
Tetzcoco (Classical Nahuatl: ''Tetzco(h)co'' ) was a major Acolhua altepetl (city-state) in the central Mexican plateau region of Mesoamerica during the Late Postclassic period of pre-Columbian Mesoamerican chronology. It was situated on the eastern bank of Lake Texcoco in the Valley of Mexico, to the northeast of the Aztec capital, Tenochtitlan. The site of pre-Columbian Tetzcoco is now subsumed by the modern Mexican ''municipio'' of Texcoco and its major settlement, the city formally known as Texcoco de Mora. It also lies within the greater metropolitan area of Mexico City. Pre-Columbian Tetzcoco is most noted for its membership in the Aztec Triple Alliance. At the time of the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire, it was one of the largest and most prestigious cities in central Mexico, second only to the Aztec capital, Tenochtitlan. A survey of Mesoamerican cities estimated that pre-conquest Tetzcoco had a population of 24,000+ and occupied an area of 450 hectares. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nezahualpilli
Nezahualpilli (Nahuatl for "fasting prince"; 1464–1515, ) was king (''tlatoani'') of the Mesoamerican city-state of Texcoco, elected by the city's nobility after the death of his father, Nezahualcoyotl, in 1472. Nezahuapilli's mother was Azcalxochitzin, who married Nezahualcoyotl after the death of her first husband, King Cuahcuauhtzin of Tepechpan. Like his father, he was a poet, was considered a sage, and had the reputation of being a fair ruler. Only one of his poems survives: "''Icuic Nezahualpilli yc tlamato huexotzinco''" ("Song of Nezahualpilli during the war with Huexotzinco"). His court was a haven for astronomers, engineers, and soothsayers. During his reign, he abolished capital punishment for a number of crimes and struggled to keep the political independence of Texcoco during the increasing centralization of Aztec power in Tenochtitlán. When he told Moctezuma II that the Texcocan wise men had foretold foreign dominion over the Valley of Mexico, the emperor chall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tlatoani
''Tlatoani'' ( , "one who speaks, ruler"; plural ' or tlatoque) is the Classical Nahuatl term for the ruler of an , a pre-Hispanic state. It is the noun form of the verb "tlahtoa" meaning "speak, command, rule". As a result, it has been variously translated in English as "king", "ruler", or "speaker" in the political sense. Above a tlahtoani is the ''Weyi Tlahtoani,'' sometimes translated as "Great Speaker", though more usually as "Emperor" (the term is often seen as the equivalent to the European "great king"). A ' () is a female ruler, or queen regnant. The term refers to "vice-leader". The leaders of the Mexica prior to their settlement are sometimes referred to as , as well as colonial rulers who were not descended from the ruling dynasty. The ruler's lands were called , and the ruler's house was called ''Nahuatl dictionary'' (1997). Wired humanities project. Retrieved January 1, 2012, frolink/ref> The city-states of the Aztec Empire each had their own tlatoani, or l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hernán Cortés
Hernán Cortés de Monroy y Pizarro Altamirano, 1st Marquess of the Valley of Oaxaca (; ; 1485 – December 2, 1547) was a Spanish ''conquistador'' who led an expedition that caused the fall of the Aztec Empire and brought large portions of what is now mainland Mexico under the rule of the King of Castile in the early 16th century. Cortés was part of the generation of Spanish explorers and conquistadors who began the first phase of the Spanish colonization of the Americas. Born in Medellín, Spain, to a family of lesser nobility, Cortés chose to pursue adventure and riches in the New World. He went to Hispaniola and later to Cuba, where he received an '' encomienda'' (the right to the labor of certain subjects). For a short time, he served as '' alcalde'' (magistrate) of the second Spanish town founded on the island. In 1519, he was elected captain of the third expedition to the mainland, which he partly funded. His enmity with the Governor of Cuba, Diego Velázquez de Cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
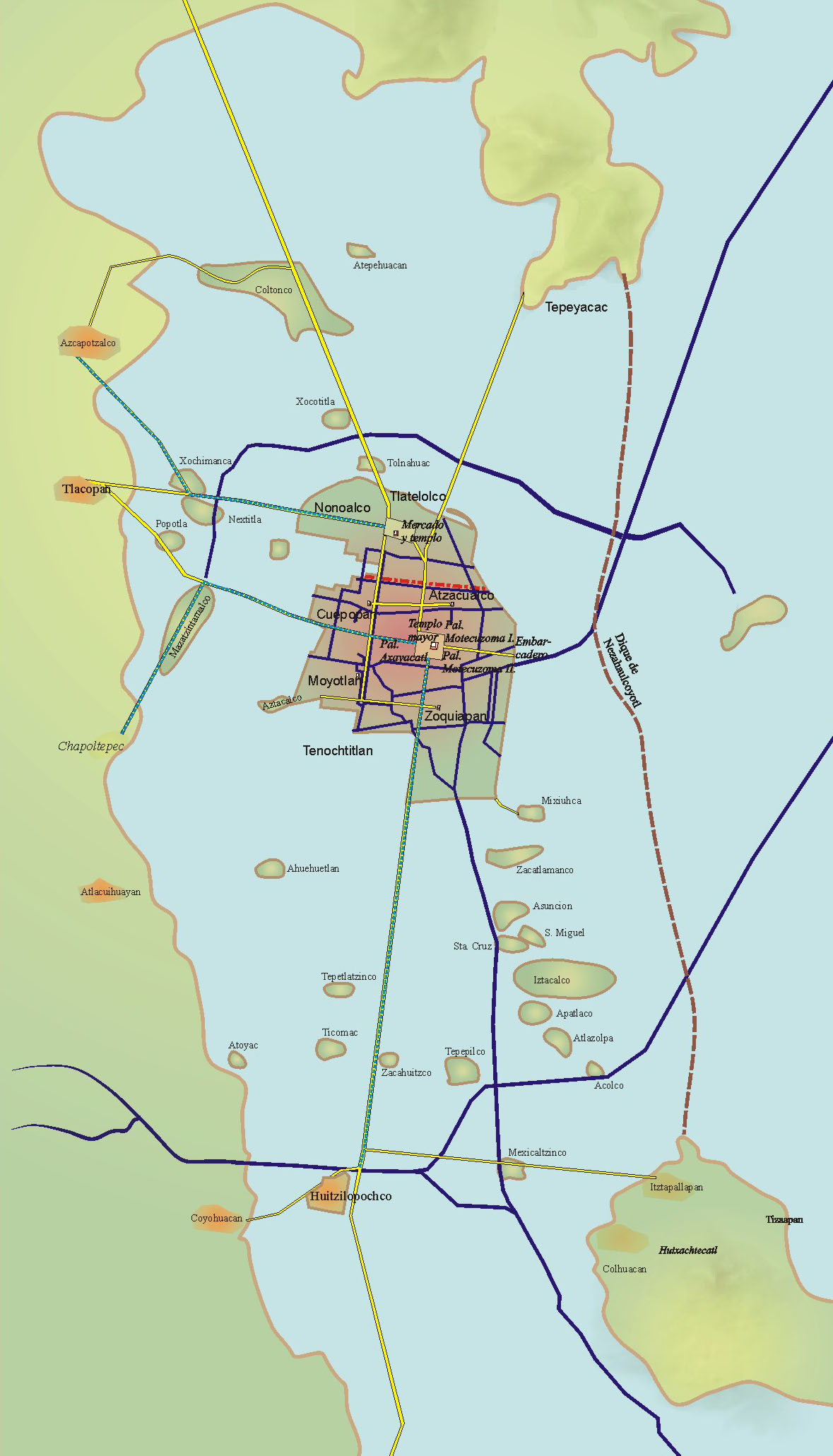
Tenochtitlan
, ; es, Tenochtitlan also known as Mexico-Tenochtitlan, ; es, México-Tenochtitlan was a large Mexican in what is now the historic center of Mexico City. The exact date of the founding of the city is unclear. The date 13 March 1325 was chosen in 1925 to celebrate the 600th anniversary of the city. The city was built on an island in what was then Lake Texcoco in the Valley of Mexico. The city was the capital of the expanding Aztec Empire in the 15th century until it was captured by the Spanish in 1521. At its peak, it was the largest city in the pre-Columbian Americas. It subsequently became a '' cabecera'' of the Viceroyalty of New Spain. Today, the ruins of are in the historic center of the Mexican capital. The World Heritage Site of contains what remains of the geography (water, boats, floating gardens) of the Mexica capital. was one of two Mexica (city-states or polities) on the island, the other being . The city is located in modern-day Mexico City. Etymolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Year Of Birth Missing
A year or annus is the orbital period of a planetary body, for example, the Earth, moving in its orbit around the Sun. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by change in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons are generally recognized: spring, summer, autumn and winter. In tropical and subtropical regions, several geographical sectors do not present defined seasons; but in the seasonal tropics, the annual wet and dry seasons are recognized and tracked. A calendar year is an approximation of the number of days of the Earth's orbital period, as counted in a given calendar. The Gregorian calendar, or modern calendar, presents its calendar year to be either a common year of 365 days or a leap year of 366 days, as do the Julian calendars. For the Gregorian calendar, the average length of the calendar year (the mea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |